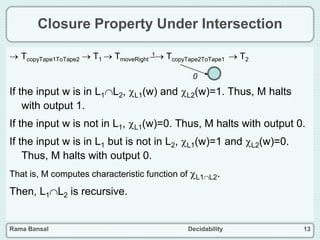
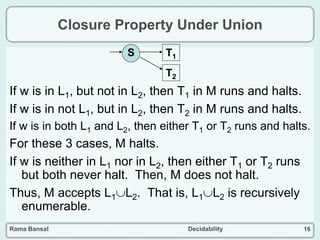
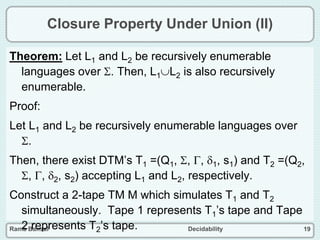
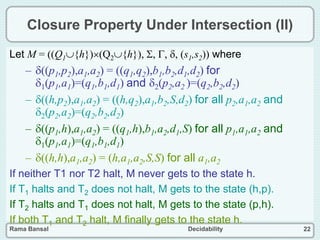
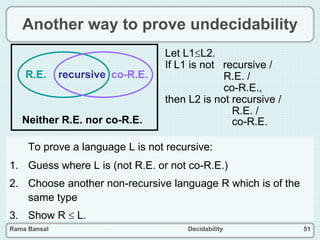
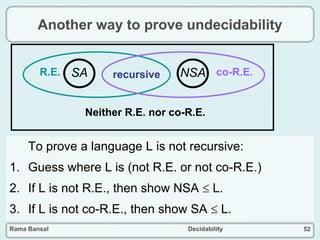
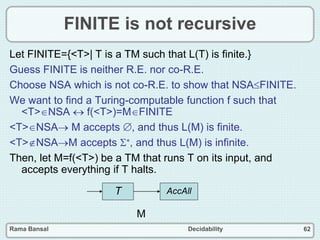
The document discusses decidability and defines key concepts such as:
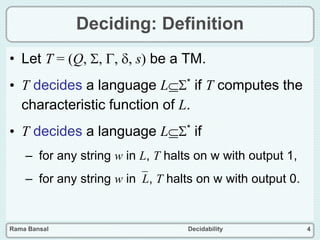
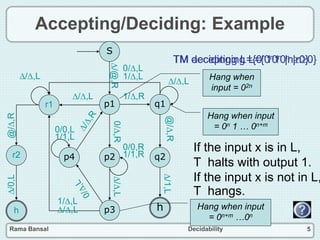
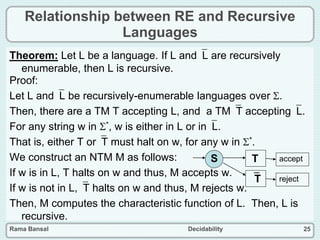
- A language is decidable if there is a Turing machine that can decide its characteristic function.
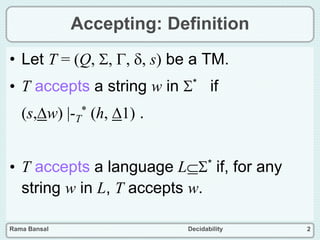
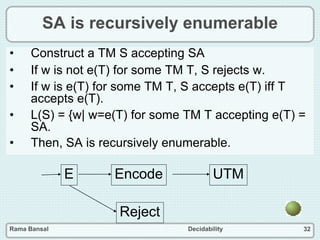
- A language is recursively enumerable if there is a Turing machine that can accept it.
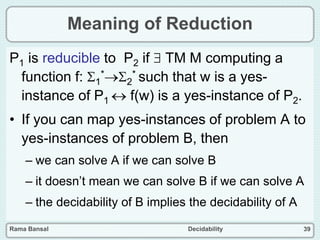
- The halting problem, which asks whether a Turing machine will halt on a given input, is undecidable.
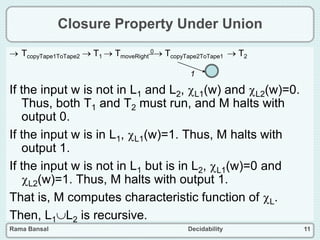
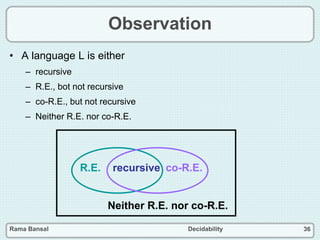
- Closure properties are discussed, showing that the classes of recursive and recursively enumerable languages are closed under union, intersection, and complement.