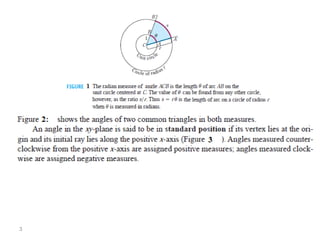
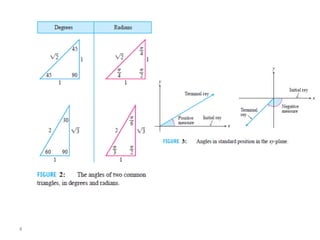
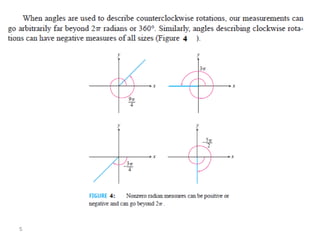
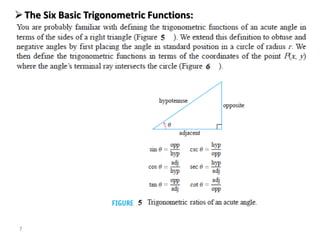
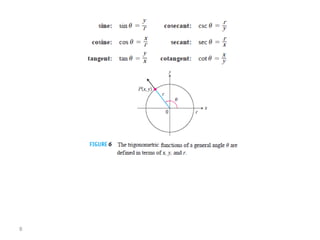
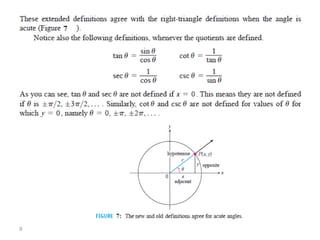
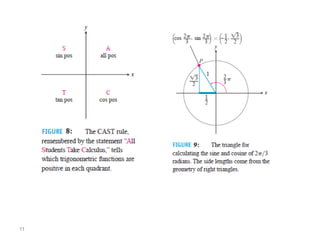
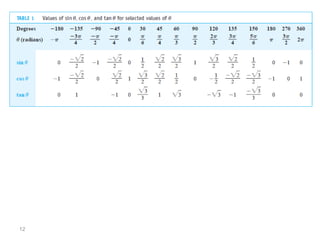
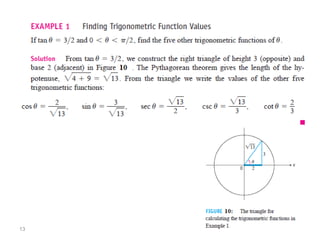
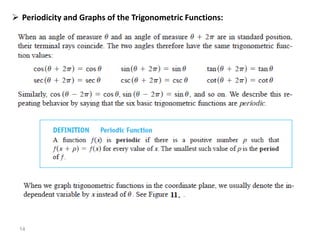
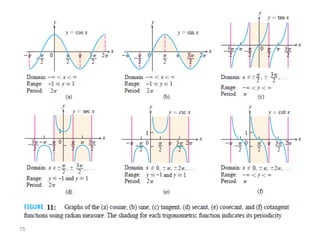
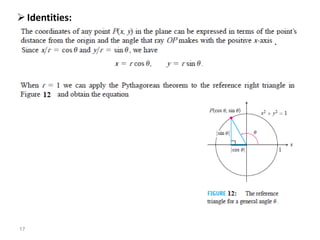
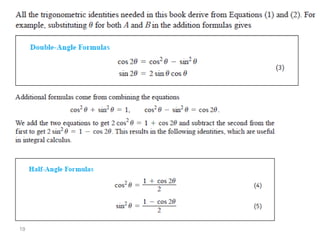
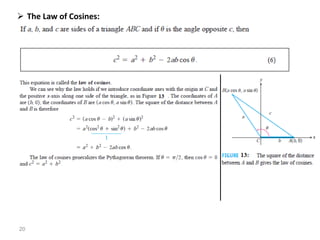
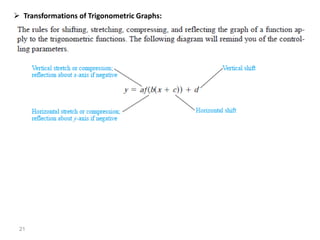
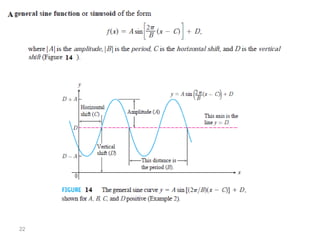
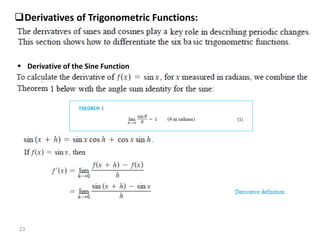
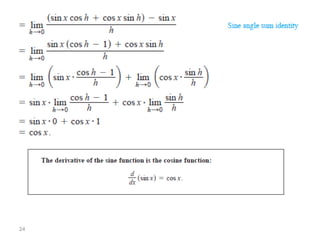
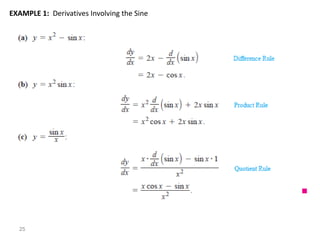
