Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times
![A Mini Presentation
On
‘ Windowing ’
Tanjarul Islam Mishu
[@tanjarul26]
Dept. of CSE
Jatiya Kabi Kazi Nazrul Islam University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apresentaiononwindowing-170925192055/75/A-presentation-on-windowing-1-2048.jpg)

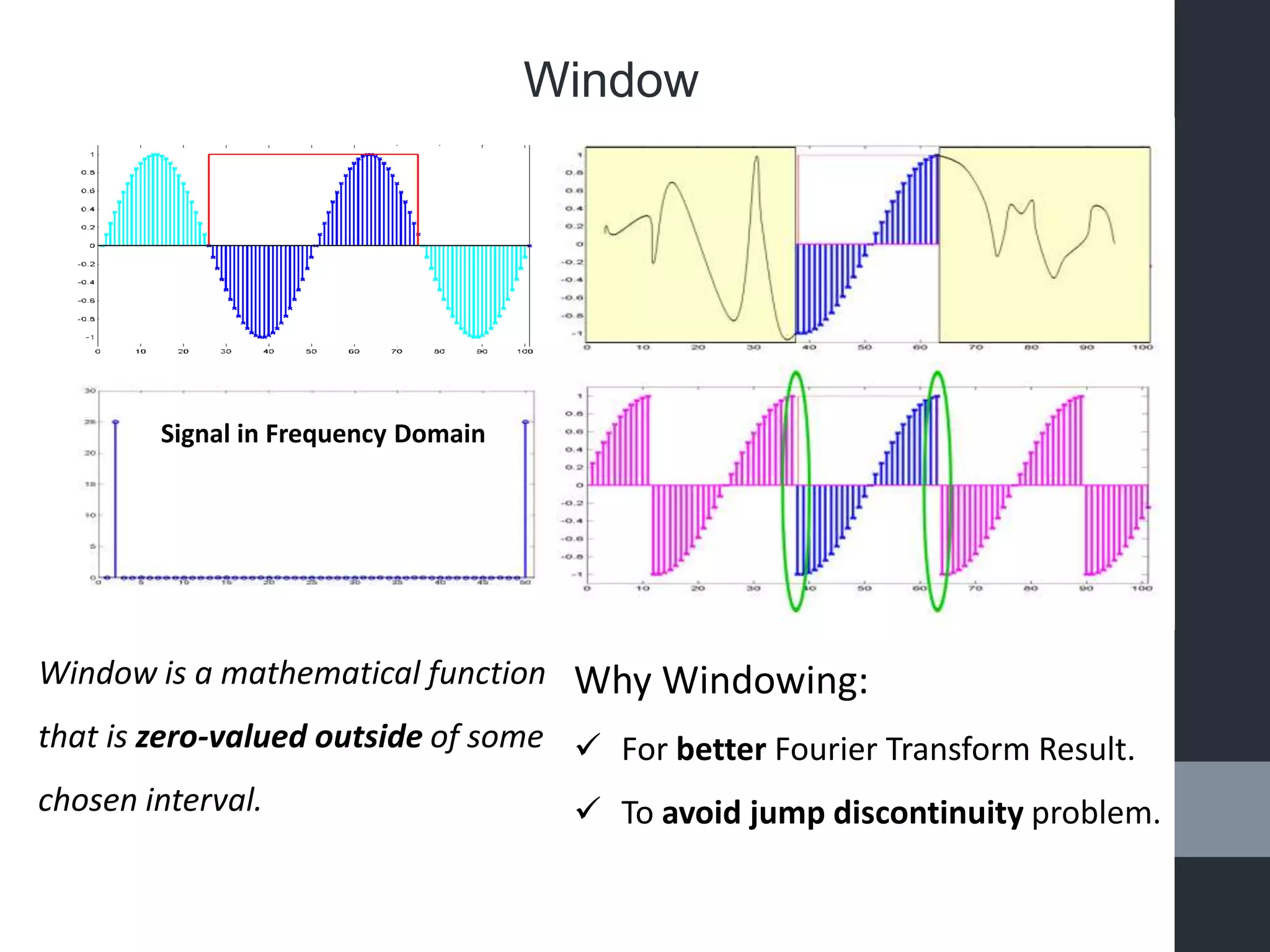
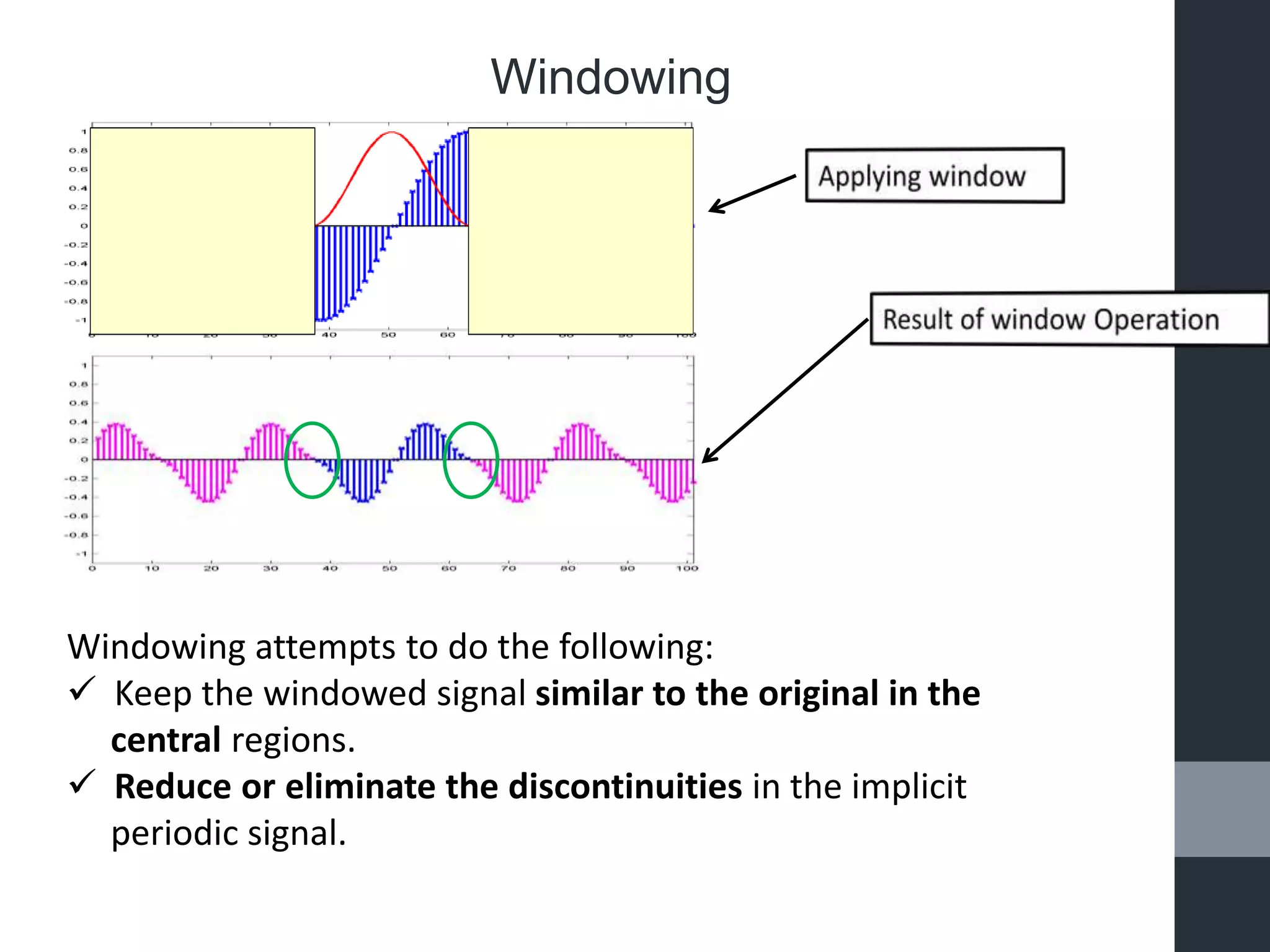
