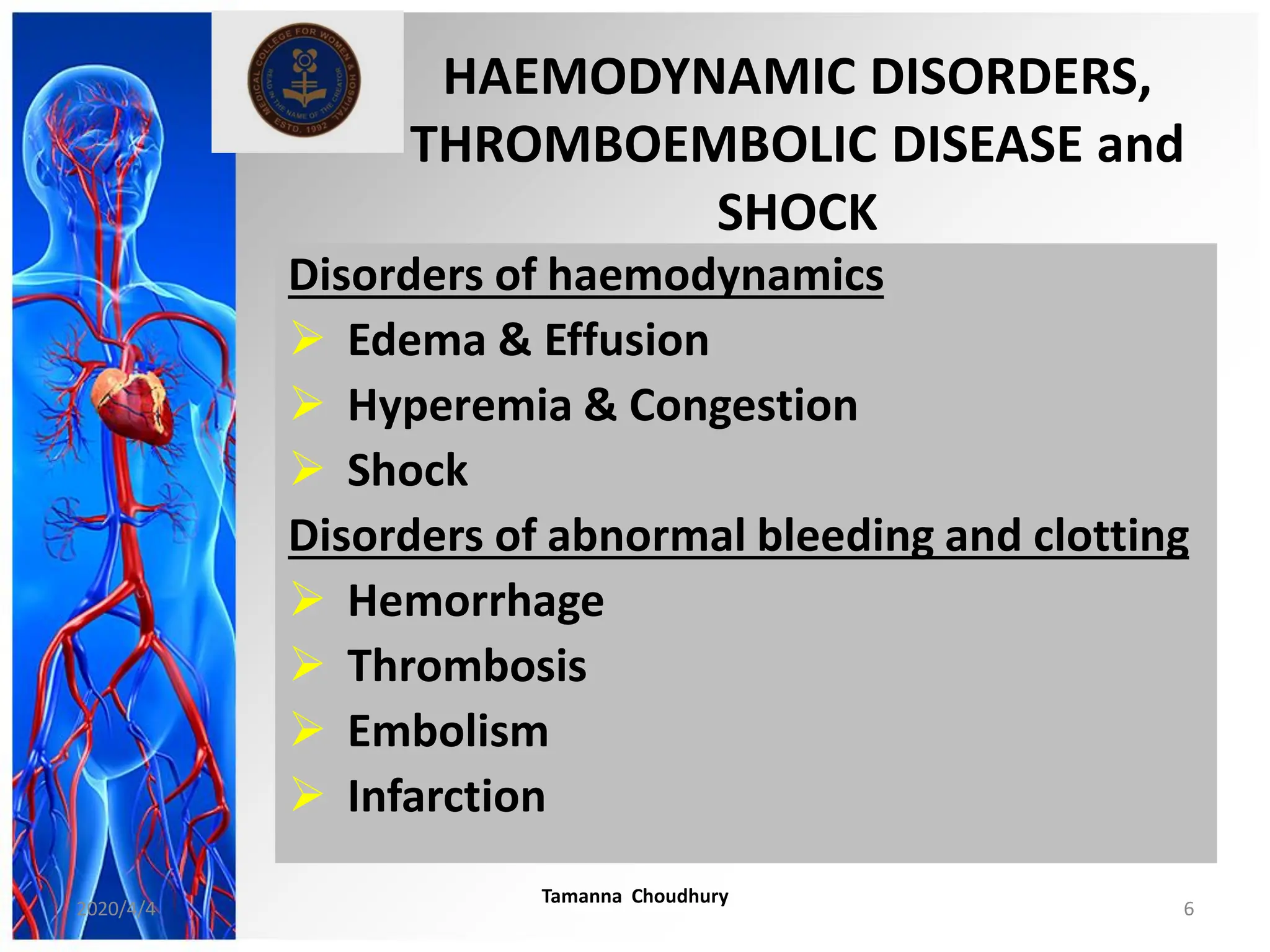
