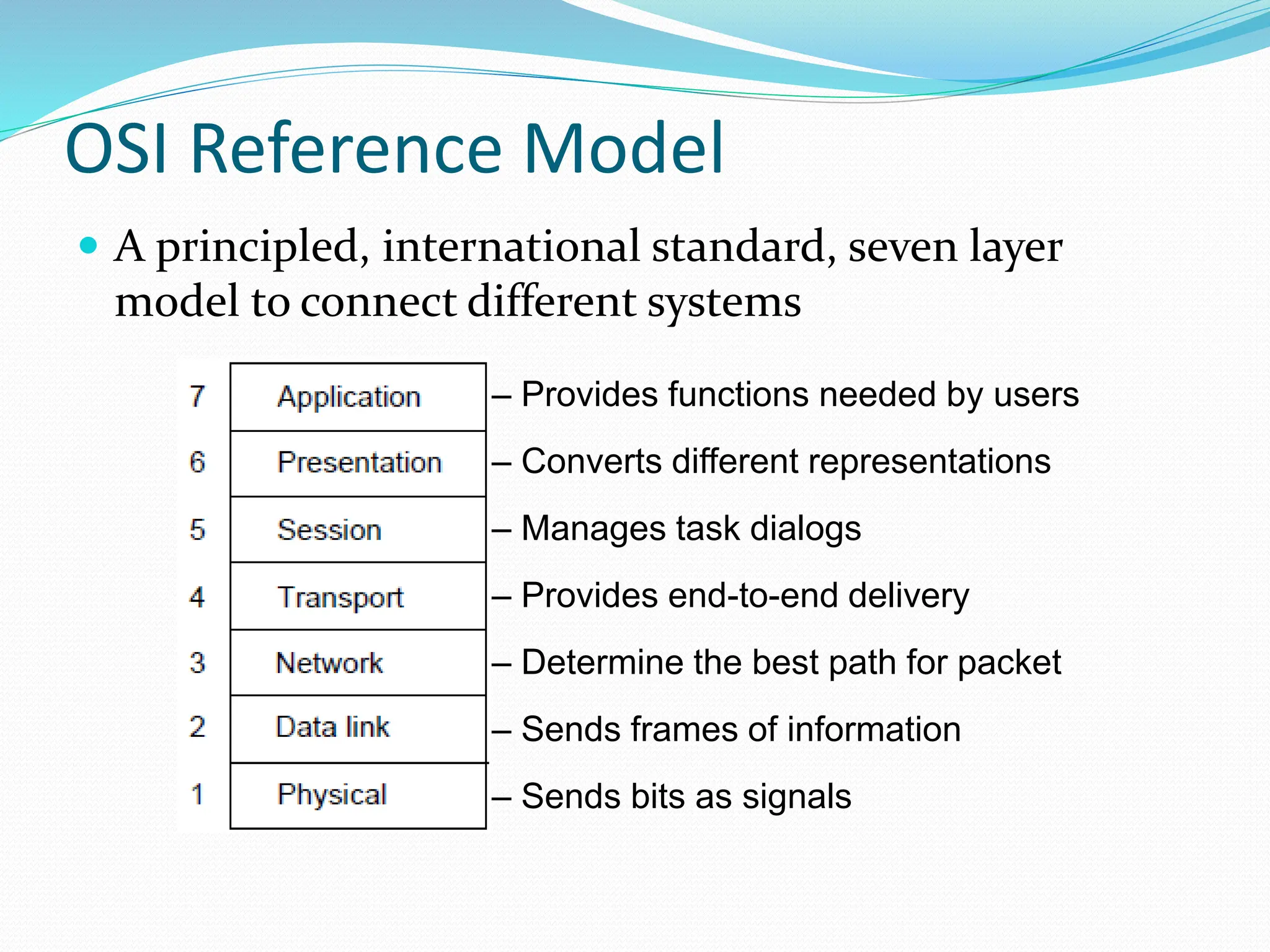
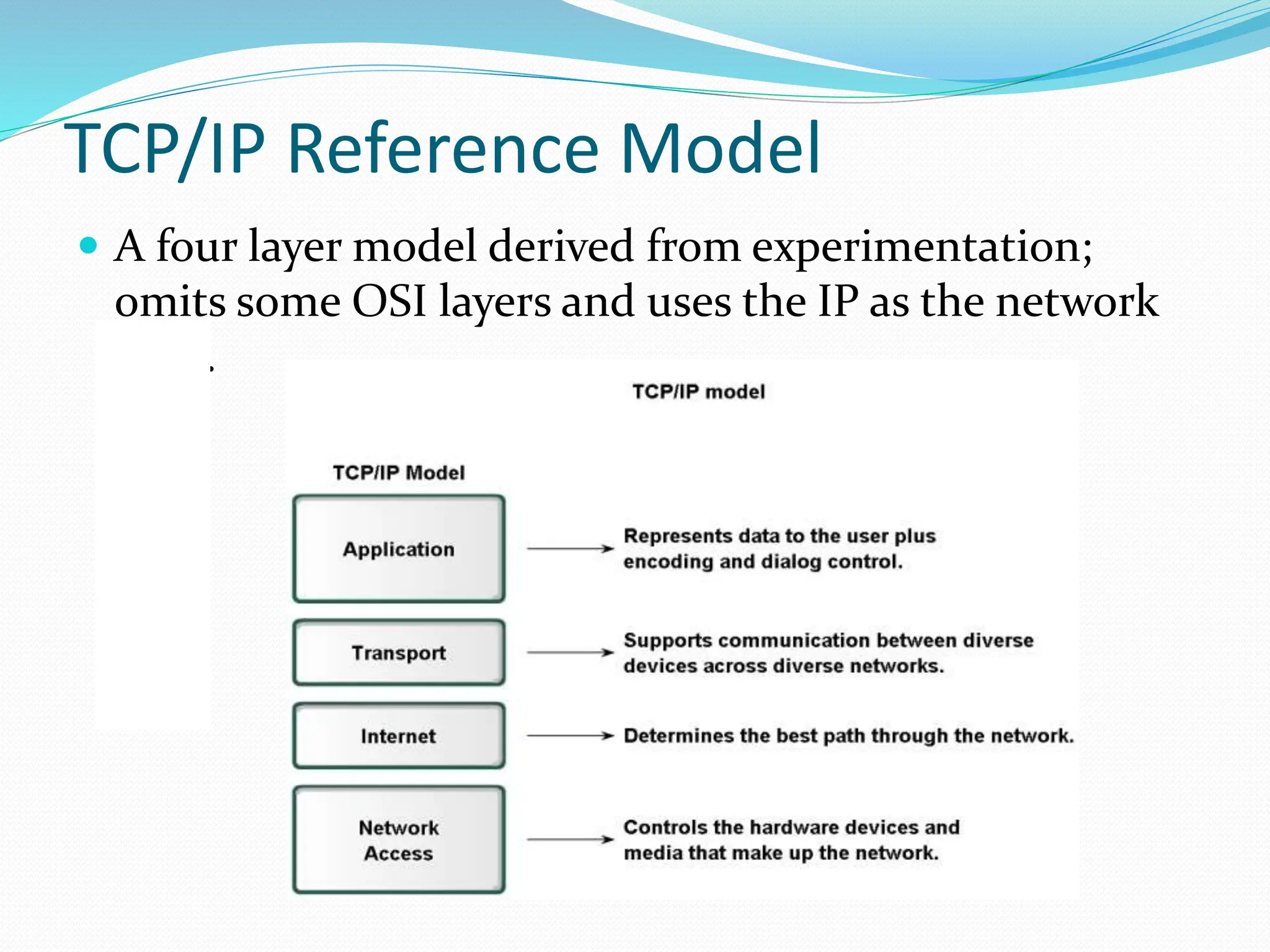
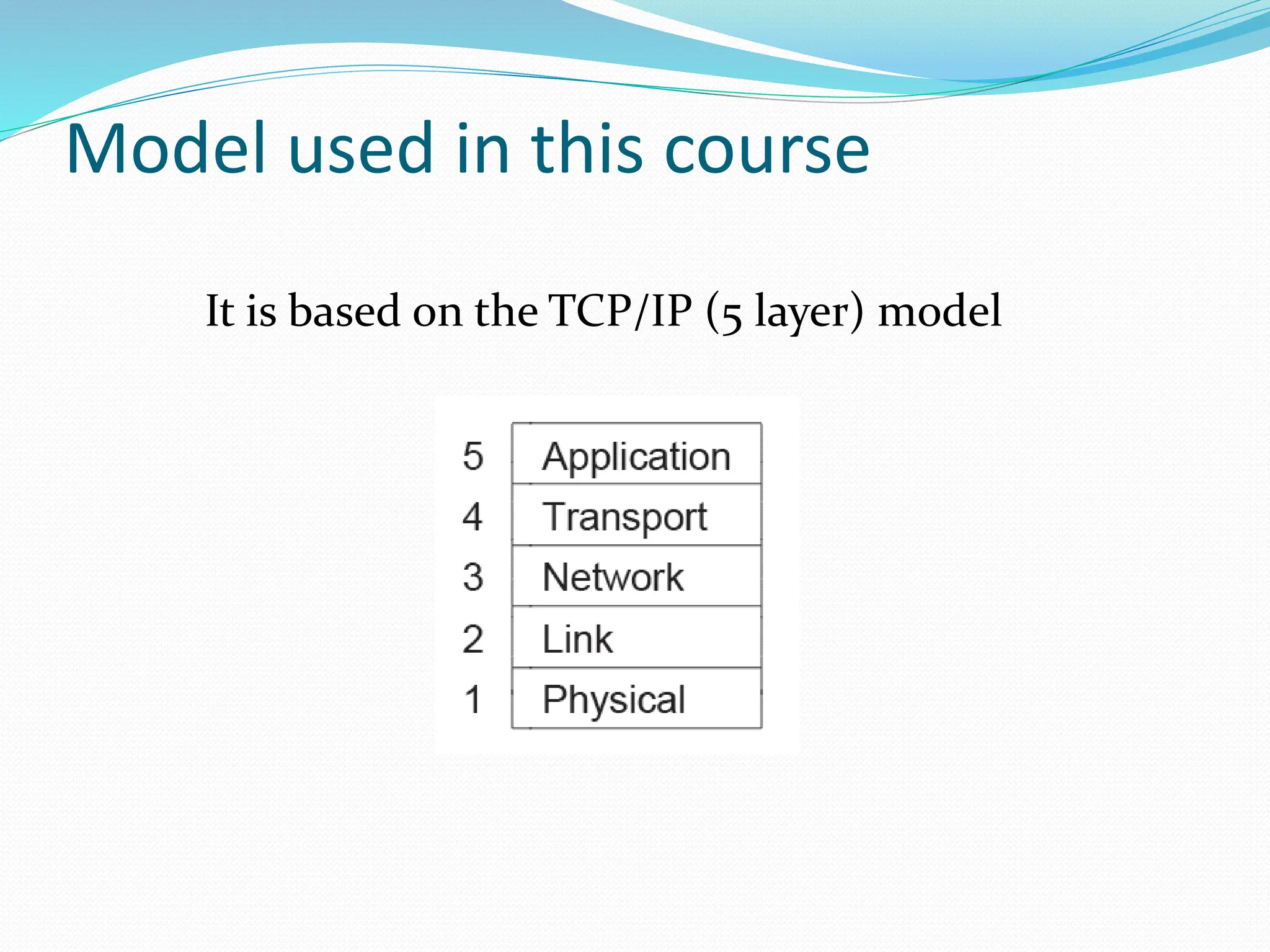
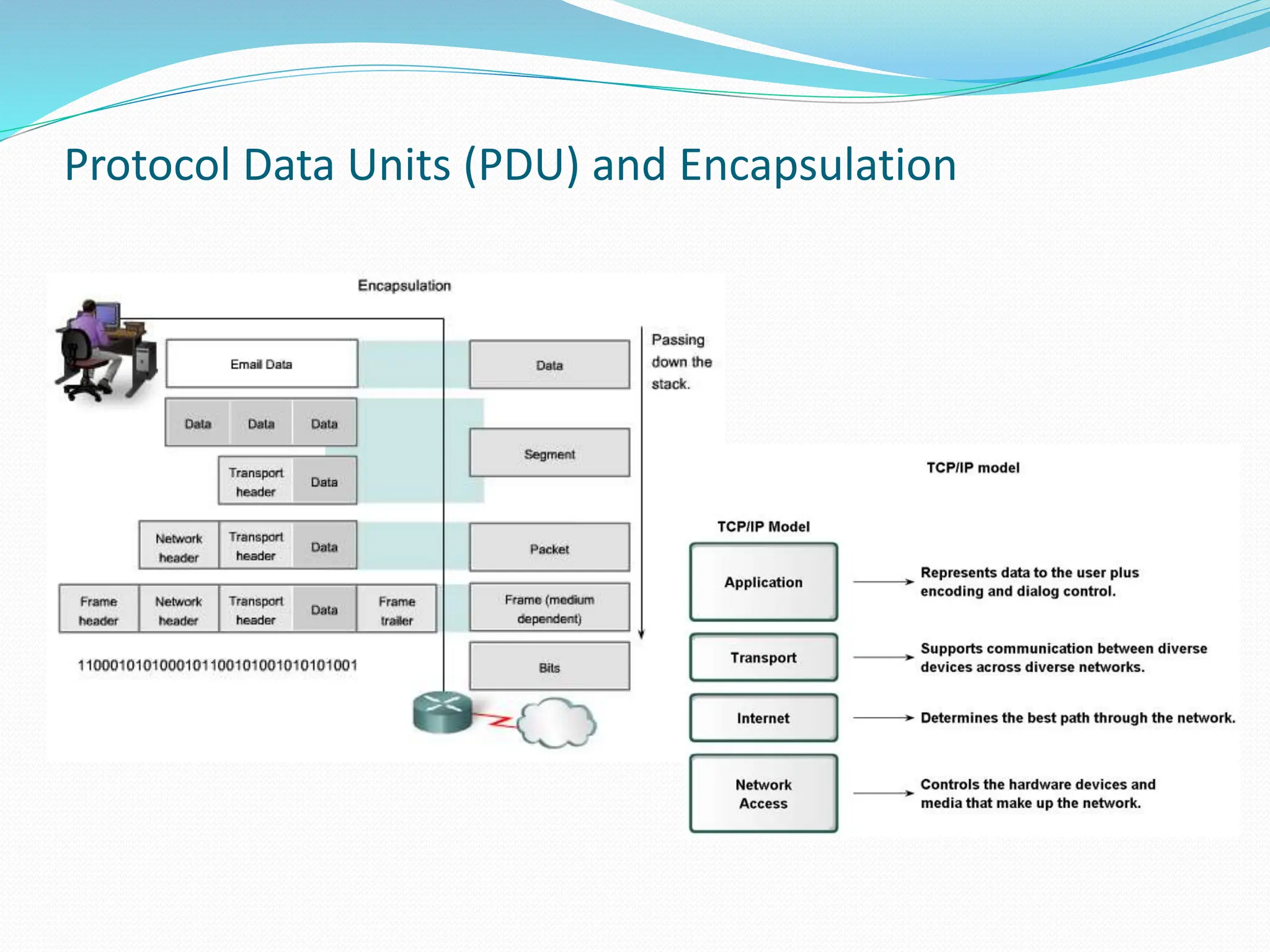
