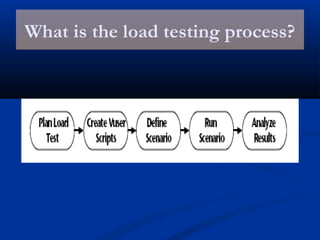
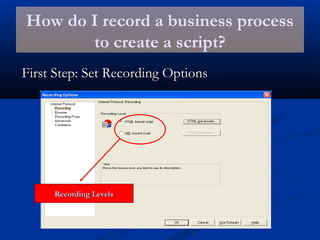
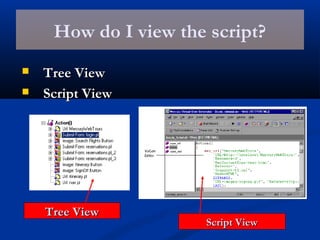
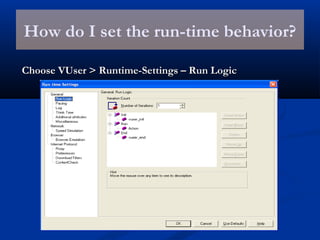
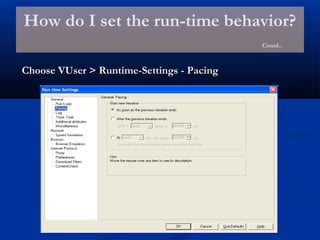
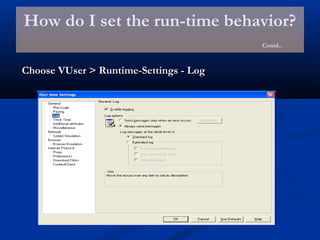
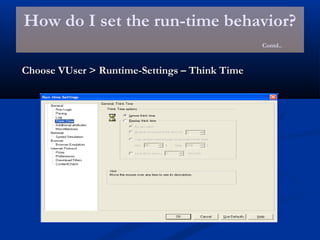
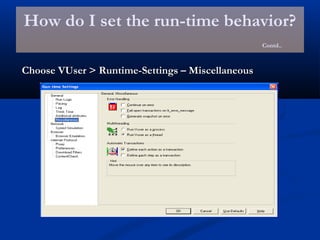
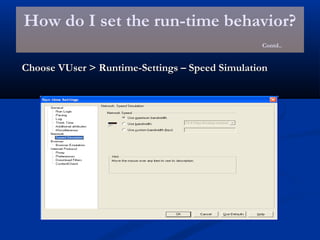
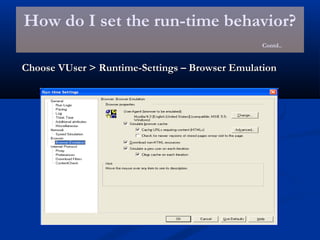
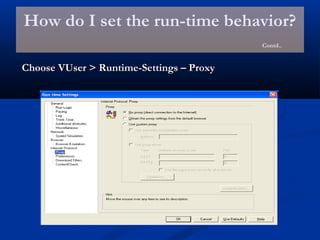
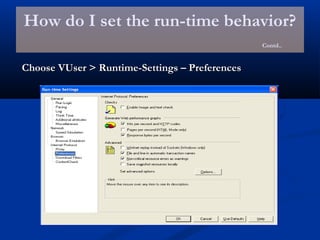
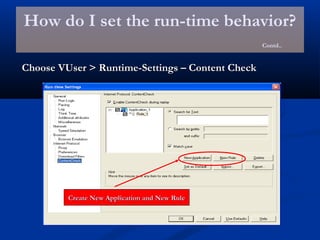
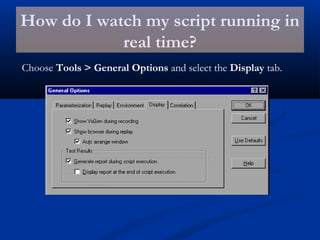
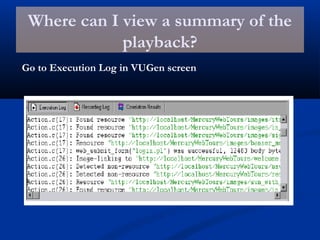
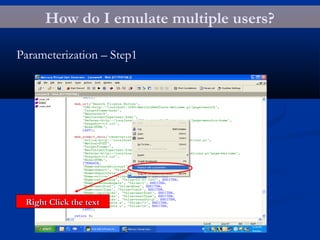
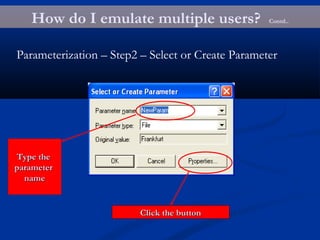
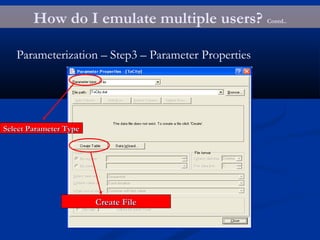
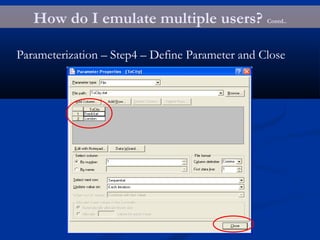
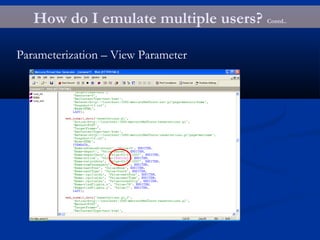
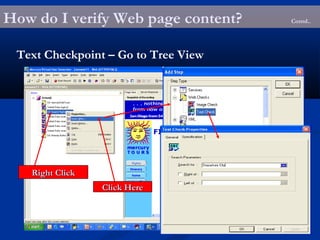
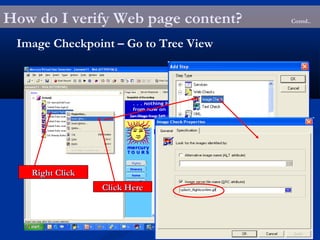
The document provides an overview of load testing with LoadRunner. It discusses topics like why performance testing is important, definitions of stress, load and performance testing, benchmark design, LoadRunner components and the load testing process. It also describes how to record a script with LoadRunner's Virtual User Generator, set runtime behavior, solve common playback issues, prepare a script for load testing by adding transactions and checkpoints, and verify the success of a test.