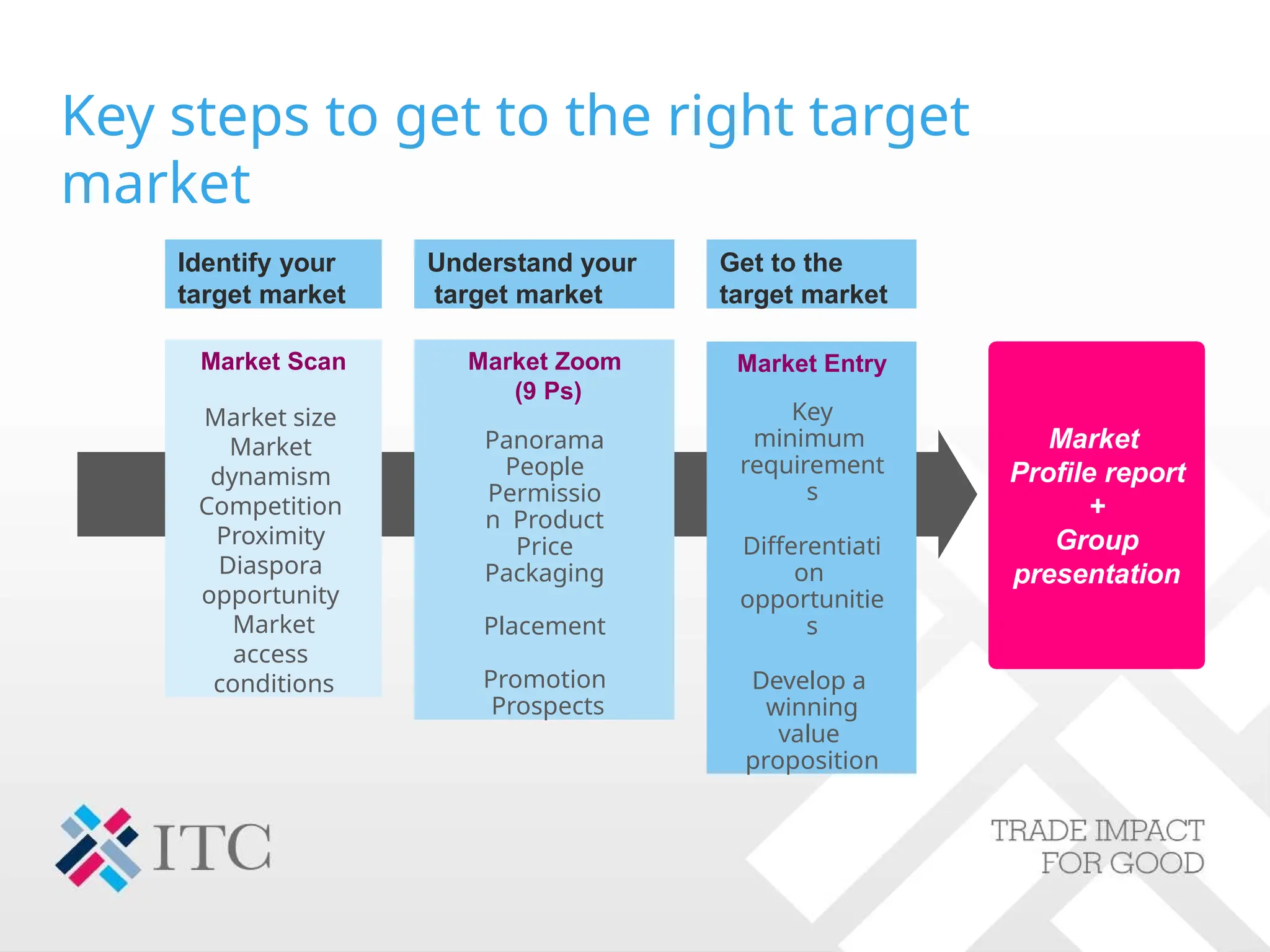
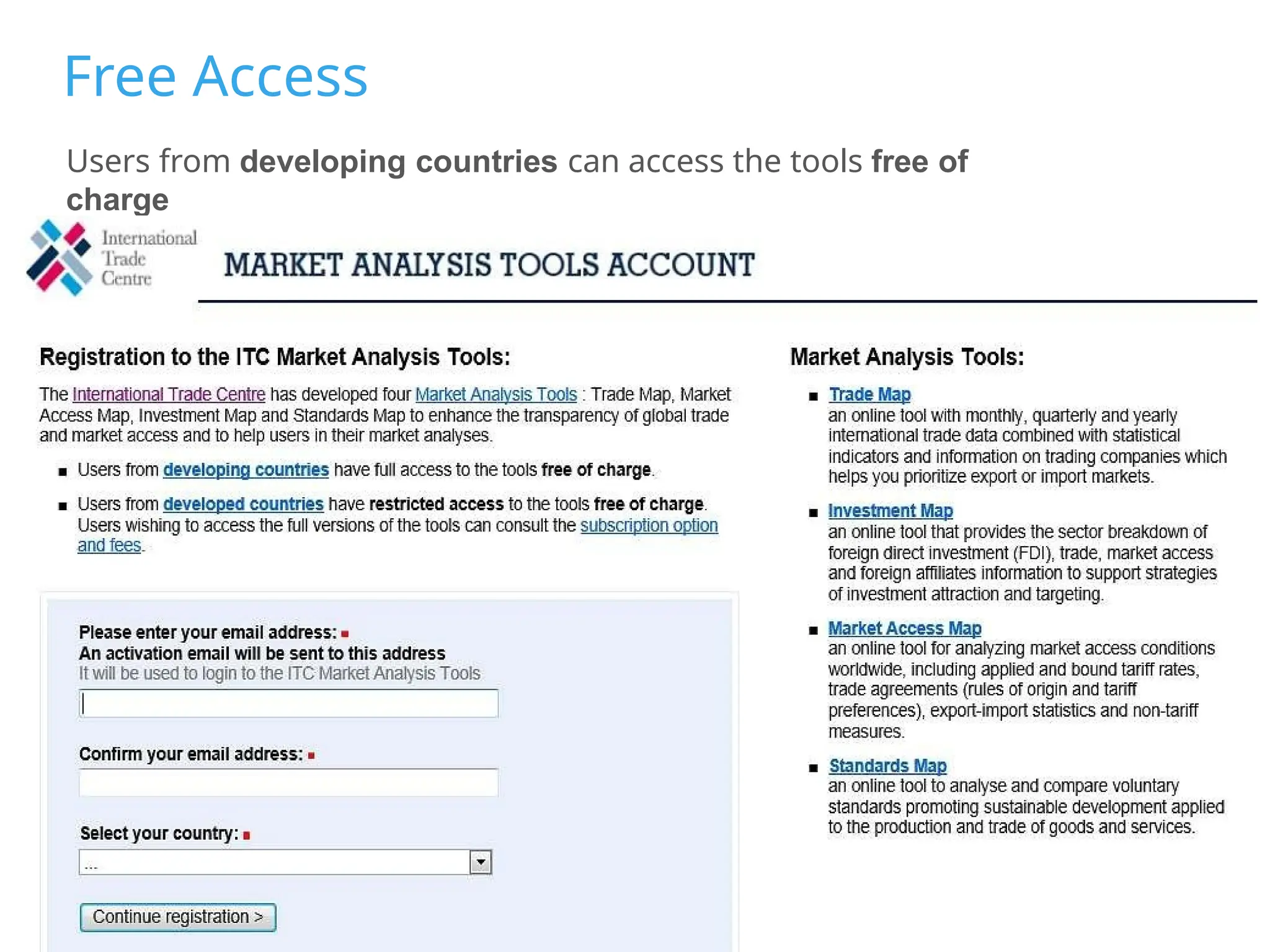
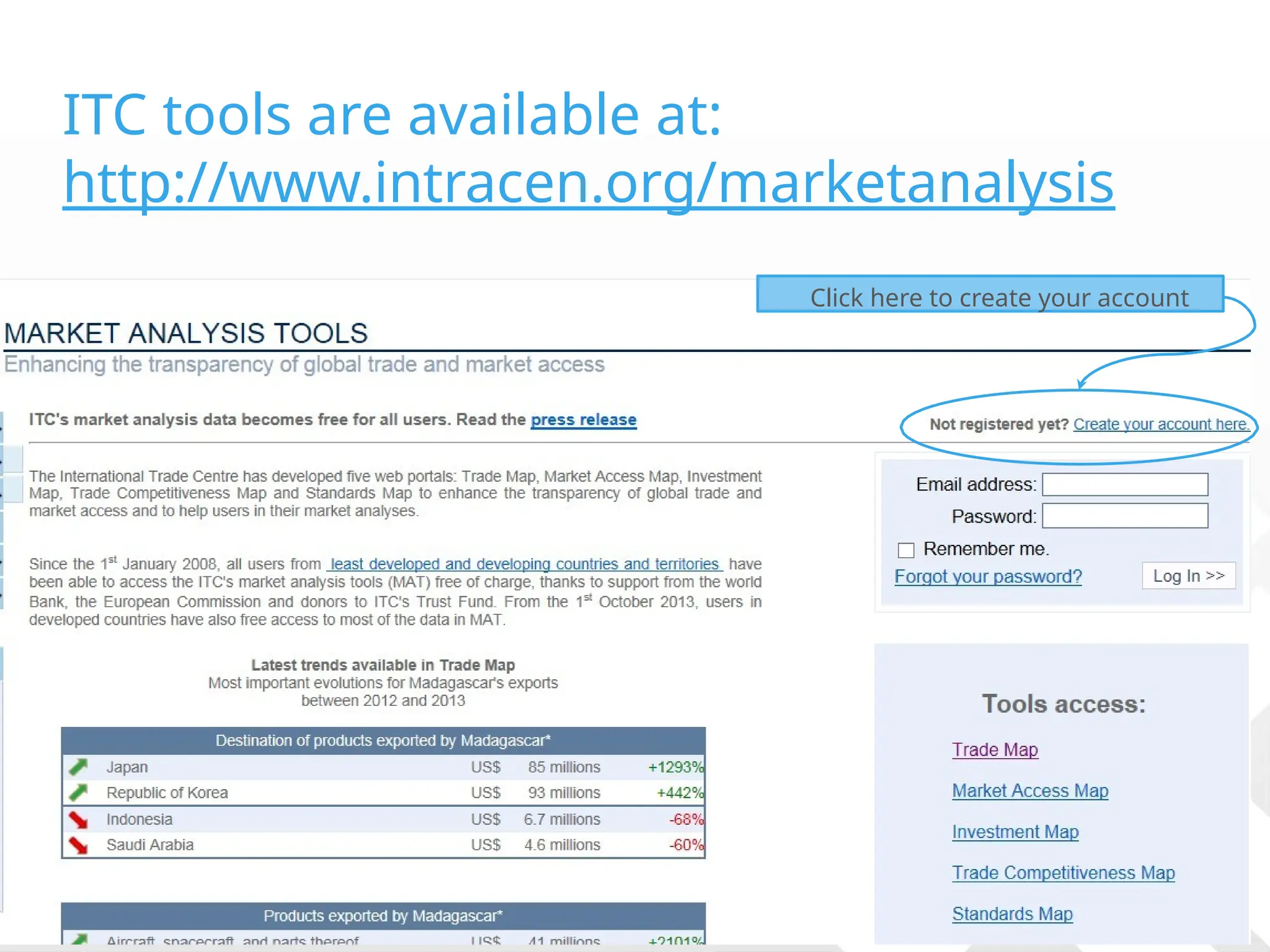
