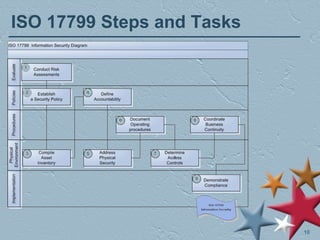
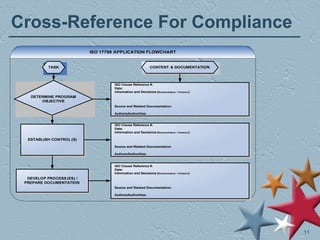
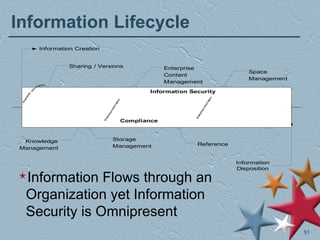
The document outlines a session focused on ISO 17799 and its implications for information security and records management. Key topics include the importance of establishing security policies, managing risks, handling security breaches, and aligning records management with information security objectives. It also emphasizes compliance with various regulations and standards to protect personal and sensitive information.