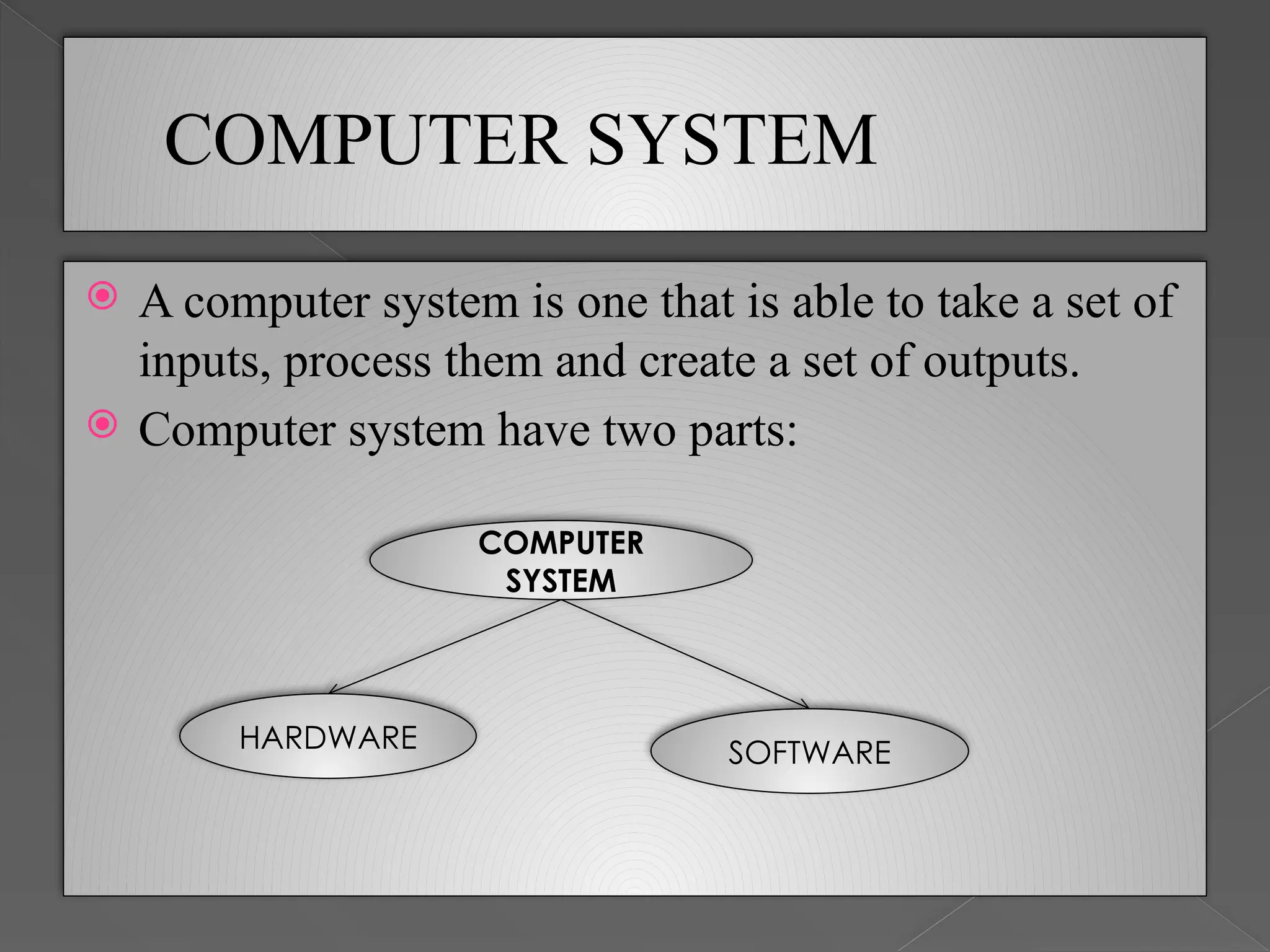
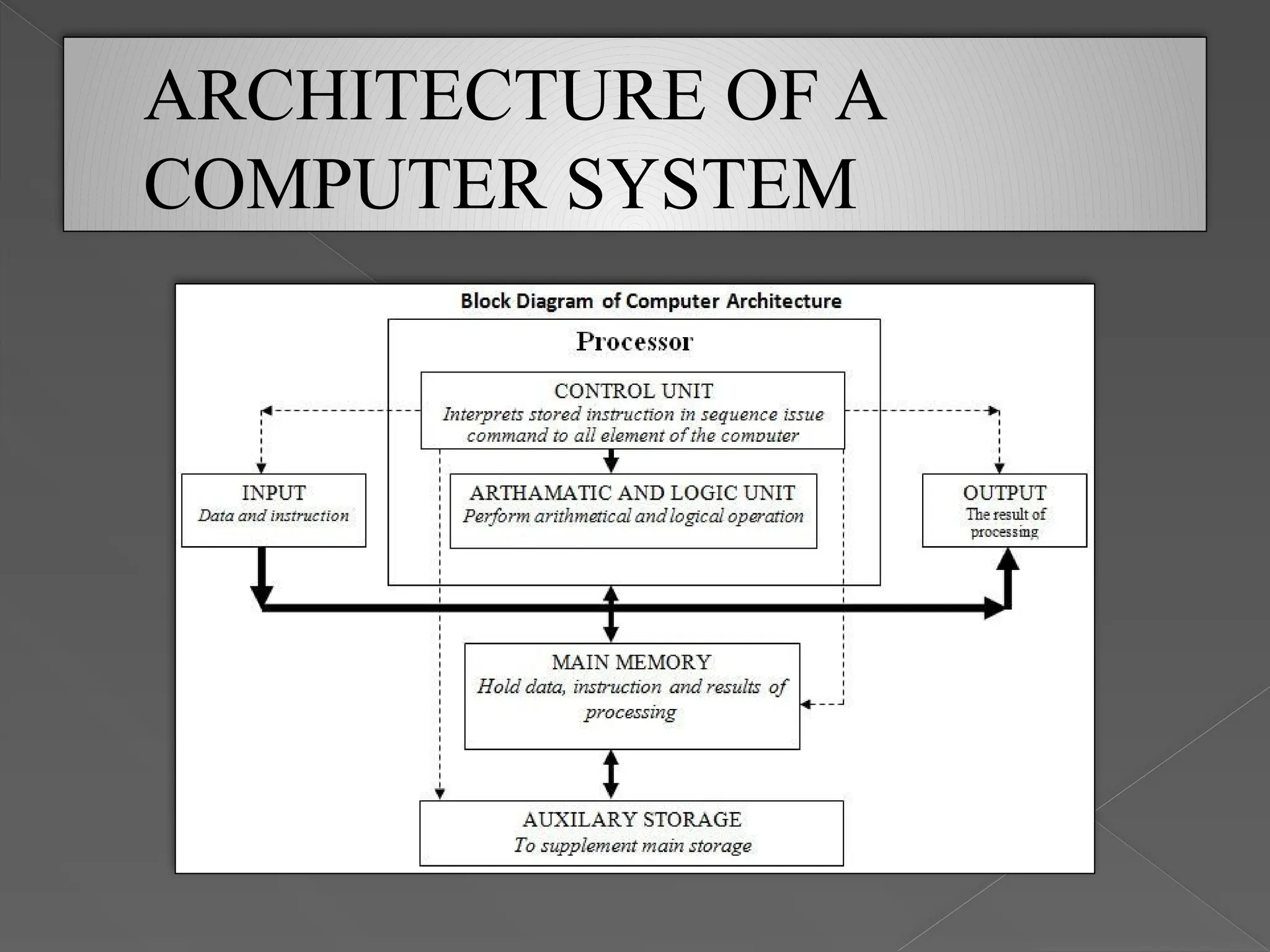
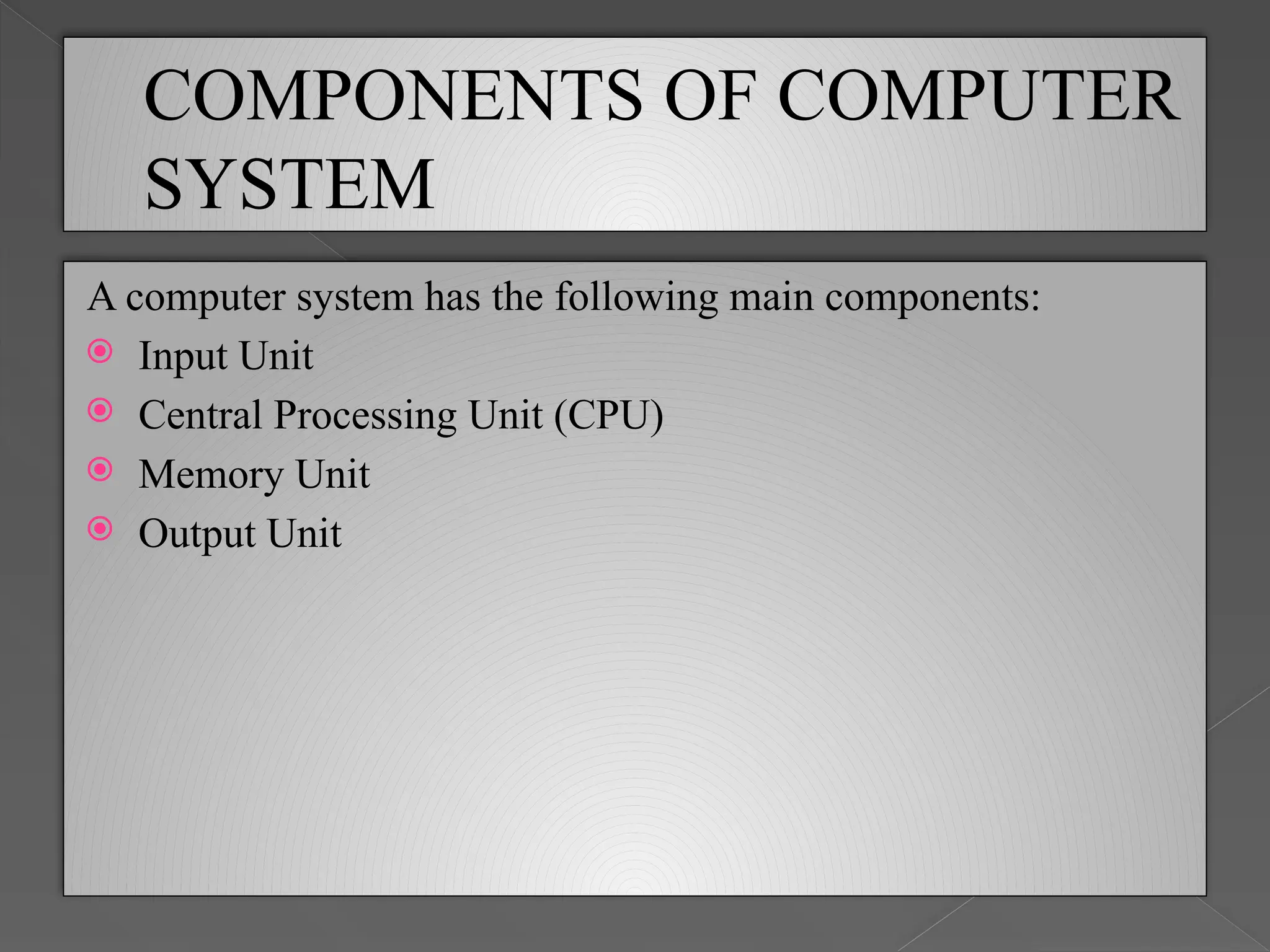
A computer system consists of hardware and software, which work together to process inputs and produce outputs. The main components include input devices (like keyboards and mice), a central processing unit (CPU), memory units, and output devices (such as monitors and printers). Memory is categorized into primary, secondary, and cache memory, each serving different roles in data processing and storage.