This document discusses corporate control and governance. It covers several topics:
- The increasing power and influence of multinational corporations globally and within countries.
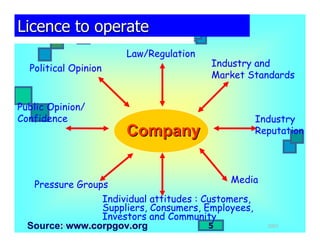
- The various stakeholders that influence a company's "license to operate" including shareholders, customers, employees, and communities.
- Whether companies in the 21st century can focus only on shareholders and financial measures, or need to consider other stakeholders and transparency.
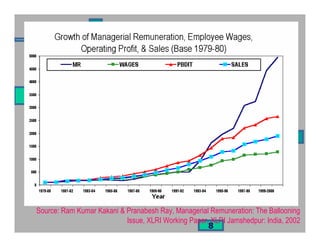
- Examples of governance issues like related party transactions and wealth transfers in some Indian companies.
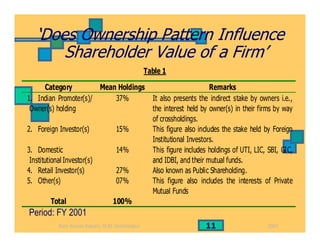
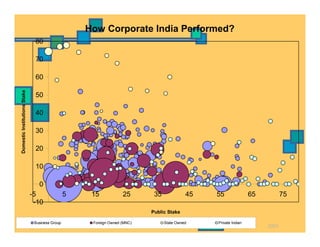
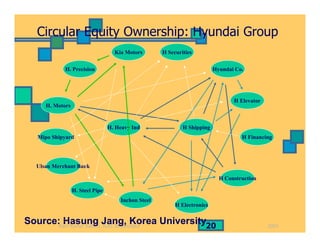
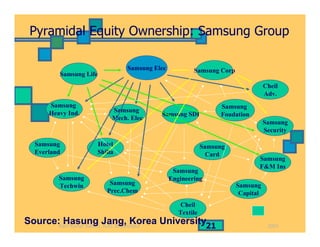
- How ownership patterns in India differ between foreign, state-owned, business group-controlled and private companies and how this influences performance.
- Some of the governance reforms and new regulations proposed or implemented in India.