This document summarizes the four main types of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions:
1. Type I or anaphylactic reactions involve IgE antibodies and mast cells/basophils, causing rapid reactions like hives, asthma, or anaphylactic shock.
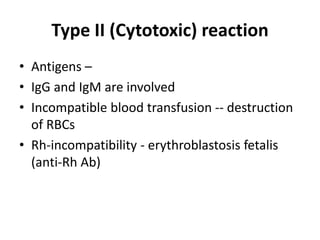
2. Type II or cytotoxic reactions involve IgG and IgM binding to antigens on cells, destroying cells like in blood transfusions.
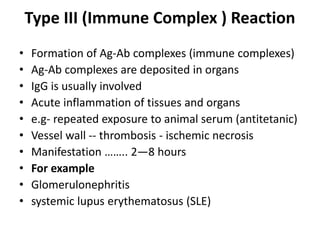
3. Type III or immune complex reactions occur when antigen-antibody complexes deposit in tissues, causing inflammation like glomerulonephritis.
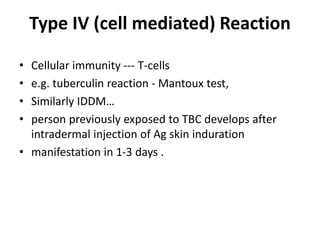
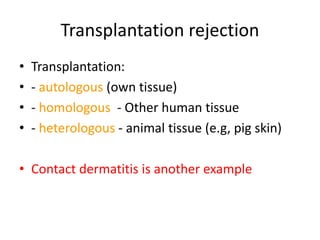
4. Type IV or cell-mediated reactions involve T-cells and cause delayed reactions like contact dermatitis or tuberculosis skin tests.