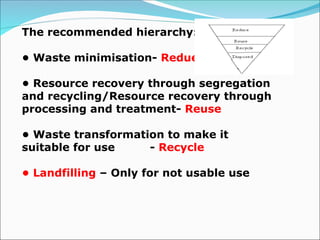
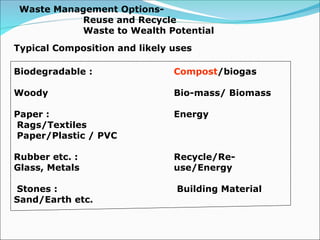
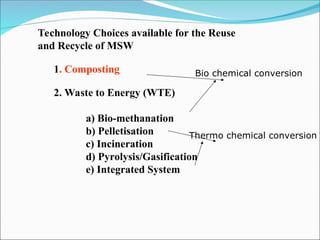
The document discusses municipal solid waste management in India, focusing on the Solid Waste Management Rules 2016 and the responsibilities of waste generators to segregate and manage waste effectively. It highlights the significant amount of waste generated annually and the need for compliance with new regulations, including segregation of waste into specific categories and ensuring proper disposal methods. Additionally, the document emphasizes the principles of reducing, reusing, and recycling waste, as well as the importance of community involvement and user fees for waste management.