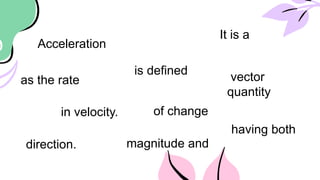
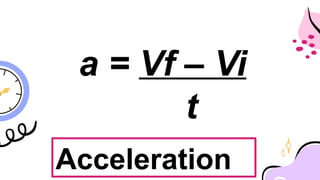
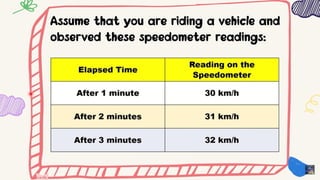
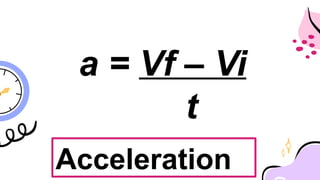
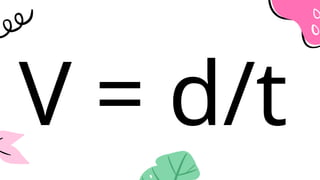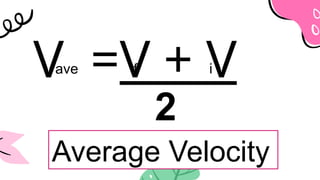The document outlines a lesson plan focused on uniformly accelerated motion (UAM) and its application in sports. It defines acceleration as the rate of change in velocity and includes objectives, activities, and quizzes to assess understanding. Additionally, it provides examples and calculations related to UAM in practical scenarios.