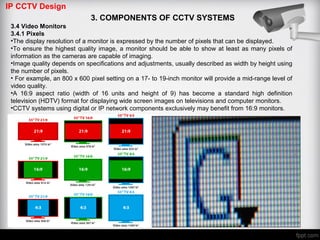
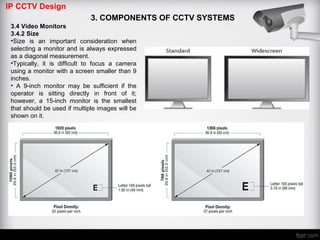
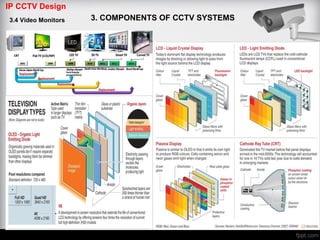
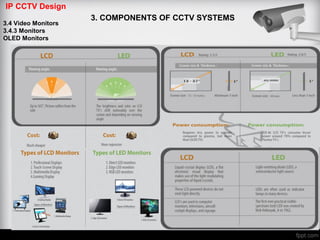
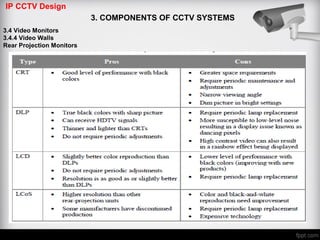
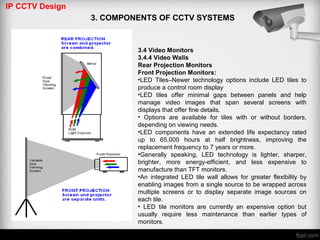
The document discusses different types of video monitors that can be used in CCTV systems. It describes key factors to consider when selecting monitors, such as pixels, size, and type (LCD, OLED, plasma, etc.). Video walls, which allow multiple monitors to be arranged together, are also covered. Important specifications and technologies for rear projection and front projection video walls are outlined.