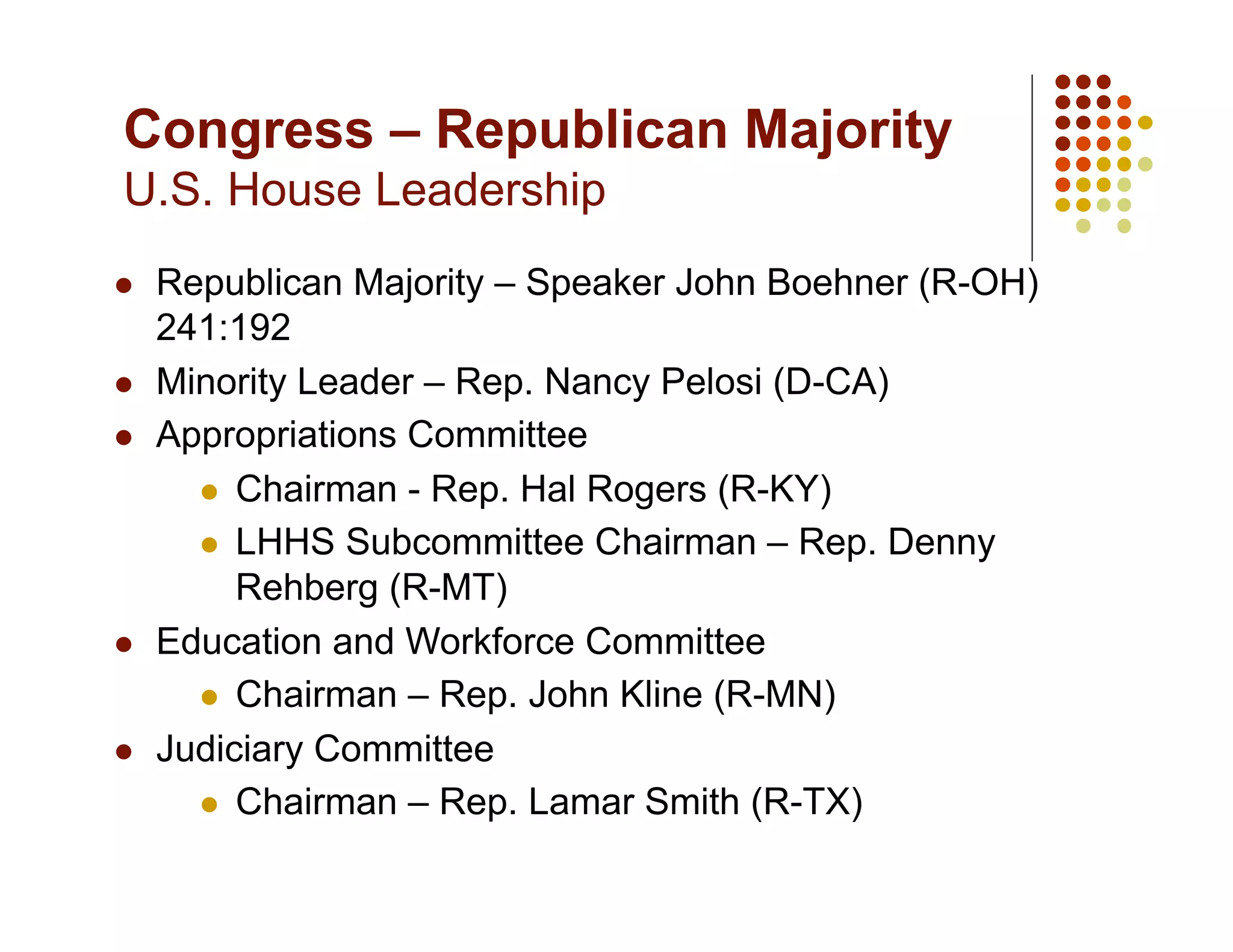
The document provides an overview of the 112th Congress and federal education priorities and budgets. It discusses:
1) Leadership changes in Congress and the Department of Education.
2) The status of the FY2011 budget, which is operating under a continuing resolution, and outlines for the FY2012 budget.
3) Key education priorities for reauthorizing the Workforce Investment Act, Elementary and Secondary Education Act, and passing the Dream Act. Disagreements around reducing deficits may impact what legislation gets passed.