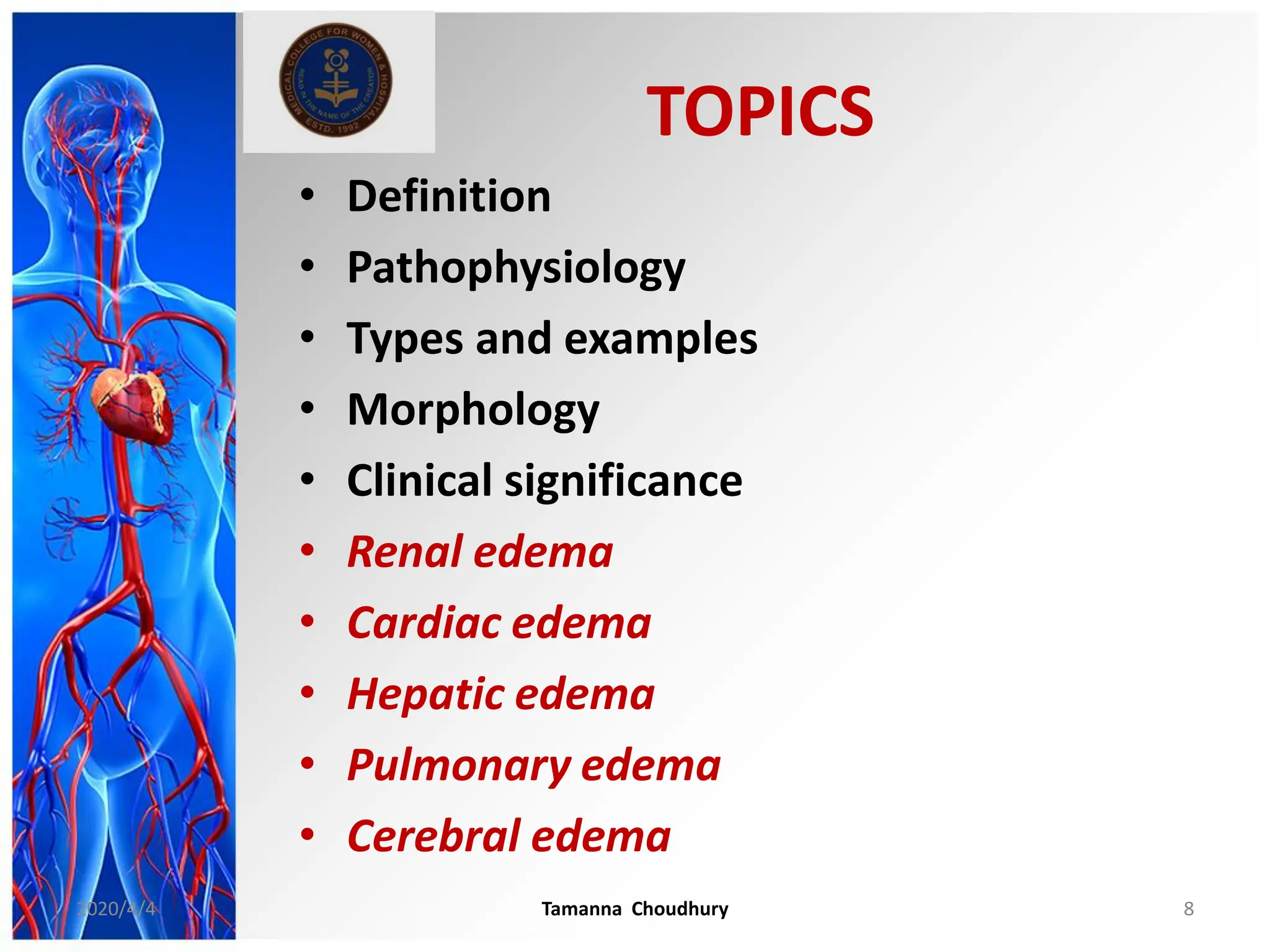
