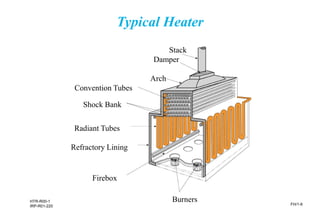
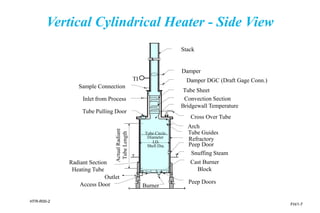
The document provides an overview of fired heater fundamentals, including their process functions, descriptions, and heat transfer basics. It discusses various heater designs, primarily focusing on vertical cylindrical heaters and their components such as radiation and convection sections. Additionally, it highlights safety concerns, costs, and the importance of heaters in industrial processes.