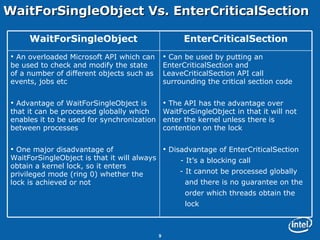
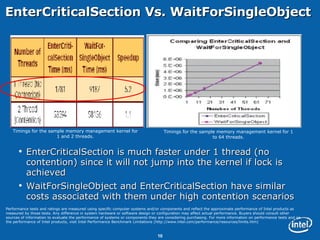
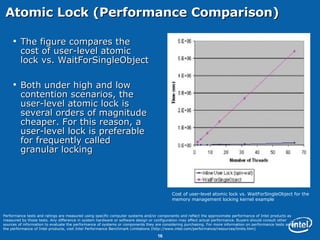
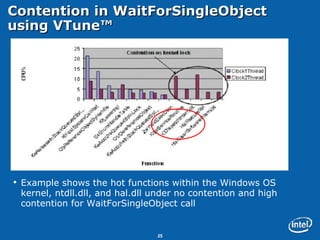
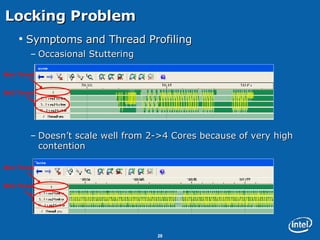
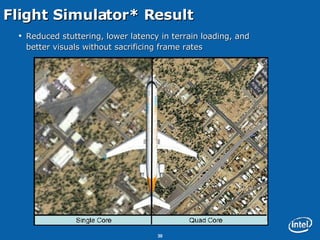
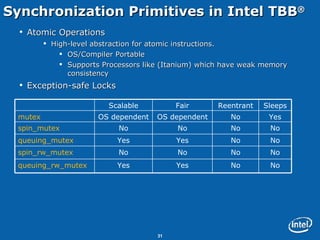
This document discusses issues related to synchronization locks in multi-threaded applications, emphasizing the importance of locking methodologies to avoid performance pitfalls such as deadlocks and contention. It explores user-level atomic locks and Intel's locking APIs, revealing that user-level locks can significantly improve performance compared to kernel-level locks. The document also shares case studies, including a detailed analysis of the Microsoft Flight Simulator, illustrating how improved locking mechanisms can enhance scalability and reduce latency.