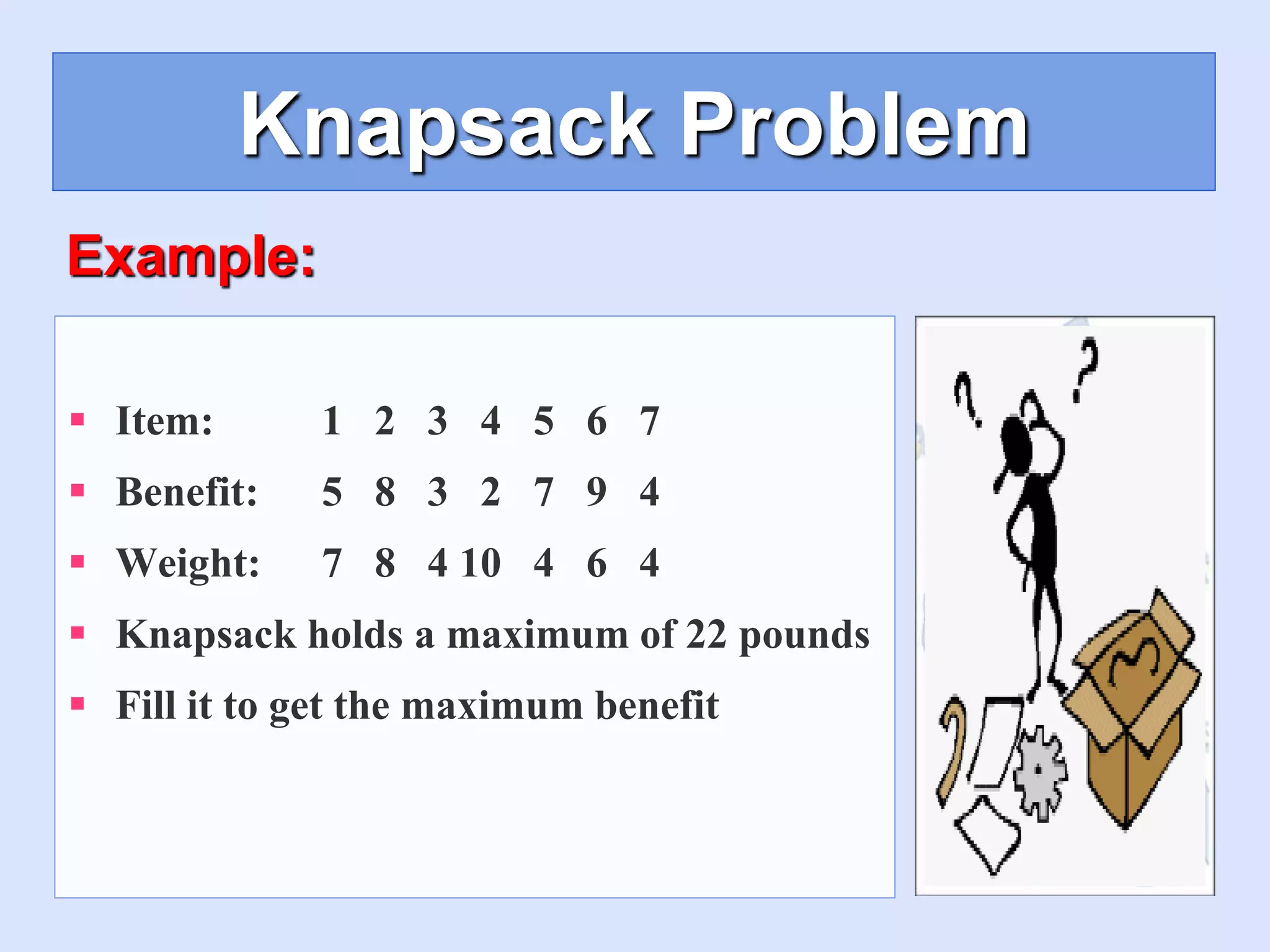
Genetic algorithms follow principles of evolution and natural selection to find optimal or near-optimal solutions to problems. The document describes using a genetic algorithm to solve the knapsack problem, where the goal is to fill a knapsack with items of maximum total value without exceeding the knapsack's weight limit. The algorithm encodes potential solutions as chromosomes, generates an initial random population, evaluates their fitness, selects parents for reproduction, performs crossover and mutation to generate new offspring, and iterates this process until finding an optimal or near-optimal solution.

