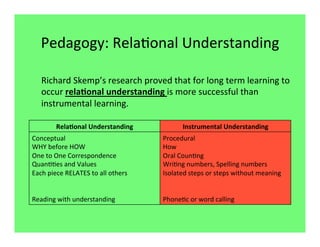
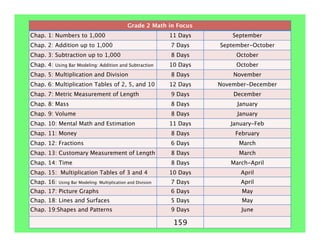
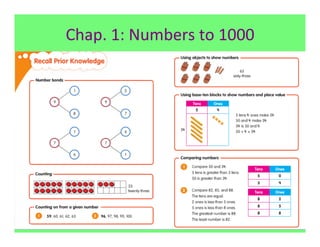
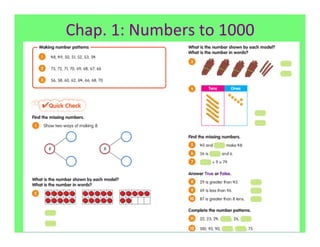
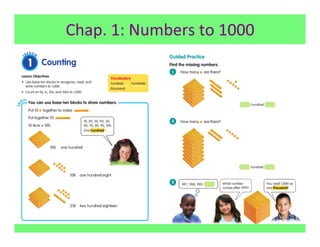
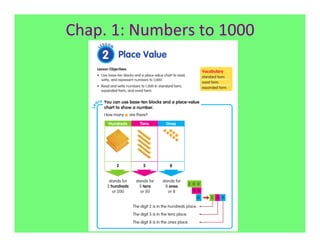
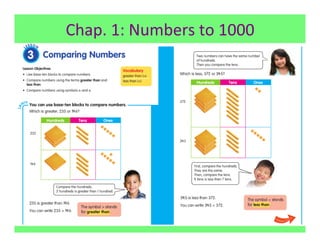
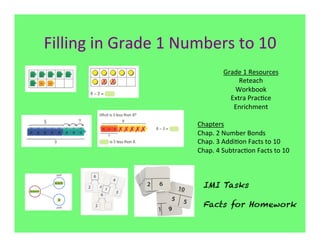
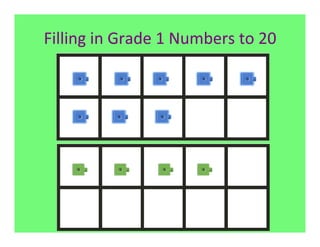
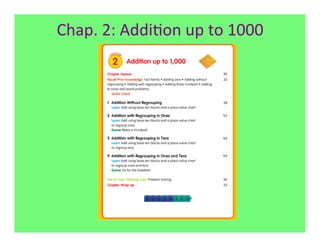
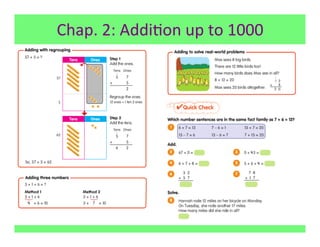
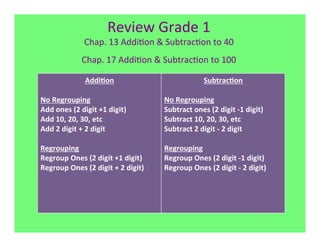
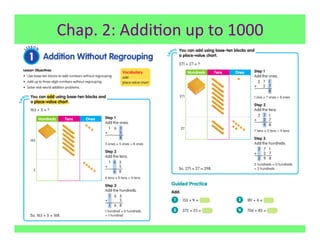
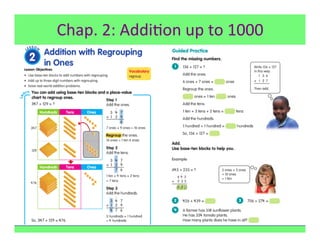
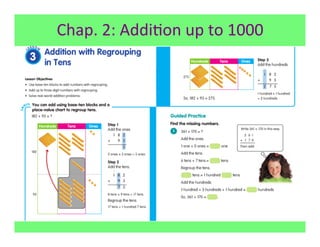
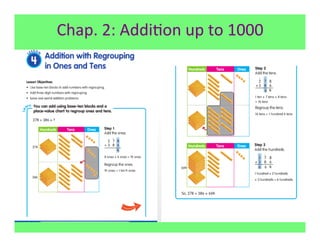
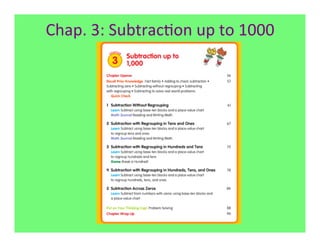
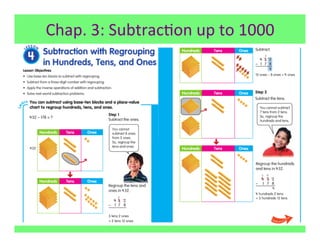
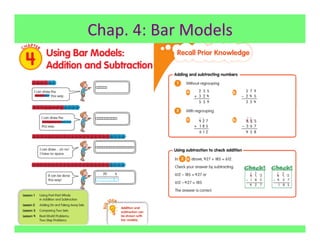
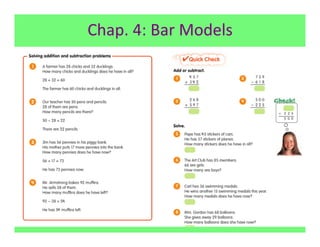
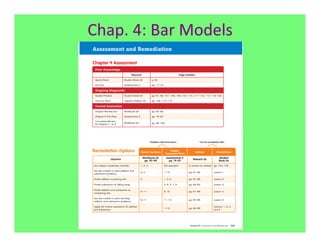
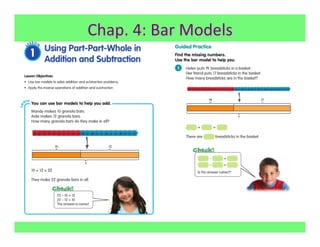
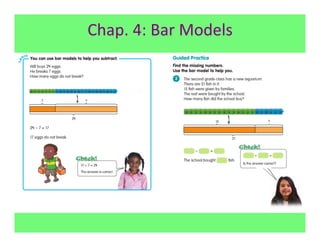
