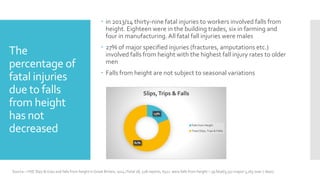
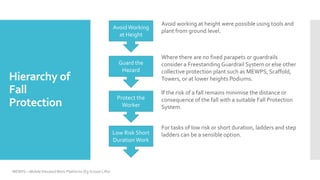
This document provides guidance on working at height using ladders and steps. It discusses selecting the appropriate equipment based on a risk assessment and hierarchy of fall protection. It emphasizes maintaining three points of contact, securing ladders, pre-use checks, and keeping records of inspections. Employers are responsible for providing suitable and safe equipment, while employees must use equipment properly and report any safety hazards.