![Genetic Algorithm
Outline of the Basic Genetic Algoritm
1. [Start]
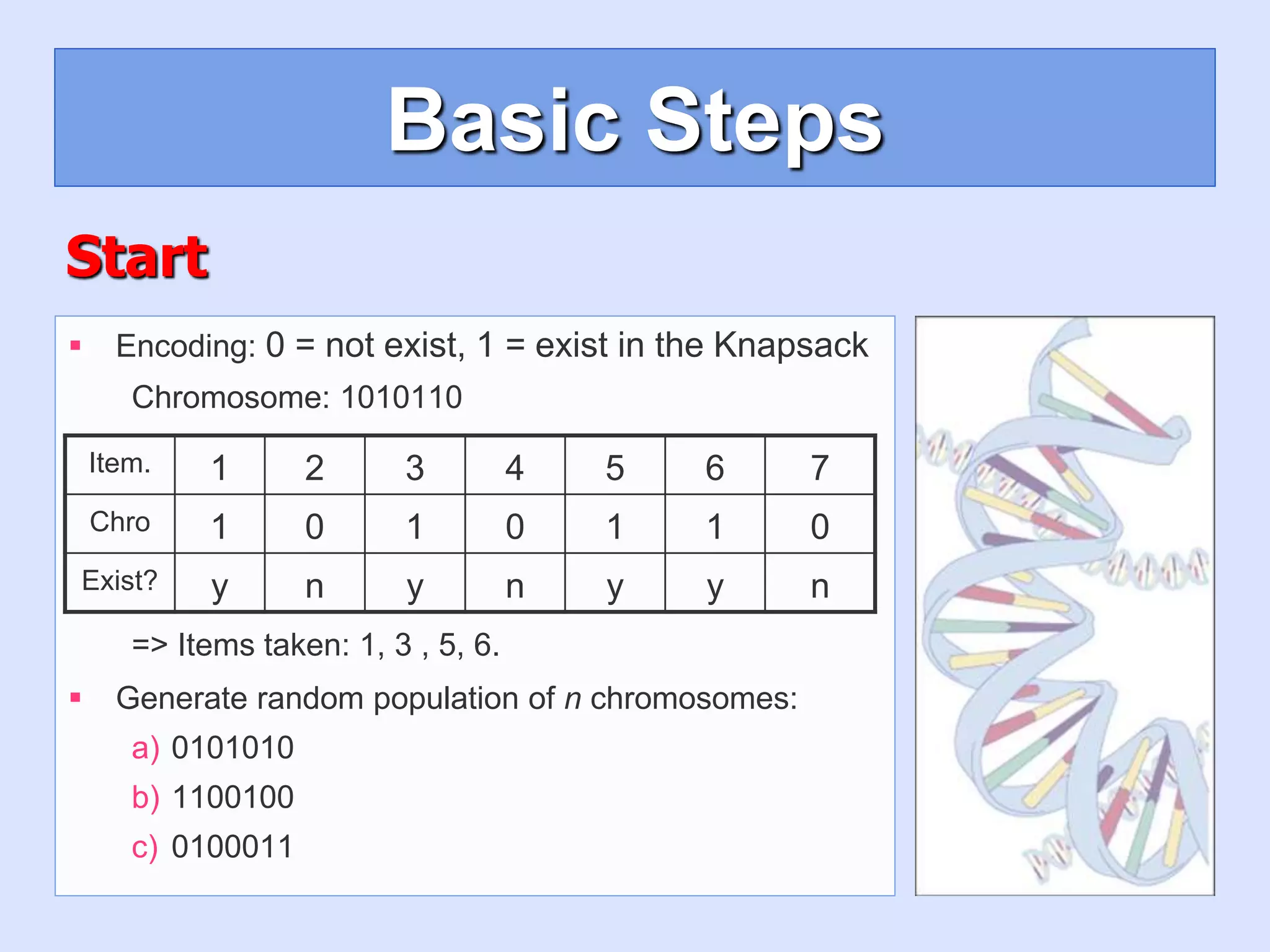
Encoding: represent the individual.
Generate random population of n chromosomes
(suitable solutions for the problem).
