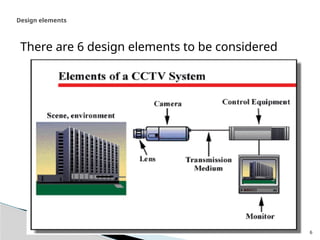
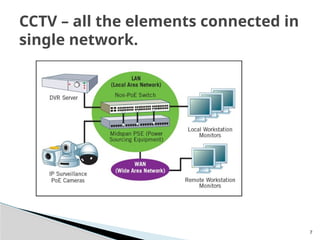
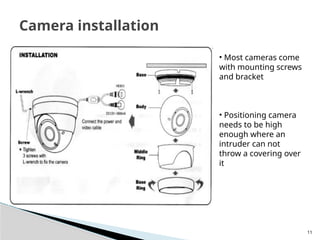
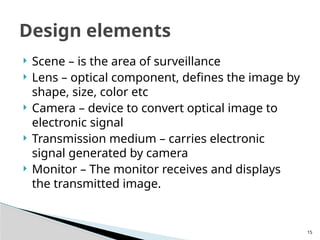
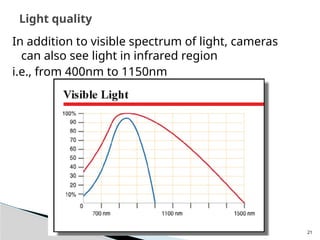
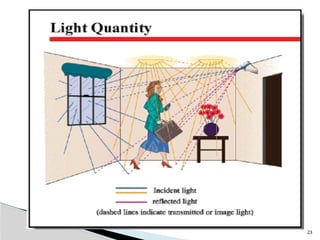
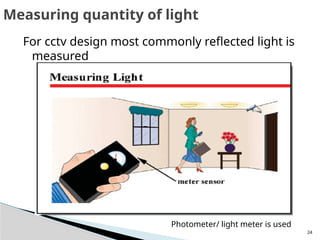
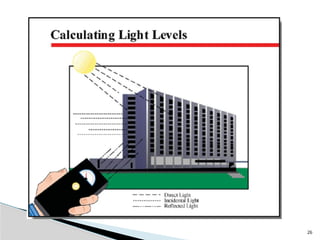
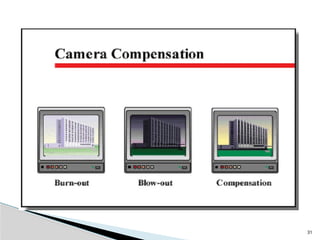
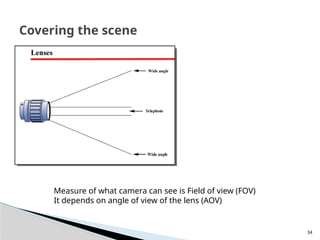
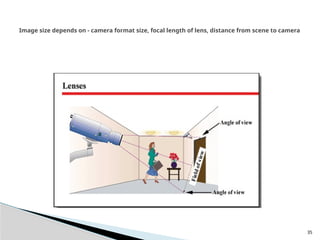
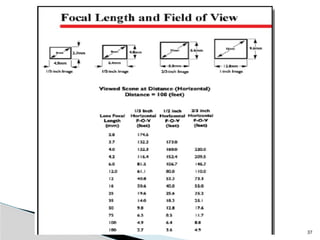
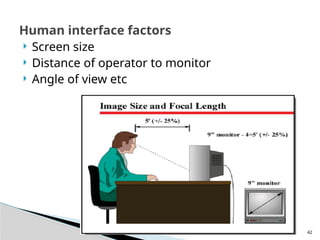
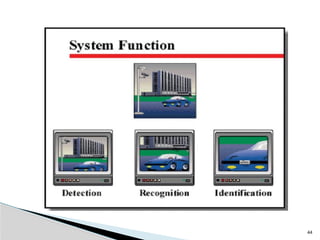
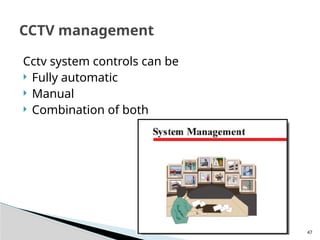
The document outlines the planning and design of CCTV security systems, detailing their history, purposes, various camera types, installation criteria, and factors affecting performance. It emphasizes the importance of proper monitoring setups in diverse environments, such as banking, education, and construction. Additionally, it discusses design elements, lighting considerations, and the ability to counter potential threats to CCTV effectiveness.