Embed presentation
Download to read offline


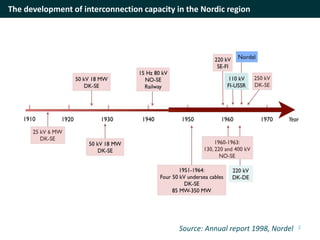
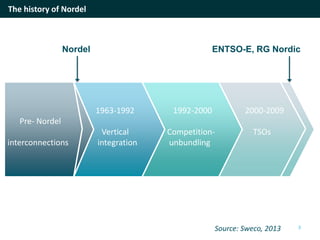
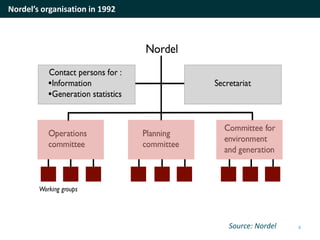
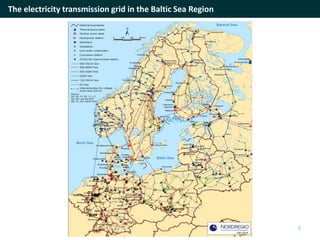
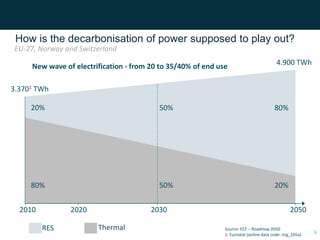
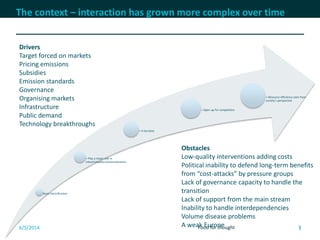

The document discusses cross-border cooperation in the electricity sector through the Nordic example. It outlines the history of interconnections between Nordic countries dating back to 1963, which grew over time through the establishment of Nordel in 1992 to facilitate cooperation between transmission system operators. Nordel later joined ENTSO-E and helped coordinate the decarbonization of the power sector in the region through increasing renewable energy and electrification while maintaining a reliable grid through 2050. The context of cooperation has become more complex over time with new drivers like emissions pricing and public demand, as well as obstacles around political will, governance capacity, and handling interdependencies across borders.







