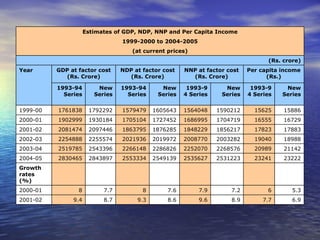
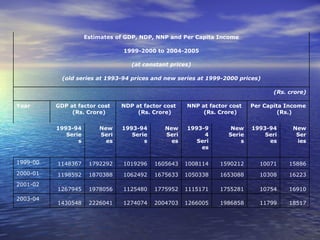
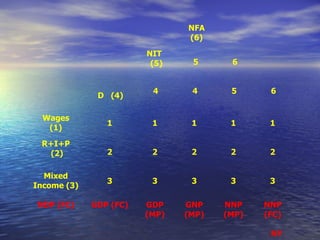
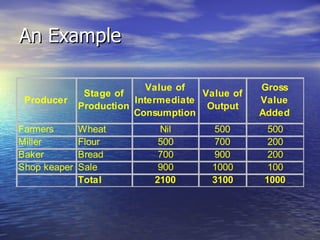
The document discusses various concepts related to national income such as GDP, NDP, NNP, per capita income. It provides estimates of these figures for India from 1999-2000 to 2004-2005 at both current and constant prices. It also explains key terms like domestic territory, normal residents, stock and flow variables, closed and open economies, and methods of measuring national income such as the product, income and expenditure methods.