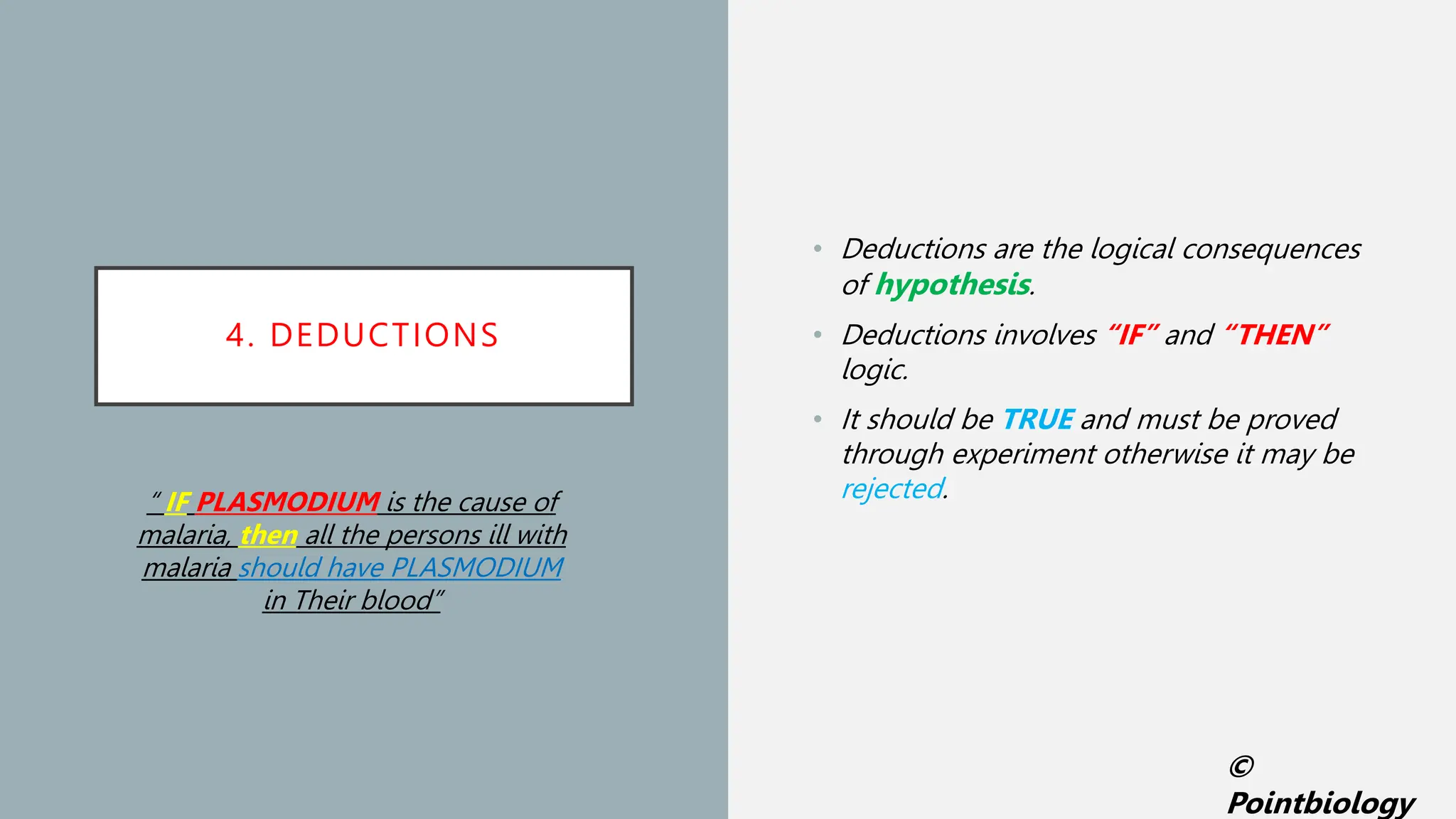
The document outlines the scientific method as it applies to solving biological problems, specifically using malaria as a case study. It describes the steps involved, including problem recognition, observation, hypothesis formulation, deductions, experimentation, and summarizing results, ultimately leading to the conclusion that plasmodium is the cause of malaria. The content emphasizes the importance of systematic observation and experimentation in biology.