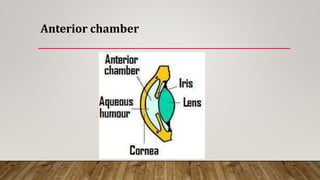
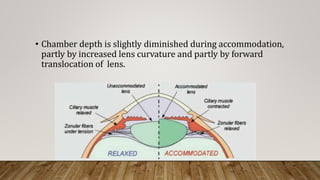
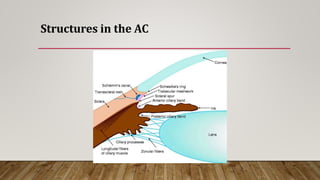
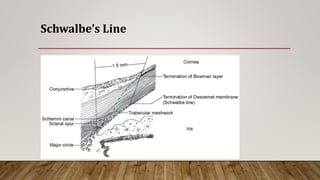
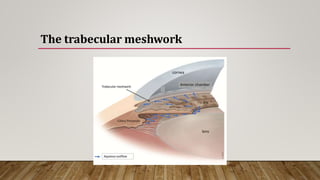
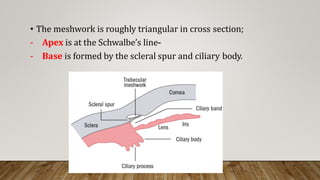
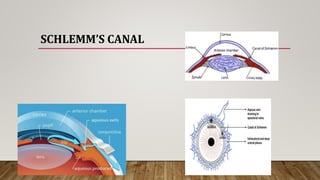
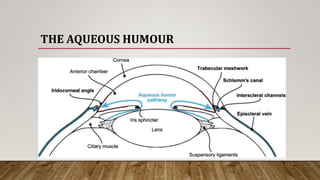
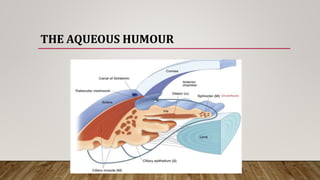
The anterior chamber is the space in the eye between the cornea and iris filled with aqueous humor. It is approximately 3mm deep and contains 0.25ml of fluid. The anterior chamber depth is determined by the lens and becomes shallower with age and in hyperopic eyes. Structures in the anterior chamber include Schwalbe's line, the trabecular meshwork, Schlemm's canal, the aqueous humor, and the anterior part of the ciliary body. The trabecular meshwork drains aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal, where it is then drained into blood vessels. Blockage of Schlemm's canal can lead to increased pressure and glaucoma.