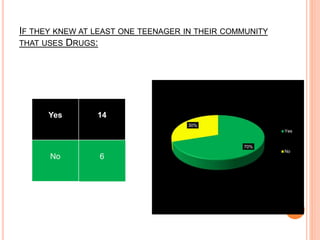
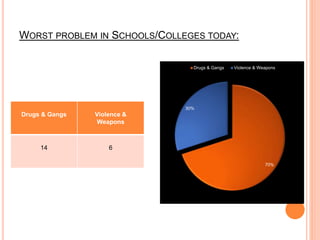
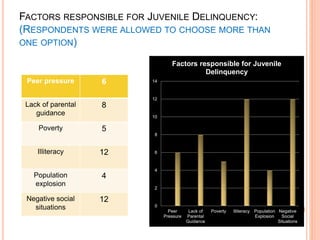
This document reports a statistical study on juvenile delinquency, outlining the causes and prevention strategies based on a survey of 22 respondents. Key findings indicate that parental neglect, lack of guidance, and negative social situations significantly contribute to delinquency, with counseling identified as the most effective intervention. The study also emphasizes the influence of peer interactions and the importance of supportive family environments in mitigating juvenile delinquency.