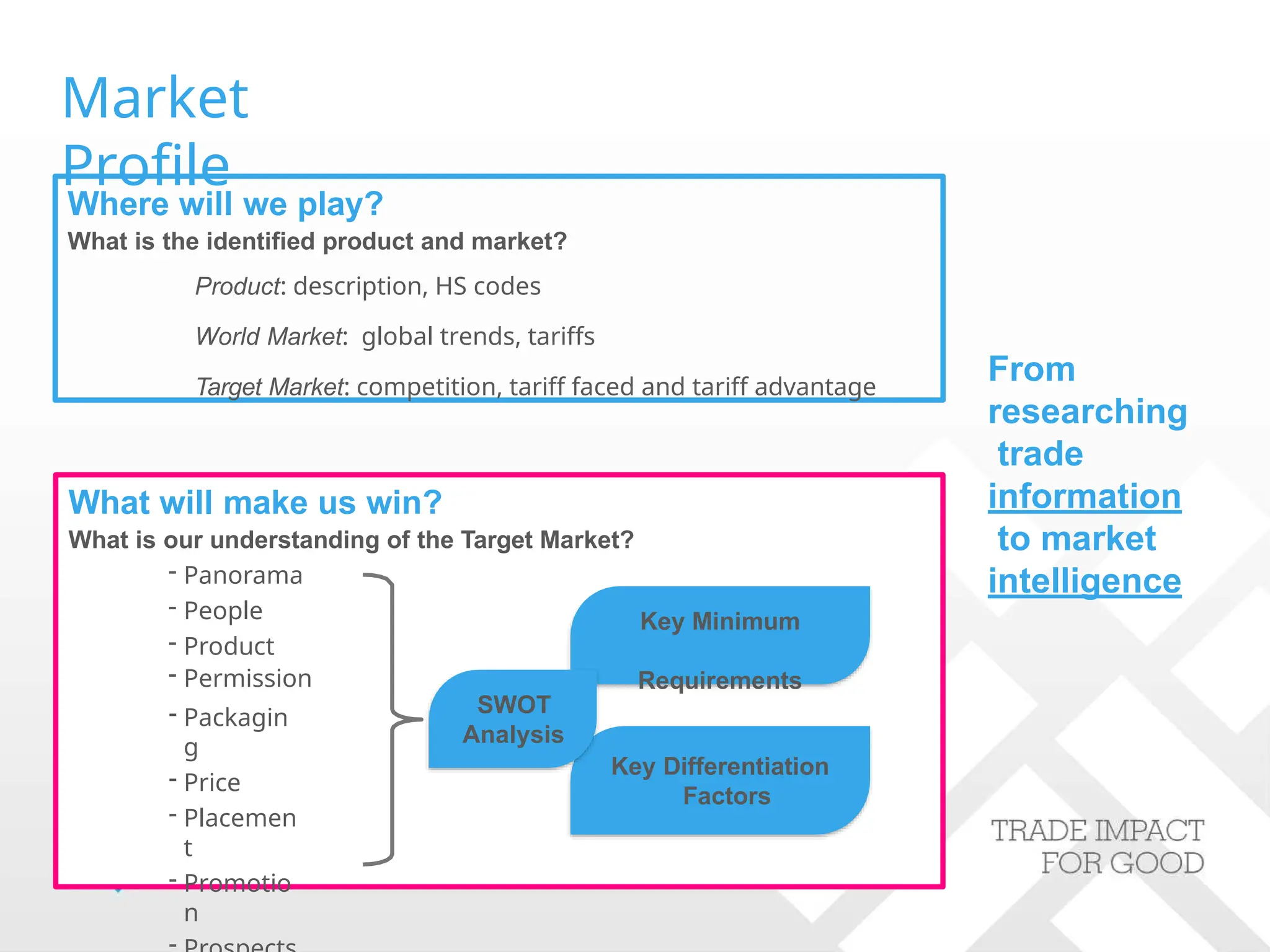
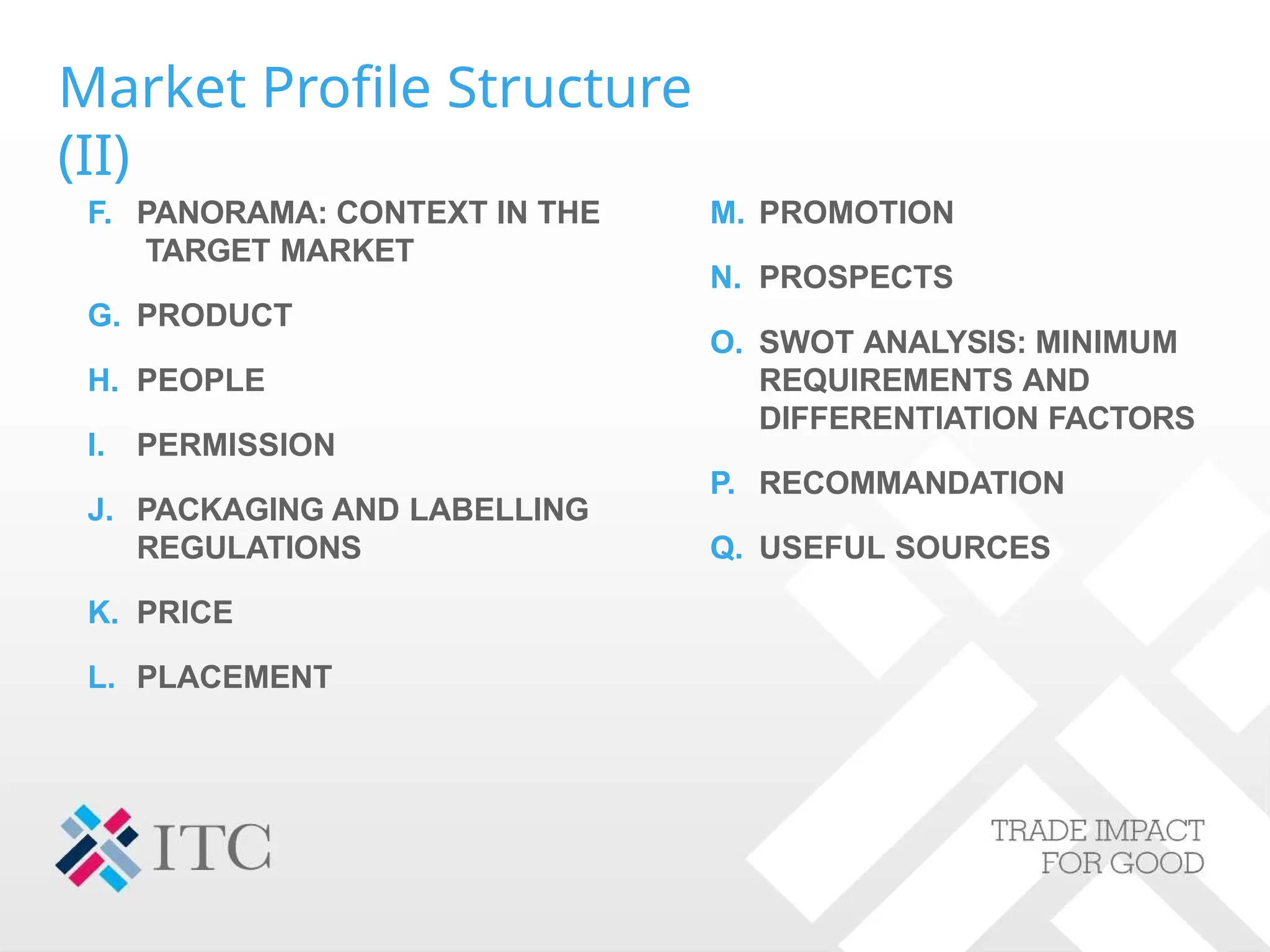
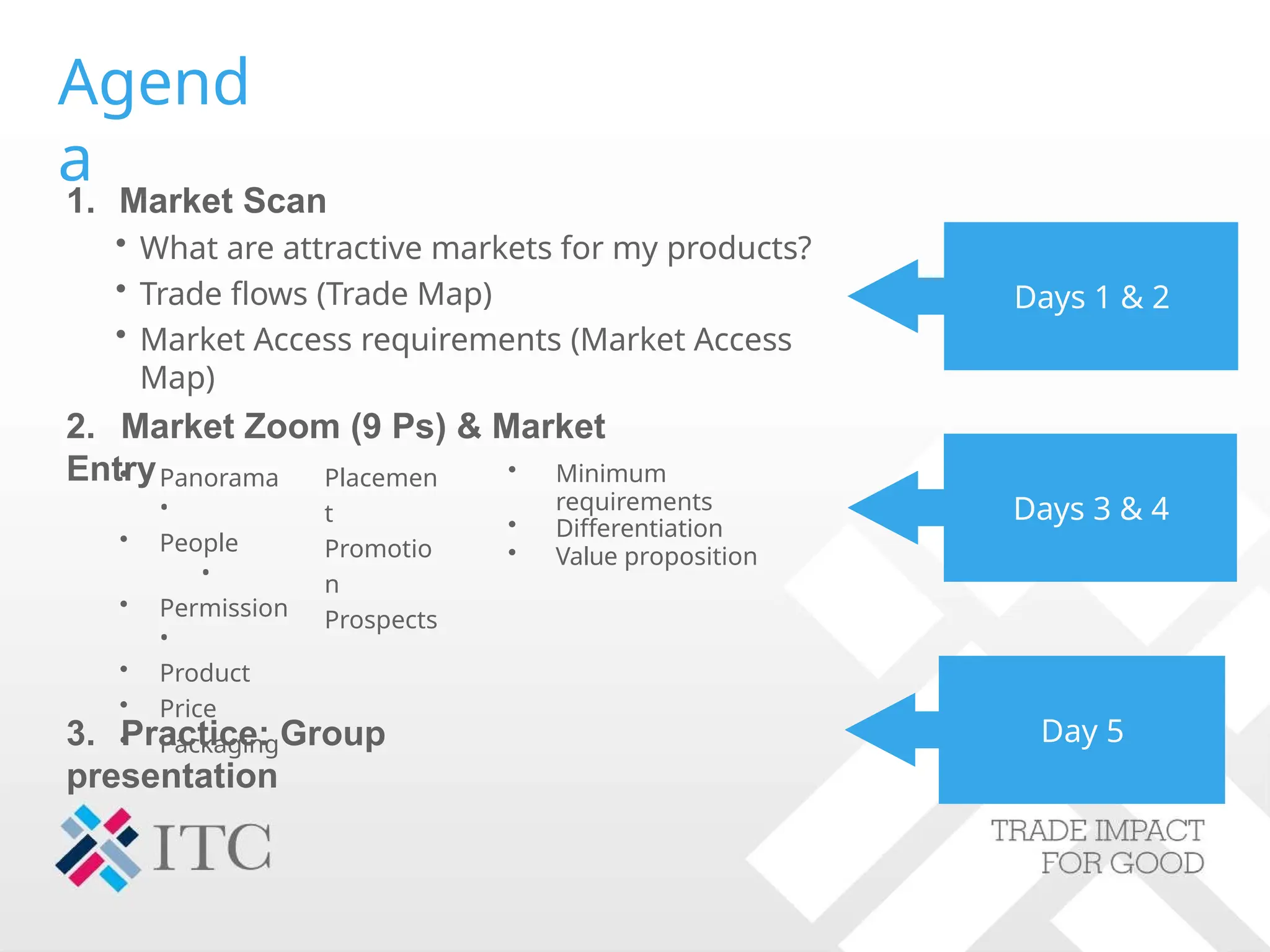
The document outlines strategies for companies considering global exports, emphasizing market identification, export marketing plans, and understanding import procedures. It details tools and frameworks for analyzing market opportunities, including the 'Market Zoom' approach and the importance of creating a comprehensive market profile. Additionally, it highlights critical factors like competition, regulatory requirements, and developing a strong value proposition for successful market entry.