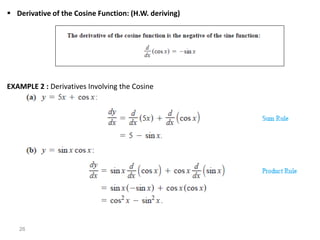
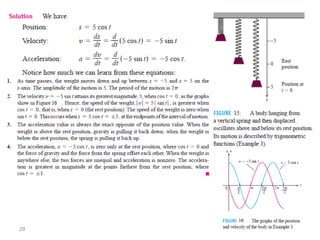
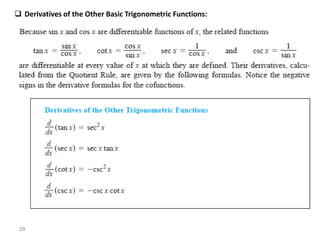
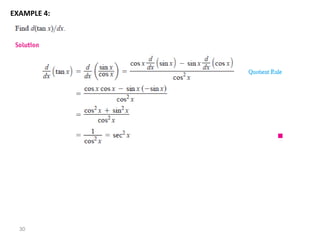
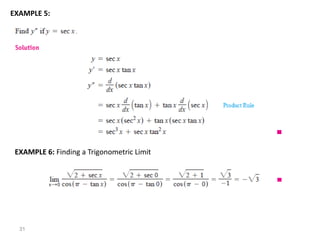
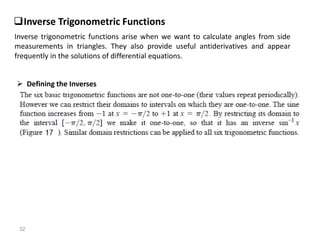
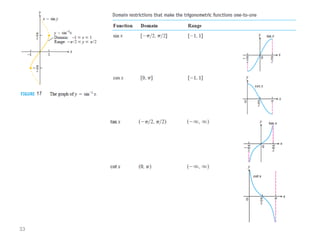
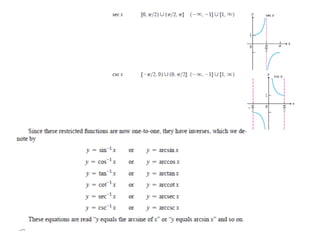
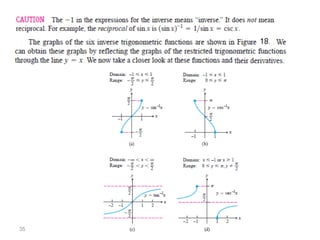
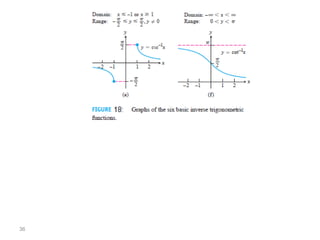
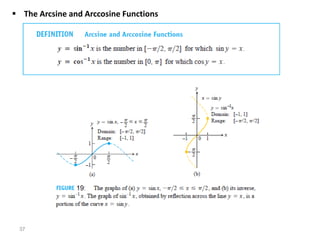
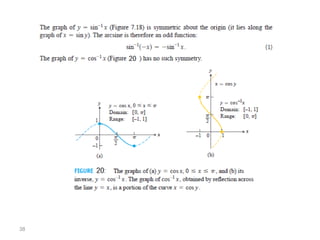
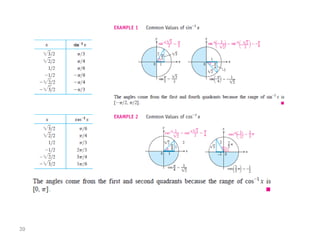
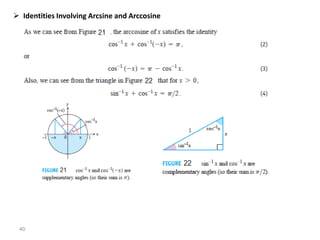
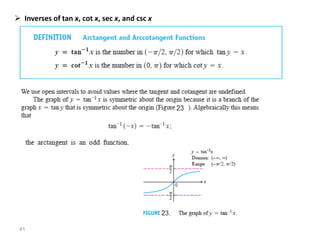
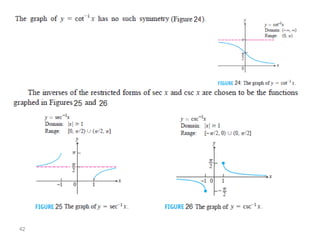
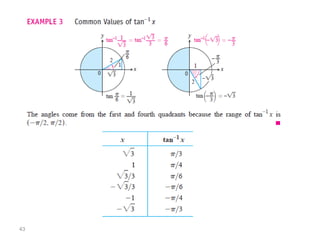
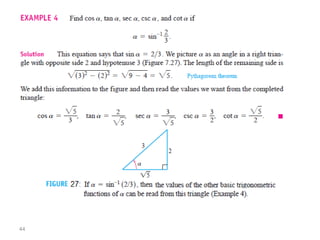
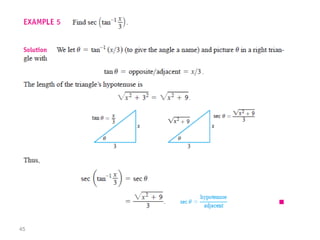
