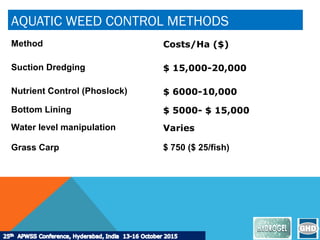
This document discusses potential future solutions for managing aquatic weeds based on experiences in Australia and New Zealand. It describes how aquatic plants can be both useful and problematic in overgrowth. Common aquatic weeds and reasons for controlling them are outlined. Methods for control include various herbicides as well as mechanical and physical removal techniques. Case studies demonstrate successful control of specific weeds like Egeria, Cabomba, and Hydrilla using herbicides in hydrogel formulations or whole lake treatments. Overall, herbicides are seen as useful when applied correctly by experts, but all aquatic weed control requires a tailored approach.