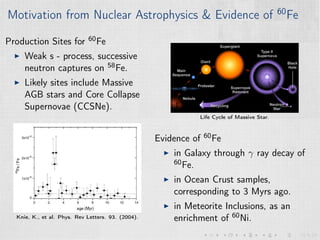
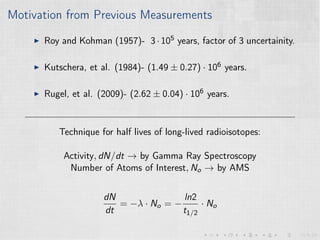
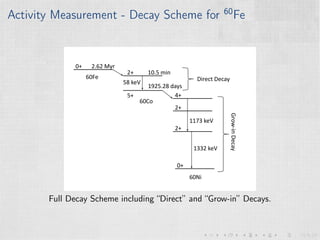
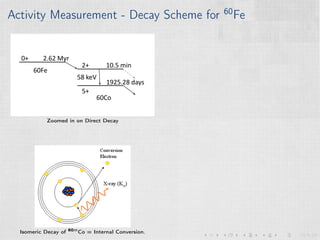
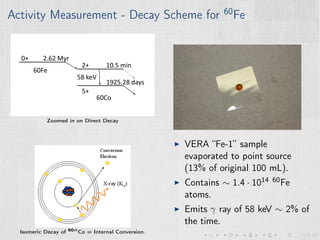
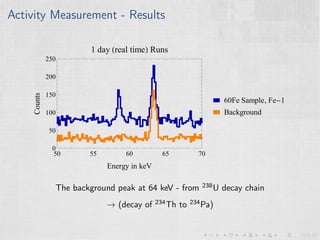
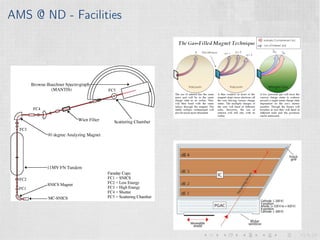
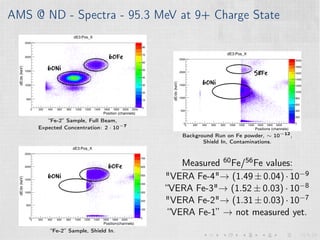
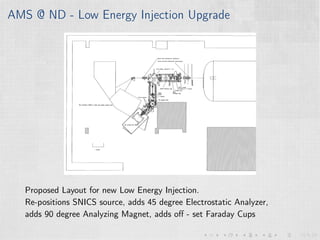
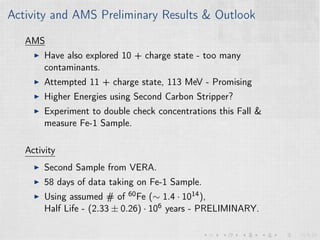
This document summarizes an experiment measuring the half-life of 60Fe using gamma ray spectroscopy and accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). Previous measurements of the 60Fe half-life ranged from 1.5-2.6 million years. The experiment aims to more precisely measure the half-life to help understand sites of 60Fe production like massive stars and supernovae. Gamma detectors measured the decay of 60Fe in ocean crust samples. AMS was used to determine the concentration of 60Fe in samples and yielded a preliminary half-life of (2.33 ± 0.26) million years. Upgrades to the AMS facility may help improve precision. The results will provide insight into nuclear astrophysics and early solar system formation