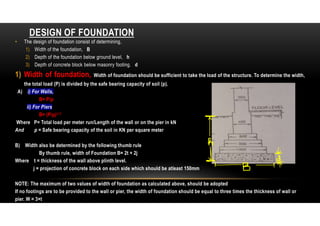
1) The width of the foundation is determined as the total load divided by the safe bearing capacity of the soil. It is also calculated using empirical thumb rules.
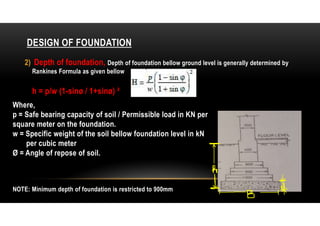
2) The depth of the foundation is calculated using Rankine's formula which considers the safe bearing capacity, soil weight, and angle of repose.
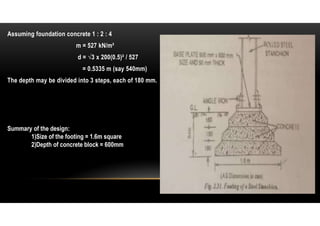
3) The depth of the concrete block is calculated using a formula considering the safe bearing capacity, projection of the block, and modulus of rupture of concrete. Empirical thumb rules are also used.