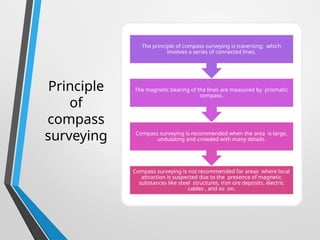
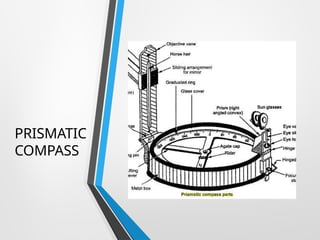
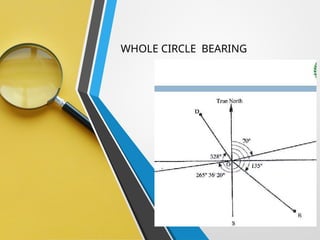
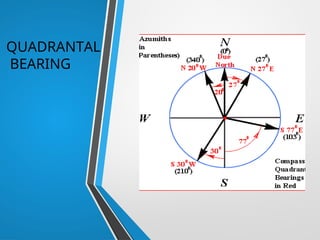
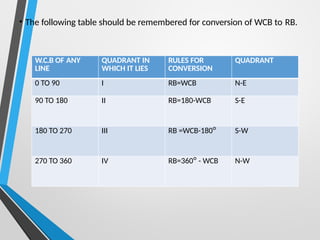
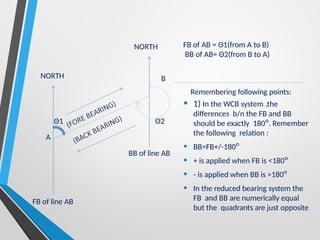
Compass surveying is suitable for large, undulating areas devoid of magnetic interference, utilizing a prismatic compass for measuring magnetic bearings and traversing lines. The prismatic compass consists of several components, including a cylindrical box, magnetic needle, and graduated ring, which work together to determine directions and angles. Bearings can be categorized into whole circle and quadrantal systems, with specific rules for conversion and measurement of fore and back bearings.