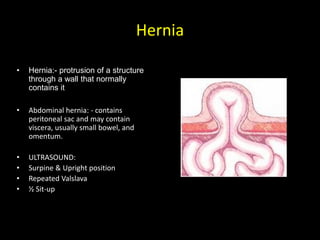
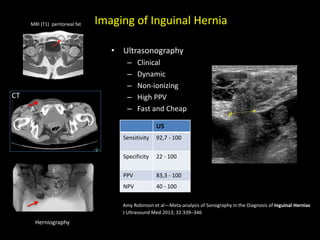
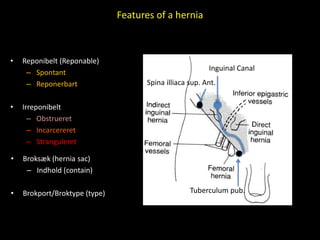
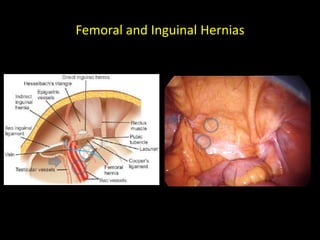
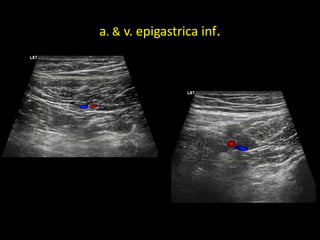
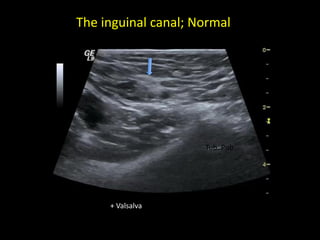
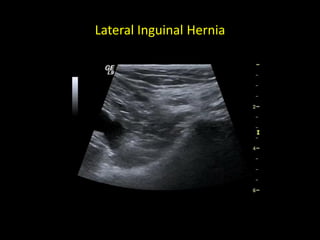
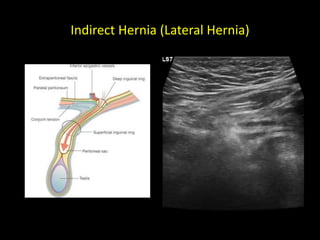
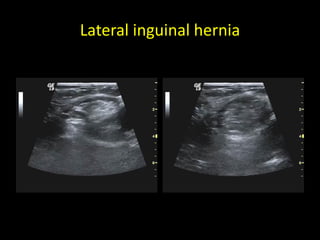
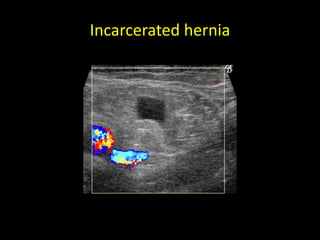
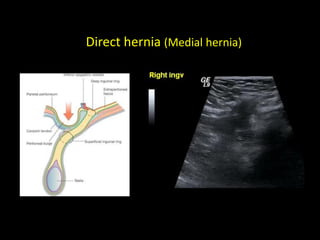
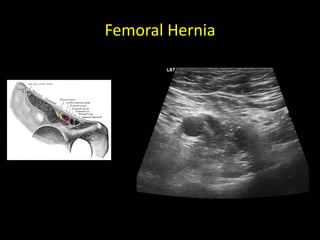
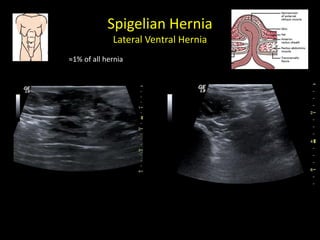
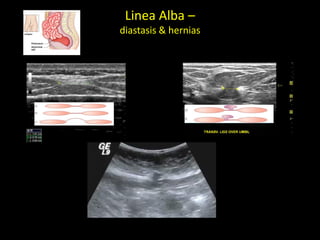
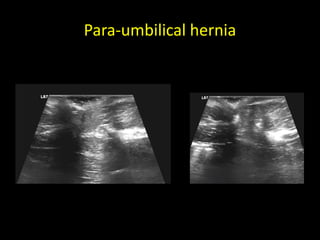
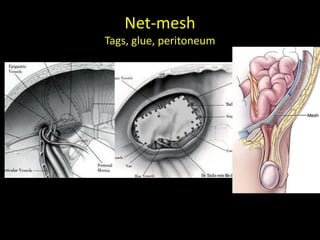
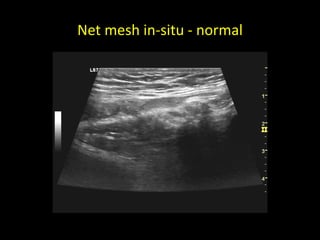
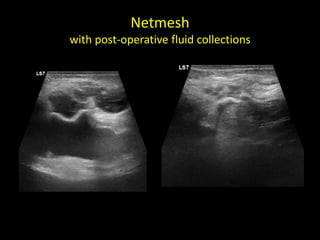
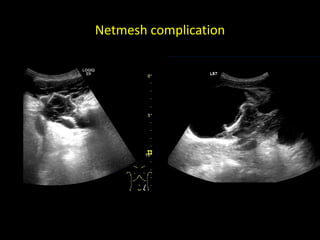
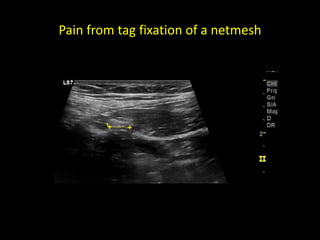
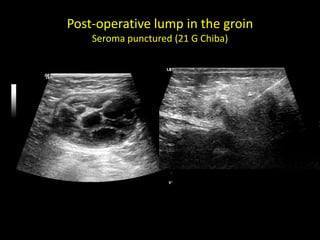
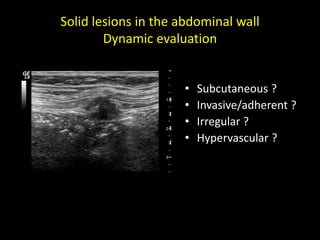
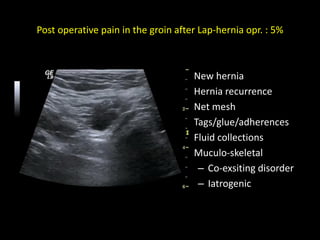
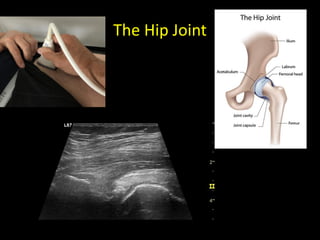
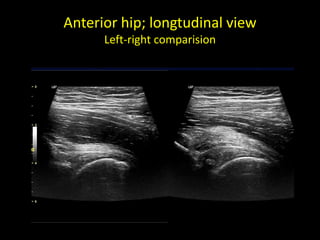
