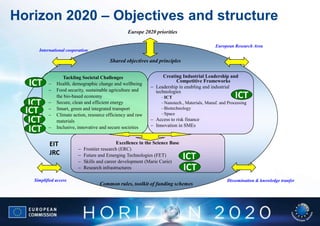
Horizon 2020 is the EU's proposed 80 billion euro research and innovation program for 2014-2020. It aims to strengthen the EU's global competitiveness and address economic, environmental and societal challenges through support for science, industrial technology, and addressing societal problems. The program consolidates separate existing initiatives and focuses on innovation across sectors. It emphasizes key technologies like ICT, and supports business innovation through measures like the SME instrument and access to risk finance.