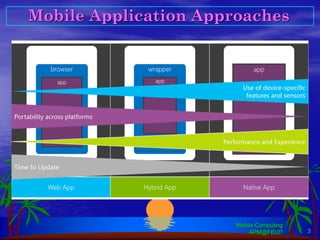
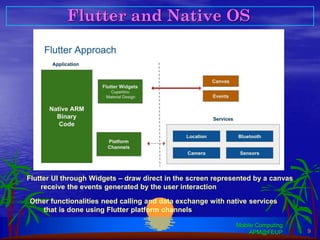
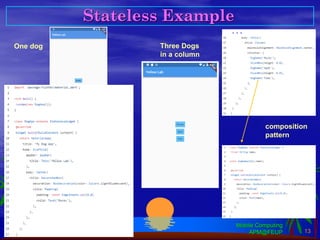
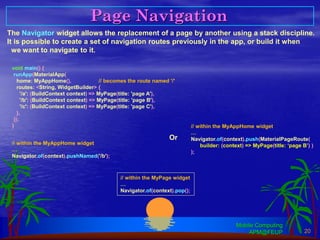
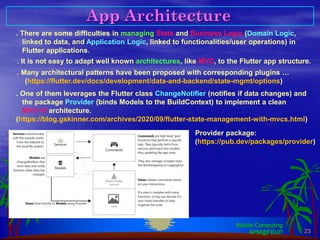
Flutter is an open-source SDK created by Google that allows building mobile, web, and desktop applications from a single codebase using the Dart programming language. It uses a widget-based framework where the UI is composed of widgets that are either stateless or stateful. Stateless widgets are immutable while stateful widgets can change their state which triggers a rebuild. Common widgets like Column, Row, and Scaffold are used to layout screens. Navigation between screens is done using the Navigator widget. Platform-specific code can be accessed through method channels. Popular architectures like MVC can be adapted by leveraging providers and change notifiers to manage state.