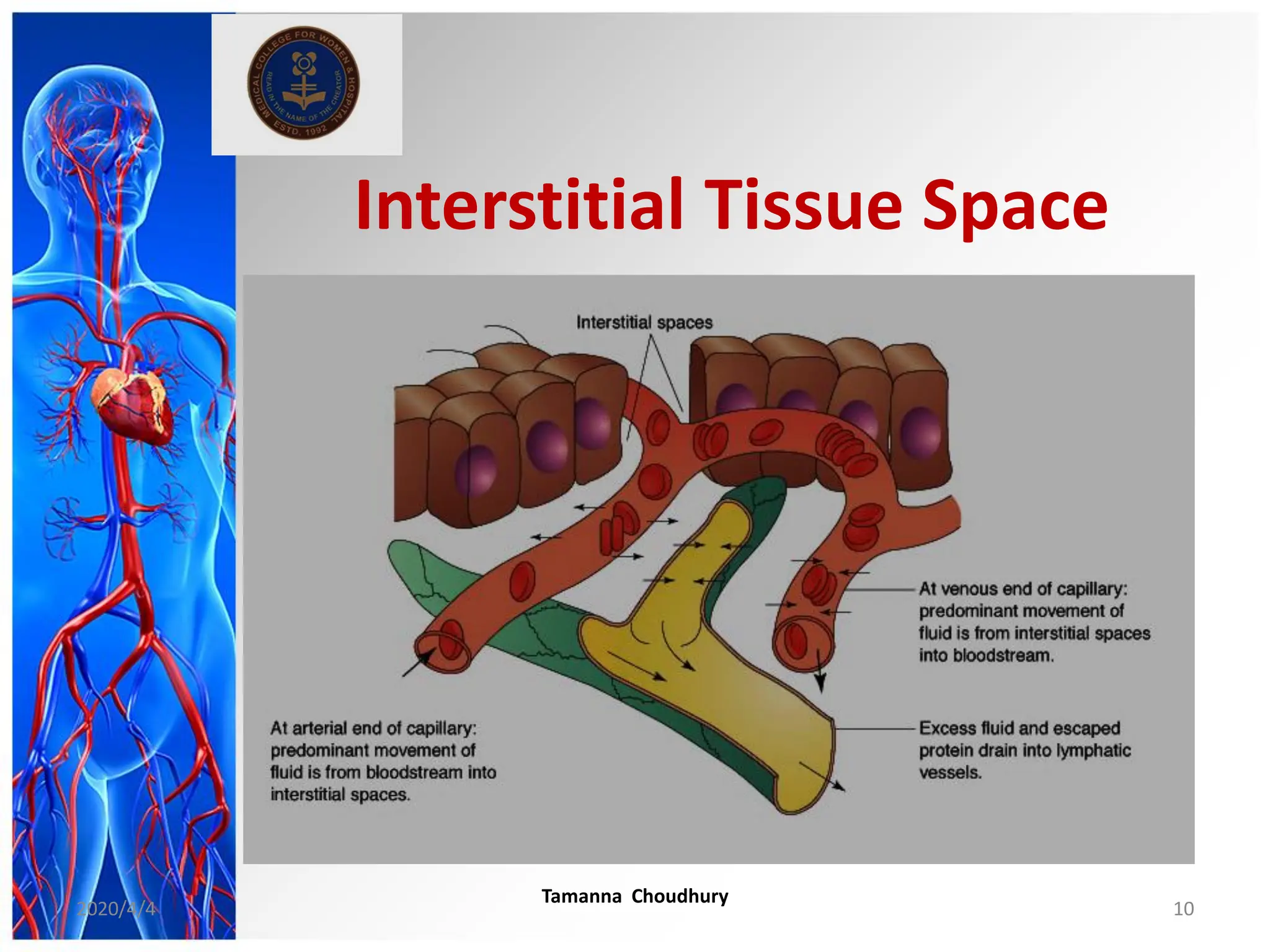
