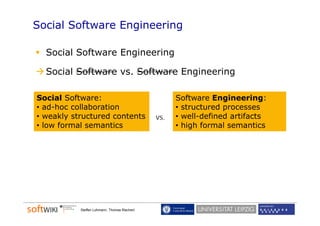
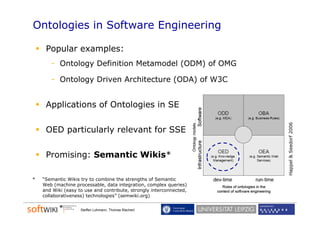
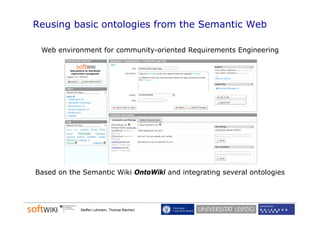
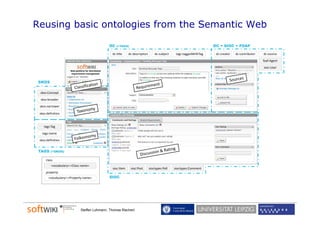
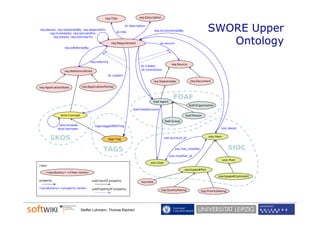
The document discusses the role of social software engineering (SSE) and the integration of ontologies to enhance community-oriented requirements engineering. It emphasizes the importance of reusing existing basic ontologies from the semantic web, such as Dublin Core and SKOS, to improve interoperability and collaboration in online environments. Future work includes addressing limitations in current ontologies and extending the SWORE upper ontology for better representation of software engineering aspects.