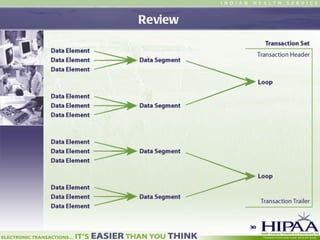
The document provides an overview of preparing for 837 electronic claim testing, including understanding key concepts like EDI standards, the 837 transaction format, software requirements, implementation guides, and establishing relationships with payers. It emphasizes obtaining implementation guides and a payer's companion guide, communicating with payers to understand testing processes, and completing necessary agreements like trading partner agreements.