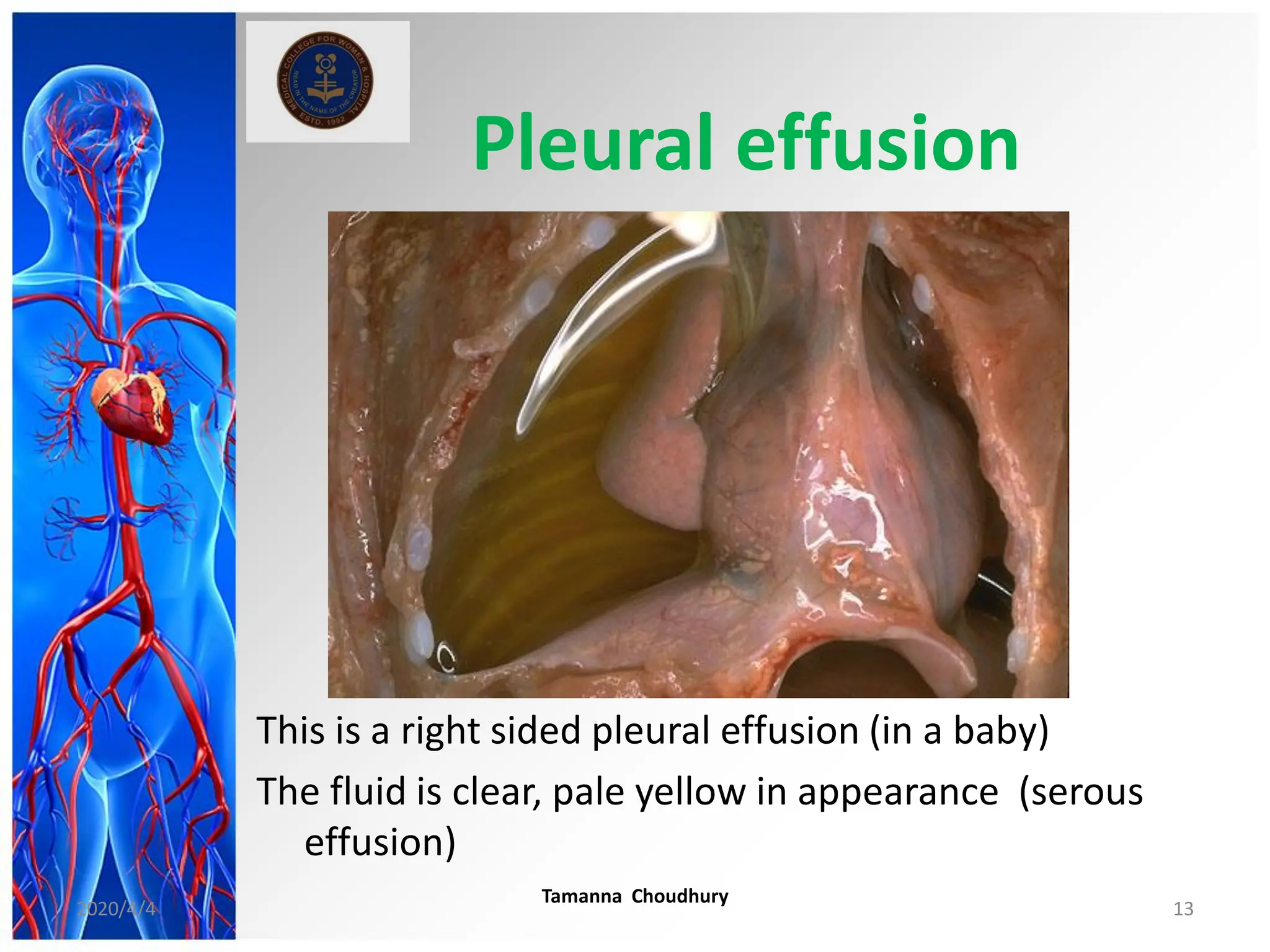