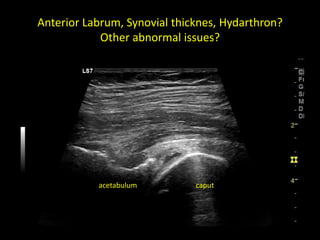
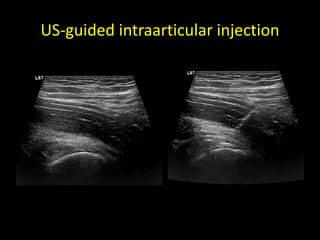
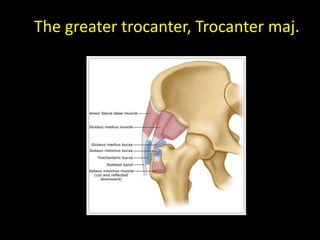
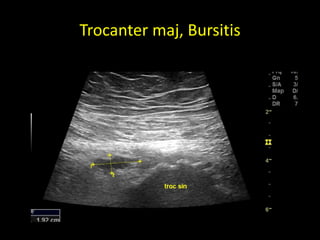
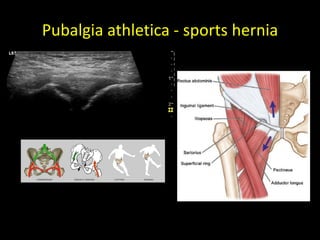
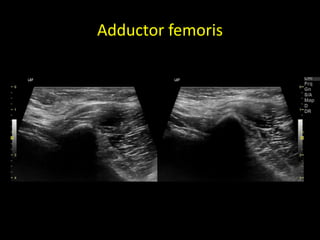
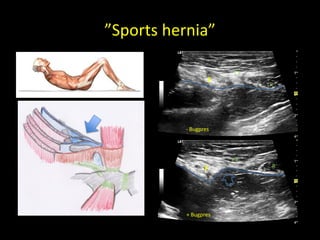
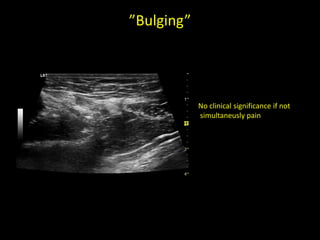
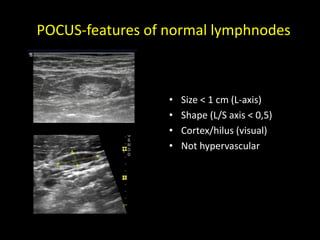
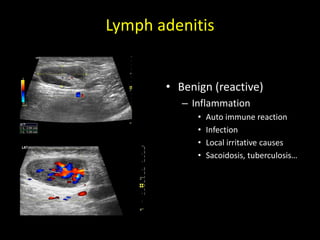
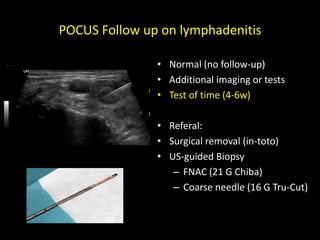
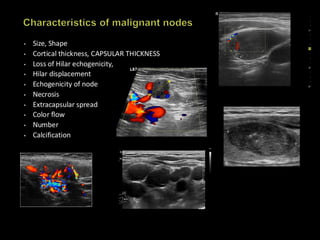
This document discusses point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) of the groin region to evaluate hernias, hip structures, and lymph nodes. It provides information on using ultrasound to diagnose common groin issues like hernias, bursitis, and lymphadenitis. Settings, techniques, and normal versus abnormal ultrasound findings are described for the inguinal canal, femoral region, hip joint, and lymph nodes. The document also discusses applications of ultrasound-guided procedures.