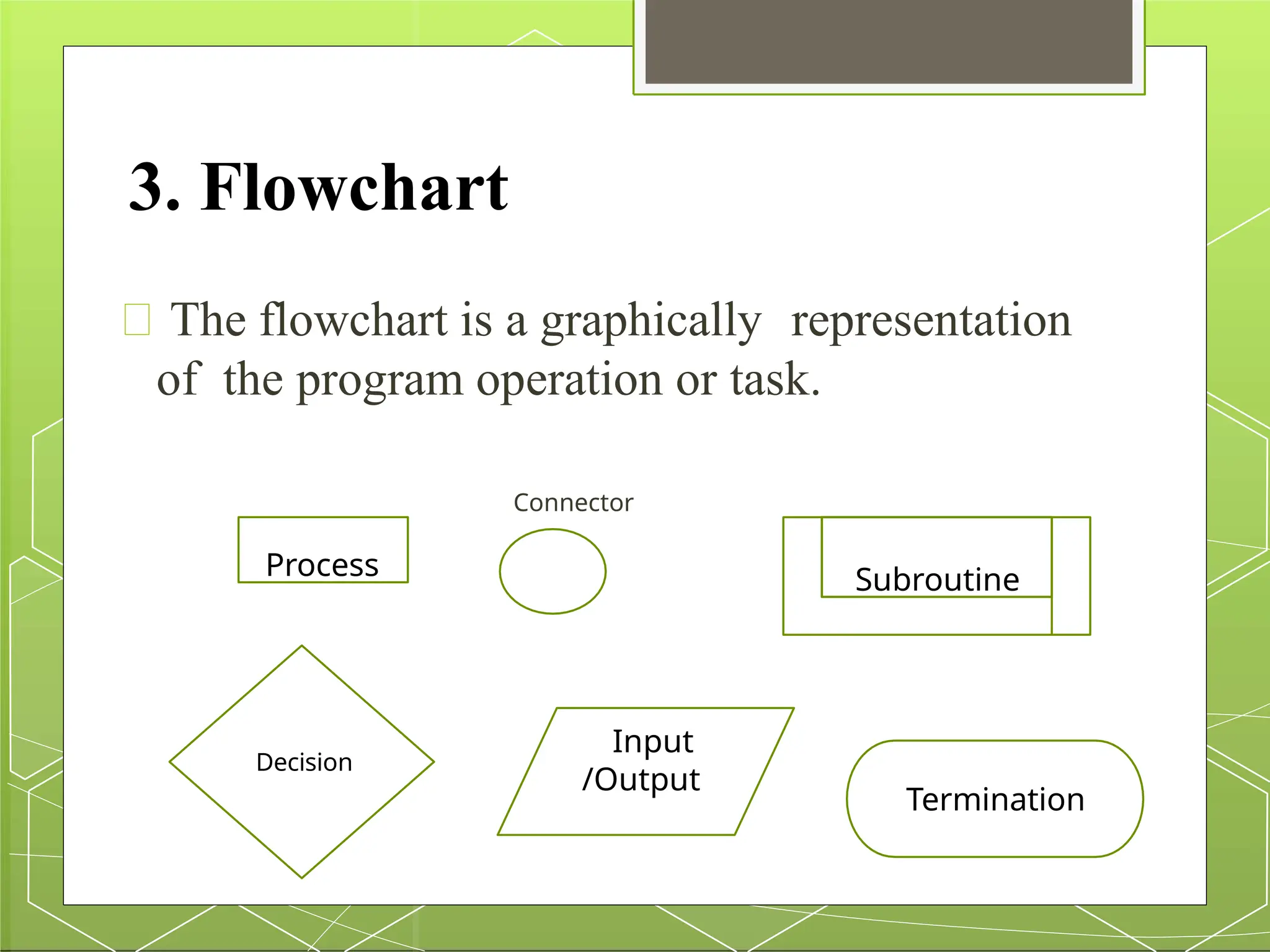
The document outlines the steps involved in assembly language programming, including problem definition, algorithm formulation, flowchart creation, and proper initialization. It details the tools used in program development like editors, assemblers, linkers, and debuggers, as well as the process from source file creation to program testing and debugging. Additionally, it covers assembler directives for data definition, such as defining bytes and words.