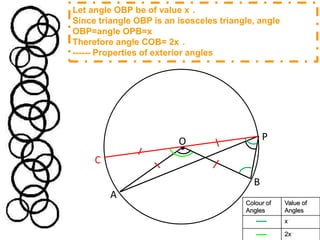
Method One proves that the angle at the centre (Angle AOB) is twice the angle at circumference (Angle APB) by showing that triangles OBP and OAP are isosceles triangles, which allows calculating the angles.
Method Two extends a radius to form a diameter and shows that triangles OCA, OAP and OBP are isosceles triangles. It then uses properties of exterior angles to calculate that the angle at the centre (Angle AOB) is twice the angle at circumference (Angle APB). Both methods demonstrate the relationship between the angles at the centre and circumference of a circle.

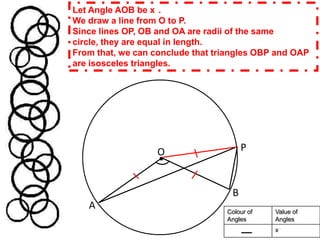
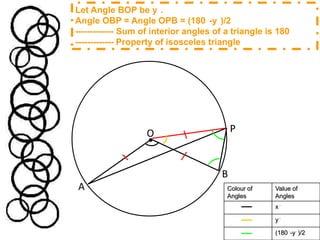
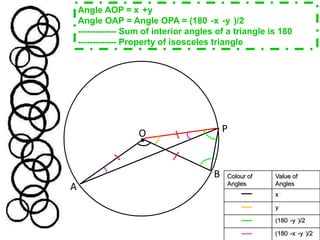
![Angle APB = Angle OPB – Angle OPA = [(180°-y°)/2] – [(180°-x°-y°)/2] = (180°-y°-180°+x°+y°)/2 = x°/2POBATherefore, this proves that the angle at the centre (Angle AOB = x°) is twice the angle at circumference (Angle APB = x°/2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma301assignmentcirclesjh304-2011edittedanimation-110409042905-phpapp01/85/Part-A-Proof-5-320.jpg)

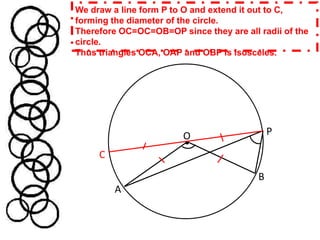
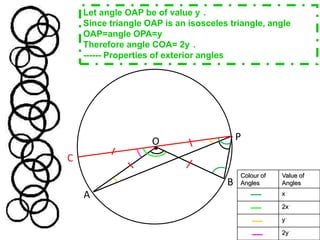
![Angle AOB= angle COB-angle COA = 2x°-2y° = 2(x-y)°Angle APB= angle OPB-angle OPA = x°- y° = (x-y)°POCBATherefore, this proves that the angle at the centre [Angle AOB = 2(x-y)°] is twice the angle at circumference [Angle APB = (x-y)°].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ma301assignmentcirclesjh304-2011edittedanimation-110409042905-phpapp01/85/Part-A-Proof-10-320.jpg)