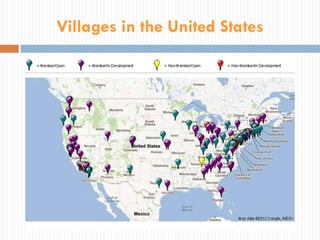
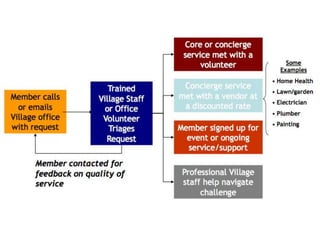
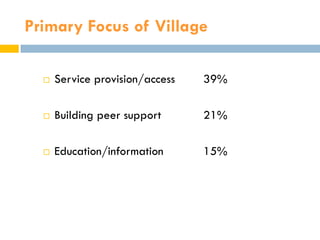
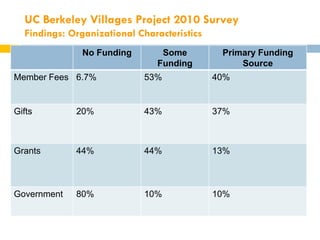
This document summarizes research on "Villages", which are membership-based community organizations that help older adults age in place. It finds that Villages provide services, build social support networks, and promote member empowerment. A survey of Villages found they predominantly serve white, female, homeowners living alone. Preliminary research on one Village program found it helped members feel less isolated and improve access to services. However, ensuring long-term sustainability, inclusiveness, and effectiveness remains a challenge for Villages. The author conducts further research to evaluate Villages and identify factors for success.



![What is a “Village”?
“Villages are self-governing, grassroots,
community-based organizations,
developed with the sole purpose of
enabling people to remain in their own
homes and communities as they age.”
[from Village-to-Village Network website]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-scharlach-ifa2012-villagemodel-120713095737-phpapp01/85/4-scharlach-ifa-2012-village-model-4-320.jpg)