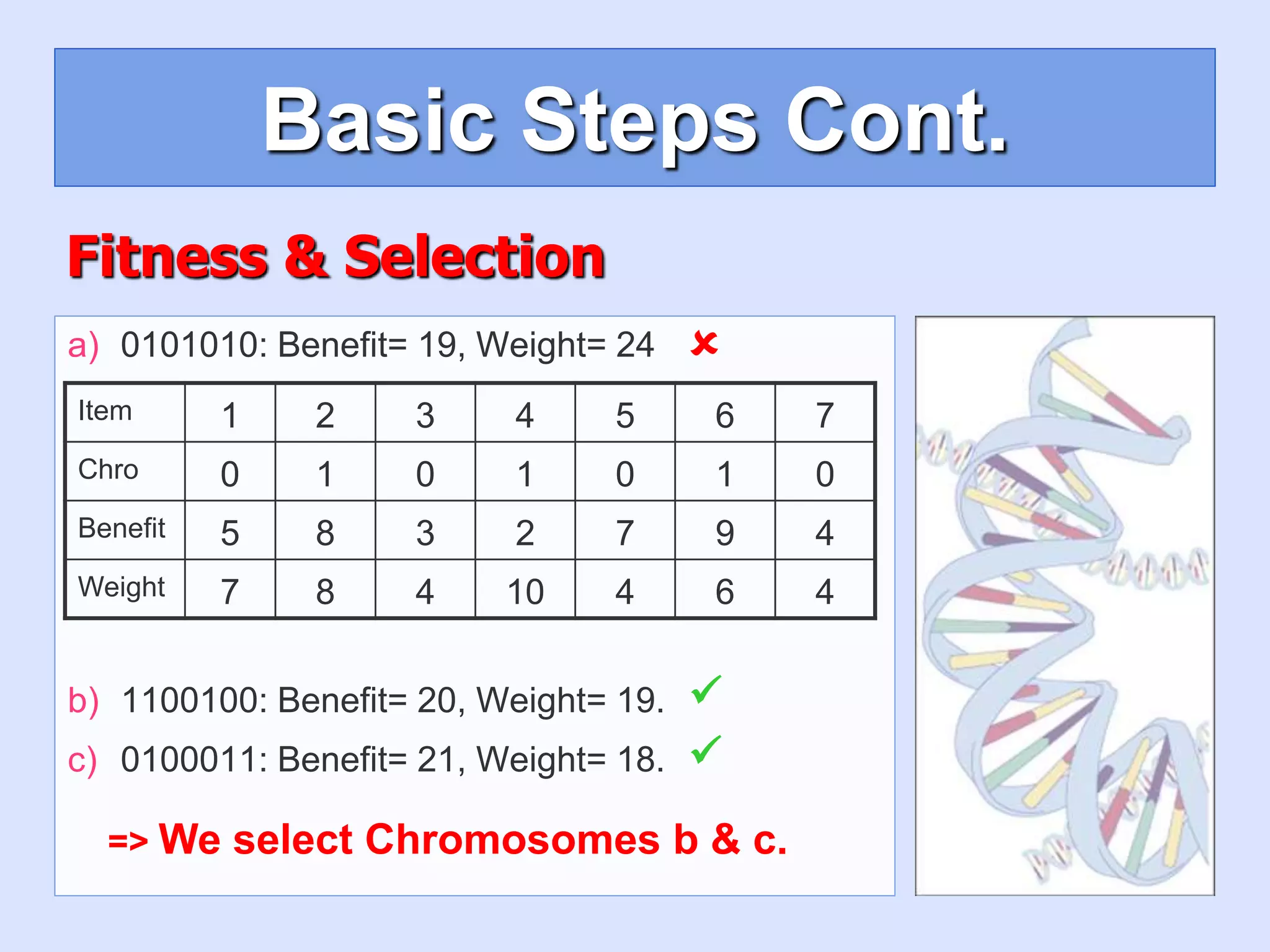
2. [Fitness] Evaluate the fitness of each
chromosome.
3. [New population] repeating following steps until
the new population is complete.
4. [Selection] Select the best two parents.
