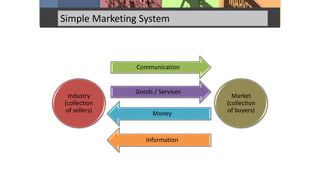
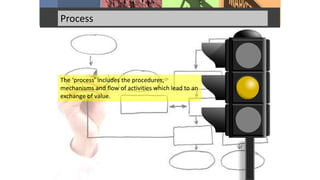
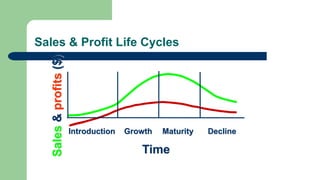
This document discusses marketing mix and product life cycles. It begins by defining marketing mix as the combination of four Ps - product, place, price and promotion. It then expands this to seven Ps with the addition of people, process and physical evidence. The document also discusses the different stages of a product's life cycle - introduction, growth, maturity and decline - and how sales and profits change over these stages. It concludes with assignment questions about identifying marketing objectives and strategies for each life cycle stage, strategic options for mature products, and assessing the most important, riskiest and highest profit potential stages.