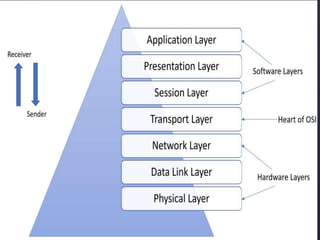
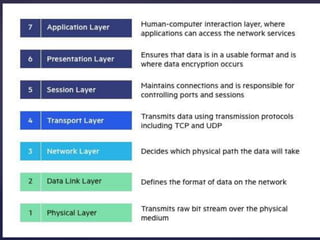
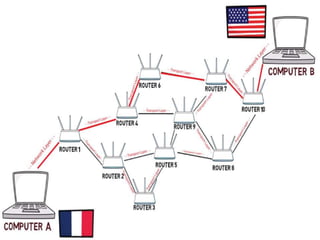
The document describes the OSI model, which is a conceptual framework that standardizes network communication functions into seven layers. Each layer is responsible for specific protocols and functions. The layers work together to allow data transmission between devices on different networks, with the physical layer transmitting bits and the application layer allowing user interaction with network services.