Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (10)
5.7 poisson regression in the analysis of cohort data

5.7 poisson regression in the analysis of cohort data
Similar to 6.4.1 designs density
Similar to 6.4.1 designs density (20)
Sampling design, sampling errors, sample size determination

Sampling design, sampling errors, sample size determination
Advanced Biostatistics and Data Analysis abdul ghafoor sajjad

Advanced Biostatistics and Data Analysis abdul ghafoor sajjad
An introduction to the stepped wedge cluster randomised trial 

An introduction to the stepped wedge cluster randomised trial
jhghgjhgjhgjhfhcgjfjhvjhjgjkggjhgjhgjhfjgjgfgfhgfhg

jhghgjhgjhgjhfhcgjfjhvjhjgjkggjhgjhgjhfjgjgfgfhgfhg
More from A M
More from A M (20)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx

ICT Role in 21st Century Education & its Challenges.pptx
Plant propagation: Sexual and Asexual propapagation.pptx

Plant propagation: Sexual and Asexual propapagation.pptx
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx

Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf

Food safety_Challenges food safety laboratories_.pdf
Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom

Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom
Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...

Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...
6.4.1 designs density
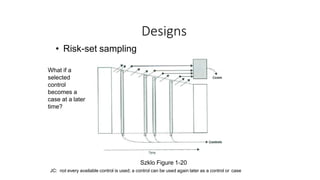
- 1. Designs • Risk-set sampling What if a selected control becomes a case at a later time? Szklo Figure 1-20 JC: not every available control is used; a control can be used again later as a control or case
- 2. Designs • Density sampled design – Sampling approach to estimate the incidence density ratio – Incident cases of disease are identified (numerator) – Controls (non-diseased) are a sample from the study base that gave rise to the cases, with sampling probabilities based on the person-time of observation (denominator) – This type of sampling of controls is called density sampling because OR estimates IDR (we will go through that in a bit) – Data are analyzed as matched on time (usually with conditional logistic regression) – Design often called a nested case-control study if it is carried out within an actual cohort study If you had a cohort study, why would you nest a case-control study inside it? • Even if not in an actual cohort study a density sampled case-control design can be thought of as nested in an enumerated source population
- 3. Designs • With our case-control designs we capture: • With a cohort design we captured:
- 4. Designs exposed PTe d b • Risk-set sampling c a PTu If b/d = PTe/Ptu then the exposure distribution in the controls represents the exposure distribution in the total cohort person-time
- 5. Designs • Pseudo-rates • Controls selected so that exposure distribution among the controls is the same as it is in the person-time in the study base for the cases • This is met if: – b/d = PTe/PTu – b/PTe and d/PTu are control sampling fractions (r) • Actual rates vs. pseudo-rates – IDe = α/PTe Pseudo-ratee = a/b – IDu = γ/PTu Pseudo-rateu = c/d – Note: typically α=a and γ=c
- 6. Designs • Compare the rates to the pseudo-rates Multiply numerator by (PTe / PTe =1) and denominator by (PTu/PTu=1) • This algebra “works” if “r” (the sampling fraction) is the same for the exposed and unexposed • In other words: This only “works” if cases and controls are selected so that the exposure distribution among each group is the same as it is in the person-time in the study base for each group...this is accomplished in the design phase (and also the requires the proper analysis method-- conditional logistic regression)