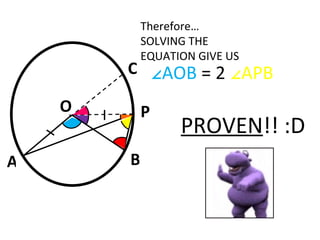
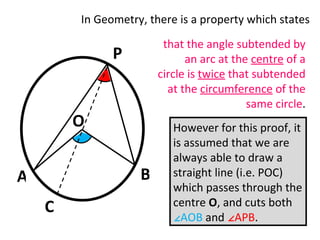
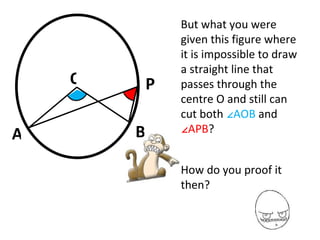
This document summarizes how to prove that the angle subtended by an arc at the centre of a circle is twice that subtended at the circumference, even when a line cannot be drawn through the centre cutting both angles. It does this by extending one arc line to the centre, then using properties of isosceles triangles and angles on a straight line to derive an equation that solves to the desired property.


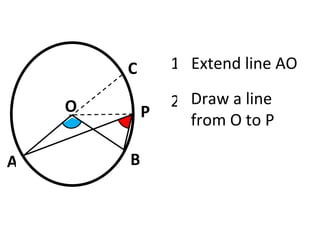
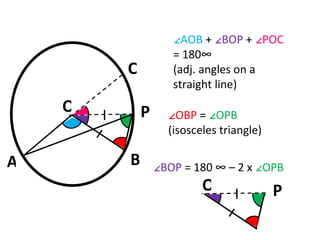
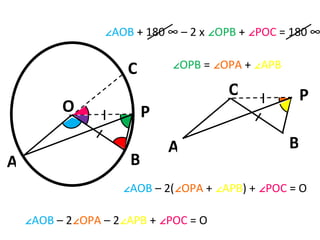
![A B P O C ∠ POC = 2 ∠OPA [ ∠OPA = ∠OAP (isosceles triangle), ∠ POC = ∠OAP + ∠OPA (external angles)] B P O C A ∠ AOB - 2 ∠OPA - 2 ∠APB + ∠POC = O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aprovinganglepropertiesofcircles-2-110410093045-phpapp01/85/A-proving-angle-properties-of-circles-2-8-320.jpg)