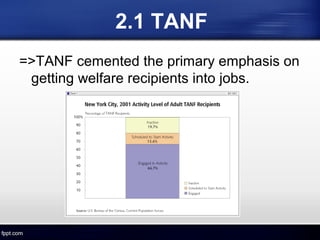
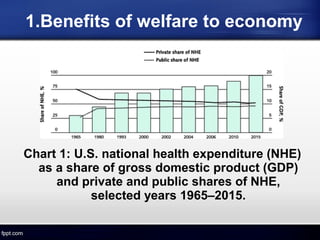
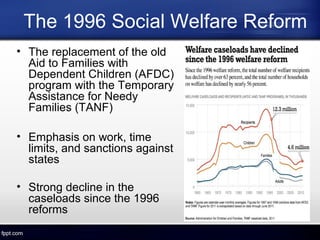
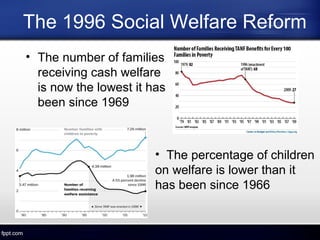
The document discusses the US welfare state. It describes the goals of preventing poverty and helping the unemployed find work. It outlines the main welfare services and programs, including TANF, which replaced AFDC and emphasizes work requirements. The welfare system provides benefits to the economy by reducing income inequality and subsidizing health costs. A major achievement was the 1996 welfare reform that established work requirements and time limits, leading to dramatic declines in caseloads.











![2. Welfare’s Programs
• Many smaller
government-assistance
programs
E.g.: Special
Supplemental Food
Program for Women,
Infants and Children
[WIC]; general
assistance [GA]…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-theuswelfarestatepresentation-130507104657-phpapp02/85/2-the-us-welfare-state-presentation-12-320.jpg)