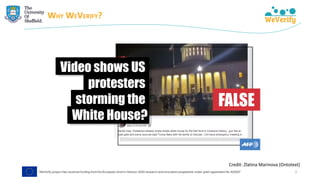
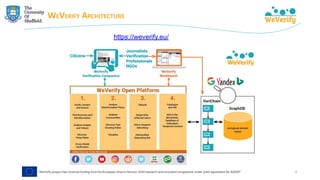
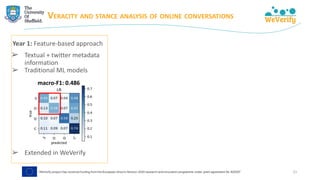
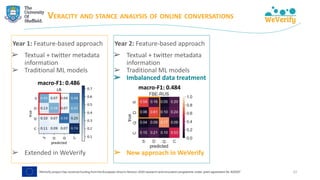
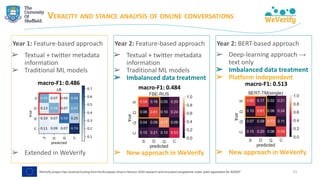
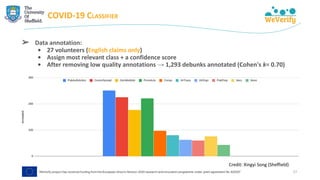
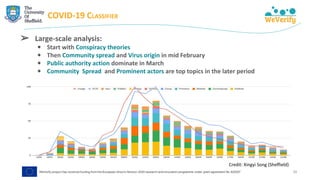
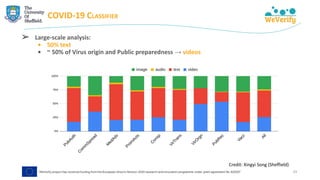
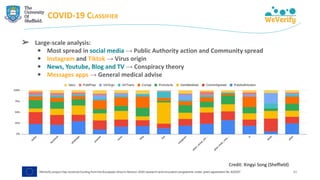
The document discusses methods for detecting and verifying online disinformation using natural language processing (NLP) and data analysis, focusing on the WeVerify architecture and collaborative tools. It outlines the COVID-19 misinformation classifier and various approaches over multiple years to analyze online conversations related to disinformation, highlighting the improvement of machine learning models. Additionally, it presents ongoing work related to multilingual misinformation analysis and the impact of social media on spreading disinformation.


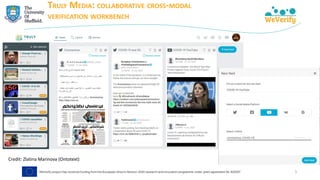
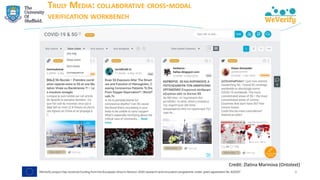
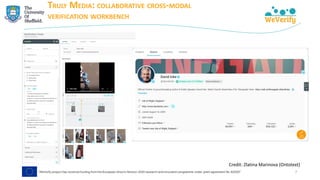



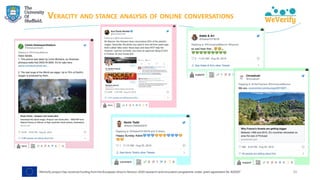




![COVID-19 SOCIAL MEDIA ANALYSIS
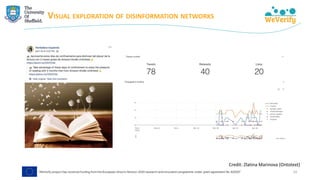
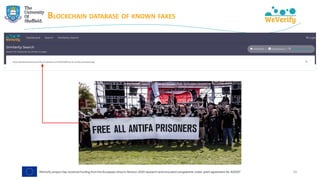
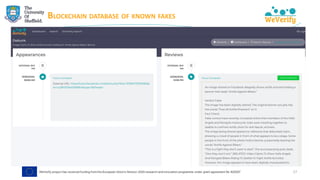
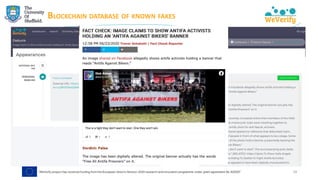
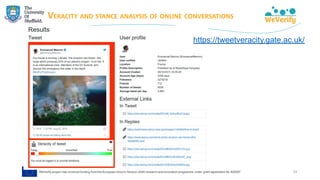
➢ Matching debunks (IFCN dataset) with tweets → finding misinformation
"[The coronavirus is] ‘new’ yet it was lab-created and patented in 2015"
https://www.poynter.org/?ifcn_misinformation=the-coronavirus-is-new-yet-it-was-lab-created-and-patented-in-2015
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ndworkshopemdatascience08022021-211101111022/85/2nd-workshop-em-data-science-08-02-2021-33-320.jpg)