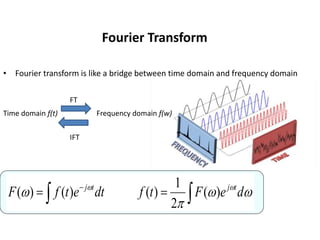
The document provides an overview of the Fourier transform, its implementation in Matlab, and its applications. The Fourier transform maps a function from its original domain (typically time) to the frequency domain. It has various uses including revealing hidden information, solving differential equations, and performing operations like convolution more easily in the frequency domain. Matlab functions for computing the Fourier transform numerically include FFT, IFFT, abs() to find the magnitude spectrum, and angle() to find the phase spectrum. An assignment involves implementing the Fourier transform in Matlab and analyzing effects of changes to the time domain signal and number of FFT points.