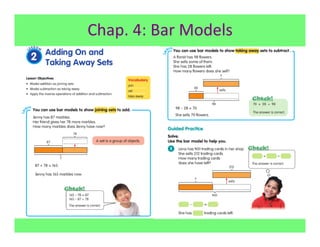
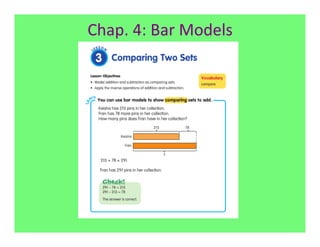
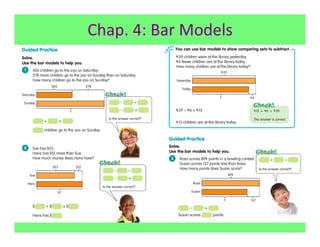
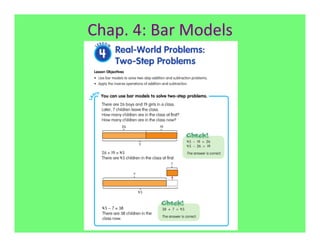
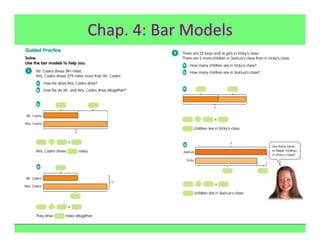
The document outlines the agenda and goals for a 2nd grade teaching staff meeting. The agenda includes updating the training and implementation plan, identifying strategies for common math learning difficulties, and exploring the 2nd grade Math in Focus curriculum content, pedagogy, and pacing. Specific topics to be covered are estimating the prevalence of different math learning difficulties, discussing effective strategies, and reflecting on how the strategies connect to the Singapore Math pedagogical approaches of concrete-pictorial-abstract, relational understanding, and multiple representations. The curriculum pacing guide is also presented, outlining the chapters and time allotted for each across the school year.