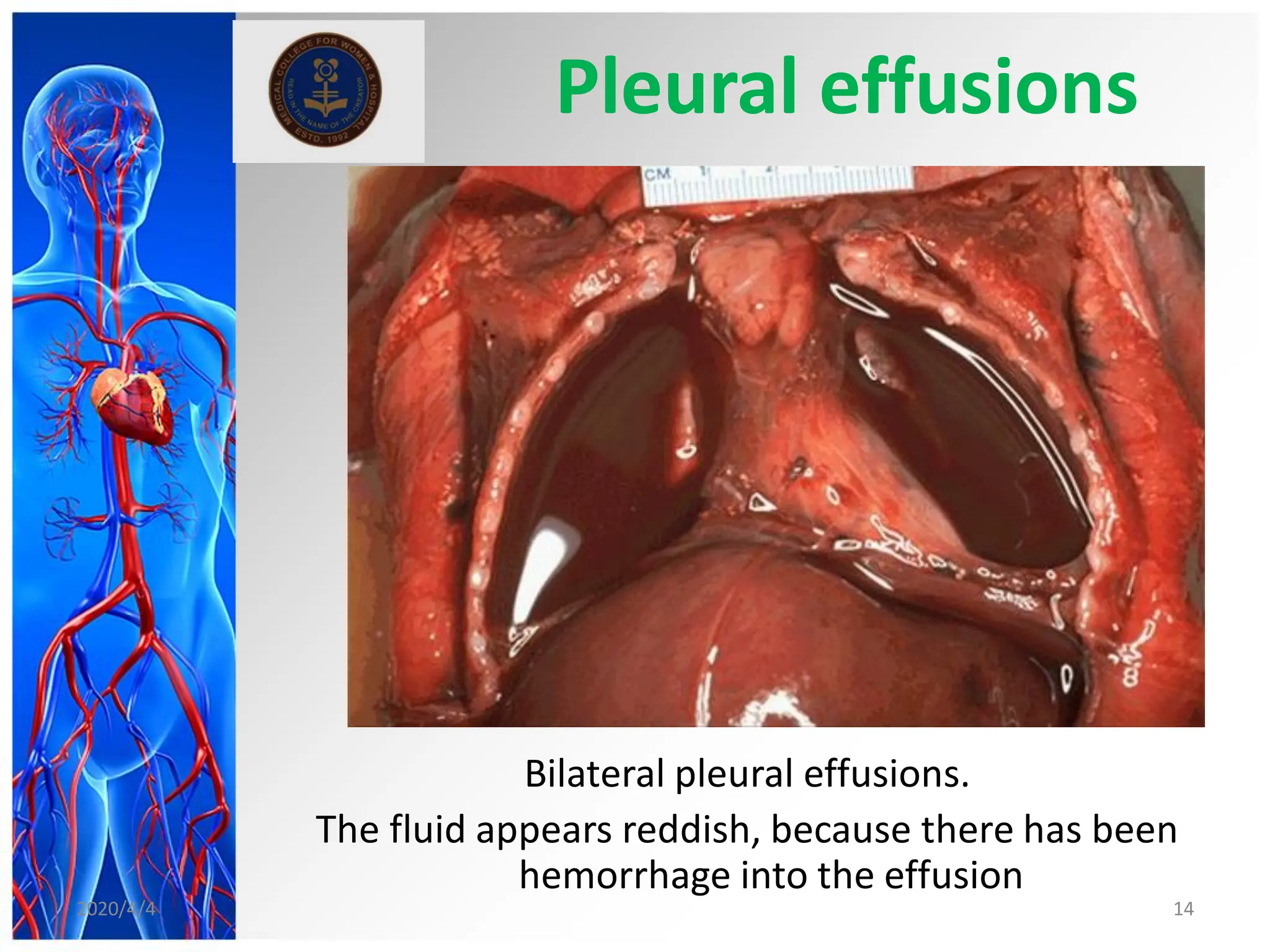