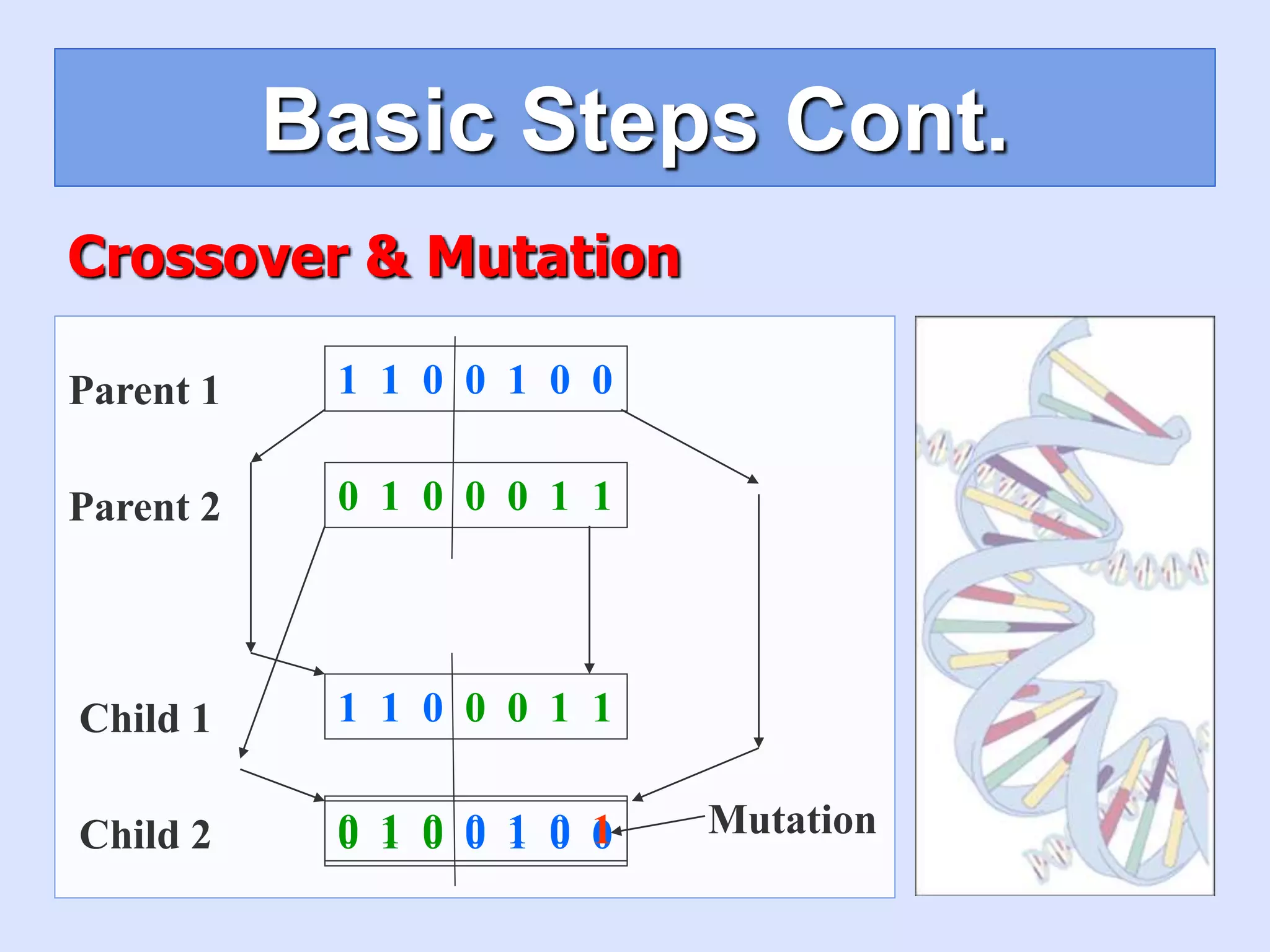
5. [Crossover] cross over the parents to form a
new offspring (children).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7geneticknapsack-221010155151-741c68a7/75/7_Genetic_knapsack-ppt-6-2048.jpg)
![Genetic Algorithm
Outline of the Basic Genetic Algoritm Cont.
6. [Mutation] With a mutation probability.
7. [Accepting] Place new offspring in a
new population.
8. [Replace] Use new generated
population for a further run of
algorithm.
9. [Test] If the end condition is satisfied,
then stop.
10. [Loop] Go to step 2 .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7geneticknapsack-221010155151-741c68a7/75/7_Genetic_knapsack-ppt-7-2048.jpg)
![Basic Steps Cont.
Accepting, Replacing & Testing
Place new offspring in a new population.
Use new generated population for a
further run of algorithm.
If the end condition is satisfied, then
stop. End conditions:
Number of populations.
Improvement of the best solution.
Else, return to step 2 [Fitness].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7geneticknapsack-221010155151-741c68a7/75/7_Genetic_knapsack-ppt-11-2048.jpg)