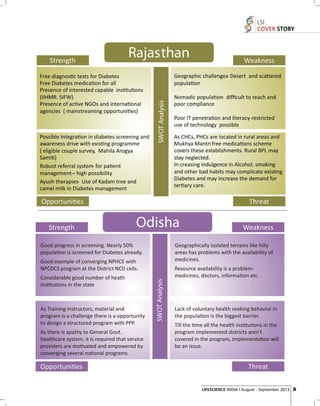
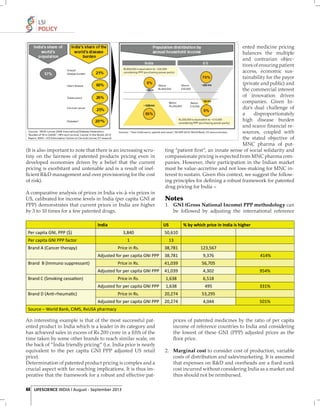
The Indian diabetes burden is expected to cross 100 million by 2030 as per estimates. Considering rising non-communicable diseases and risk factors, the Government of India initiated the NPCDCS program. It is essential to have well staffed and equipped public health facilities for treatment access. Standard treatment protocols also need to be established and followed for effective disease management. However, many challenges remain due to lack of awareness, ignorance, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure, especially in rural areas where the majority lives. Urgent multi-pronged efforts are needed to curb the growing diabetes epidemic in India.