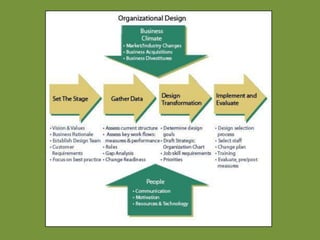
The document outlines the significance of organizational development (OD) in enhancing an organization's capacity to achieve its mission effectively and sustainably. It emphasizes the connection between OD efforts, organizational survival, and resource development while detailing the core components necessary for effective organizations. Additionally, it discusses the challenges and lessons learned in implementing OD, highlighting the importance of active involvement from leadership and staff.