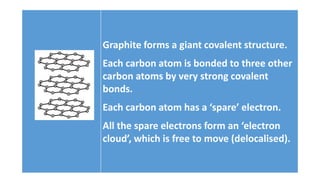
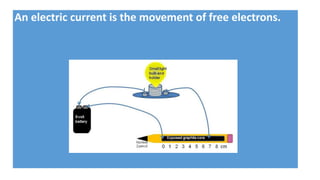
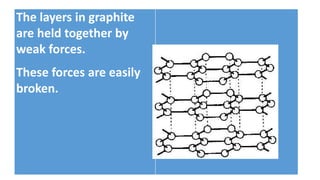
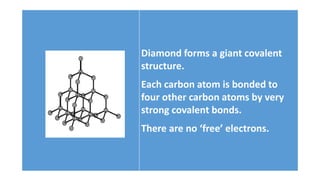
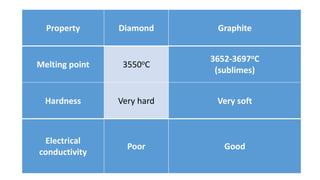
The document discusses the structural and functional differences between diamond and graphite, noting that diamond has a rigid structure with four strong covalent bonds per carbon atom, making it very hard, while graphite has a layered structure with three bonds per carbon atom and delocalised electrons, allowing it to be soft and conductive. It covers everyday uses, such as diamonds in jewelry and drills, and graphite in pencils and lubricants. Additionally, it encourages research into graphene and fullerenes related to their practical applications.