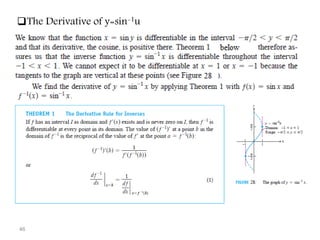
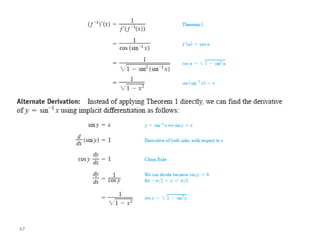
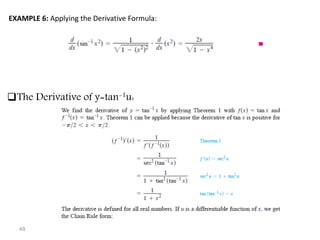
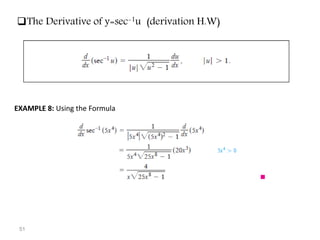
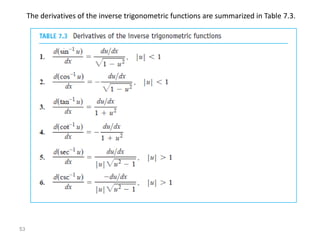
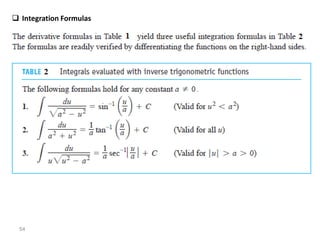
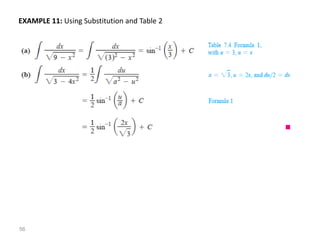
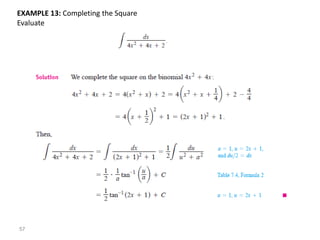
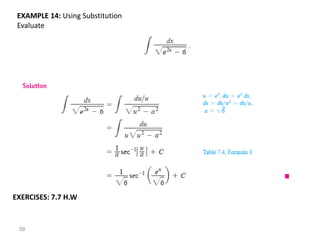
The document covers various aspects of trigonometric functions, including their definitions, periodicity, identities, and the law of cosines. It also discusses the derivatives of both basic and inverse trigonometric functions, providing examples and applications in calculus. Additionally, integration formulas related to trigonometric functions are mentioned along with exercises for practice.