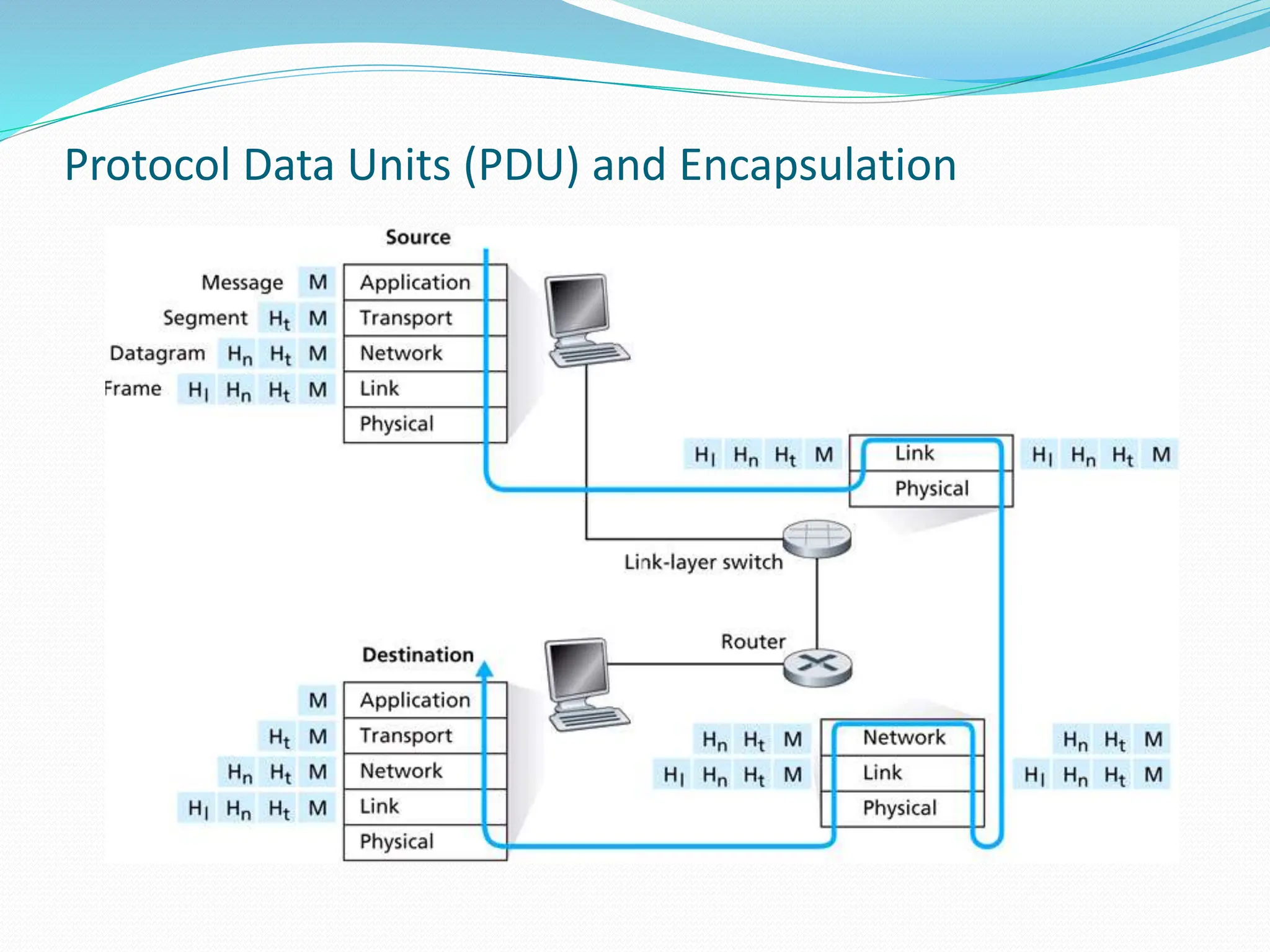
This document provides an introduction to network layer models and protocol data units. It discusses how layered models help visualize protocol interactions by breaking down network functions into standardized areas. The key reference models covered are the OSI 7-layer model, the TCP/IP 4-layer model, and the 5-layer model used in this course. Each layer in the models performs a specific task, such as determining the best packet path or sending bits as signals. Protocol data units are the messages passed between layers, with each layer encapsulating the PDU from the previous layer.