2014 BDSRA Storch CLN7
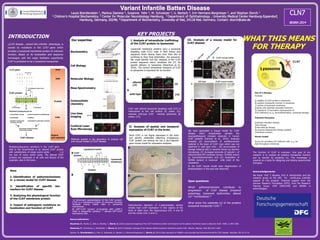
- 1. Variant Infantile Batten Disease Laura Brandenstein 1, Markus Damme 4, Susanne Fehr 2, M. Schweizer 2, U. Bartsch 3, Irm Hermans-Borgmeyer 2, and Stephan Storch 1 1 Children’s Hospital Biochemistry, 2 Center for Molecular Neurobiology Hamburg, 3 Department of Ophthalmology , University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 20246; 4 Department of Biochemistry, University of Kiel, 24118 Kiel, Germany. Contact: storch@uke.de INTRODUCTION CLN7 disease , variant late infantile phenotype, is caused by mutations in the CLN7 gene which encodes a lysosomal membrane protein of unknown function. Based on its localization and sequence homologies with the major facilitator superfamily CLN7 is predicted to be a lysosomal transporter. Mutations/sequence variations in the CLN7 gene (X) lead to the biosynthesis of an altered CLN7 protein with substitutions of single amino acids (;; ■; *) or the loss of many amino acids. The altered CLN7 proteins are expressed in all cells and tissues of the organism, also in the brain. KEY PROJECTS WHAT THIS MEANS FOR THERAPY Biochemistry Cell Biology Molecular Biology Immunohisto chemistry Methods applied in the laboratory to analyze cell and mouse models of CLN7 disease. Aims 1. Identification of pathomechanisms in a mouse model for CLN7 disease 2. Identification of specific bio-markers for CLN7 disease 3. Analyzing the physiological function of the CLN7 membrane protein 4. Impact of pathogenic mutations on localization and function of CLN7 Our expertise Mass Spectrometry Live time imaging Confocal Laser Scan Microscopy I. Analysis of intracellular trafficking of the CLN7 protein to lysosomes Lysosomal membrane proteins carry a lysosomal targeting code (LTC) code in their amino acid sequence which directs them from their site of synthesis to their final destination, the lysosome. We could identify two key residues in the CLN7 protein sequence which constitute the LTC for specific delivery to lysosomes (Steenhuis et al., 2010). The correct intracellular transport of CLN7 to lysosomes is important for its function. CLN7 with altered lysosomal targeting code (LTC) is mislocalized at the cell surface (A; green, CS), whereas wild-type CLN7 reaches lysosomes (B; yellow, LYS). II. Analysis of spatial and temporal expression of CLN7 in the brain. Since CLN7 is not highly expressed in the brain and specific antibodies detecting endogenous CLN7 protein are lacking we use a lacZ-reporter gene mouse model for expression analyses. III. Analysis of a mouse model for CLN7 disease Histochemical detection of b-galactosidase activity reveals high CLN7 expression in two regions of the brain of adult mice, the hippocampus (HC, A and B) and the cortex (Ctx, A and C). We have generated a mouse model for CLN7 disease which recapitulates partially the neuropathological changes observed in human CLN7 patients (Damme et al., 2014). Analyses revealed (A) accumulation of autofluorescent material in the brain of CLN7 mice which was not observed in wild type mice , (B) accumulation of storage material (db) in neurons shown by electron microscopy, (C) increased amounts of subunit c of mitochondrial ATP synthase (brown, SCMAS) shown by immunhistochemistry and (D) localization of SCMAS (green) in neuronal cells (red) of the cerebellum. In the CLN7 mouse model early degeneration of photoreceptors in the eyes was observed. Open questions: Which pathomechanisms contribute to progression of CLN7 disease (impaired autophagy, lysosomal dysfunction, altered Ca2+ homöostasis) ? What is/are the substrate (s) of the putative lysosomal transporter CLN7 ? The function of CLN7 is unknown. One goal of our research is to analyze its putative transporter function and to identify its substrate (s). This knowledge is required as a basis for designing and testing experimental therapies. Acknowledgements: We thank Prof. T. Braulke, Prof. A. Kohlschütter and the research group at the UKE for continuous scientific support of the projects. Financial support from the German Research Foundation (DFG), from the Research Training Group 1459 (GRK1459) and BDSRA is acknowledged. * * A B * * A) Schematic representation of the CLN7 protein. CLN7 is a membrane protein of unknown function localized mainly inside cells in lysosomal membranes. B) GFP-CLN7 (green) co-localizes with LAMP-2 (red) in lysosomes (yellow). * denote GFP-CLN7 expressing cells. Recent publications: Steenhuis, P., Herder, S., Gelis, S., Braulke, T., Storch, S. (2010) Lysosomal targeting of the CLN7 membrane protein and transport via the plasma membrane require a dileucine motif. Traffic, 11:987-1000. Steenhuis, P., Froemming, J., Reinheckel, T., Storch, S. (2012) Proteolytic cleavage of the disease-related lysosomal membrane protein CLN7. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 822:1617-1628. Damme, M., Brandenstein, L., Fehr, S., Jankowiak, A., Bartsch, U., Hermans-Borgmeyer, I., Storch, S. (2014) Gene disruption of Mfsd8 in mice provides the first animal model for CLN7 disease. Neurobio. Dis. 65:12-24.
