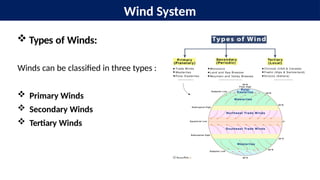
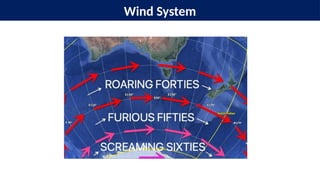
The document provides an overview of wind systems, defining wind as air in motion caused by atmospheric pressure differences. It classifies winds into primary, secondary, and tertiary types, with a focus on primary winds such as trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies, describing their characteristics and patterns. Key factors influencing planetary wind patterns include latitudinal temperature variations, pressure belt emergence, the distribution of land and water, and the Earth's rotation.