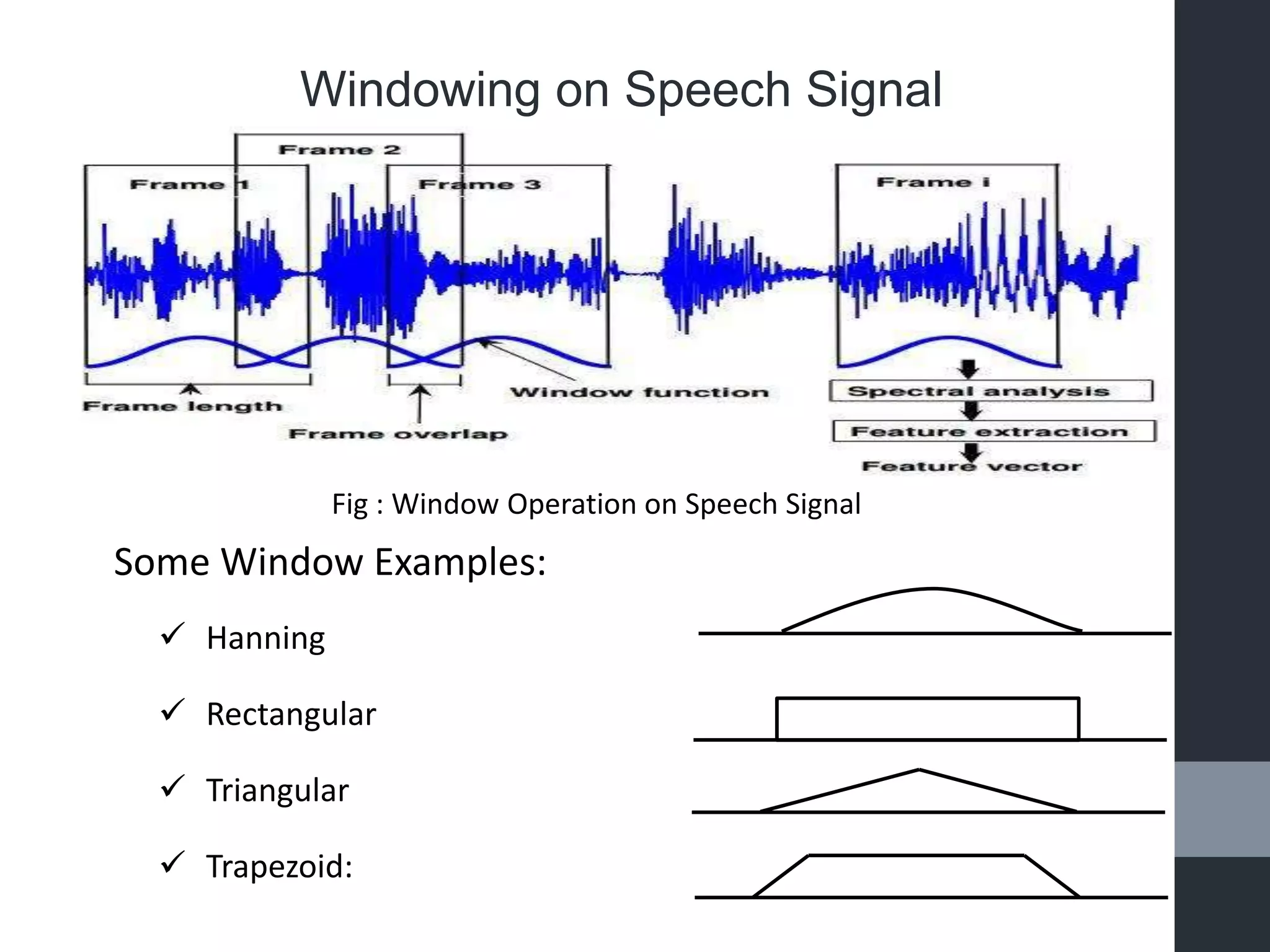
This document presents a mini presentation on the topic of "windowing". It discusses the necessity of windowing signals to avoid discontinuity problems and improve Fourier transform results. Windowing involves multiplying a signal by a mathematical function that is zero outside of a chosen interval. Several common window functions are described such as Hanning, rectangular, triangular, and trapezoid windows. An example of windowing a speech signal is shown.
![A Mini Presentation
On
‘ Windowing ’
Tanjarul Islam Mishu
[@tanjarul26]
Dept. of CSE
Jatiya Kabi Kazi Nazrul Islam University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apresentaiononwindowing-170925192055/75/A-presentation-on-windowing-1-2048.jpg)