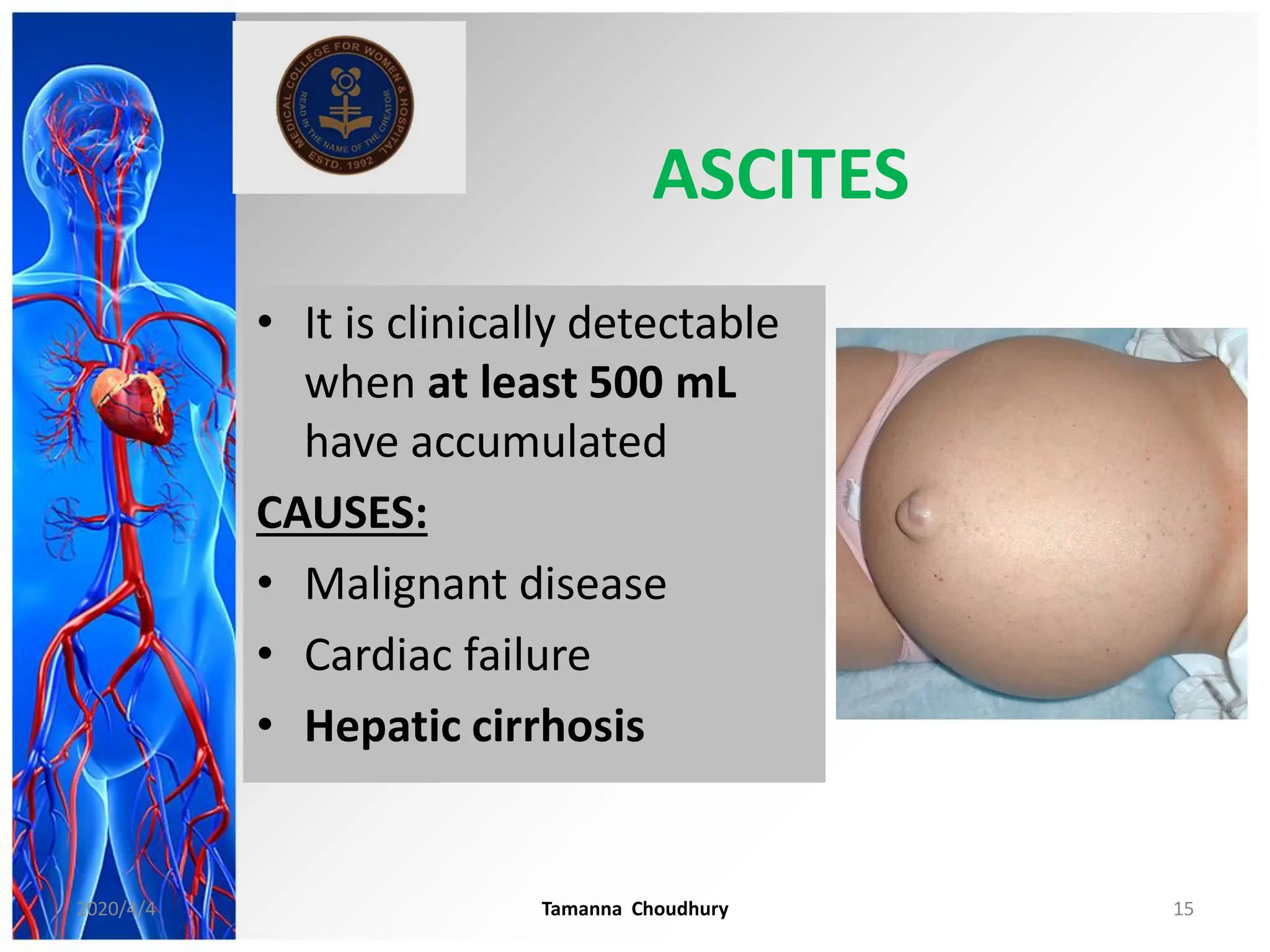
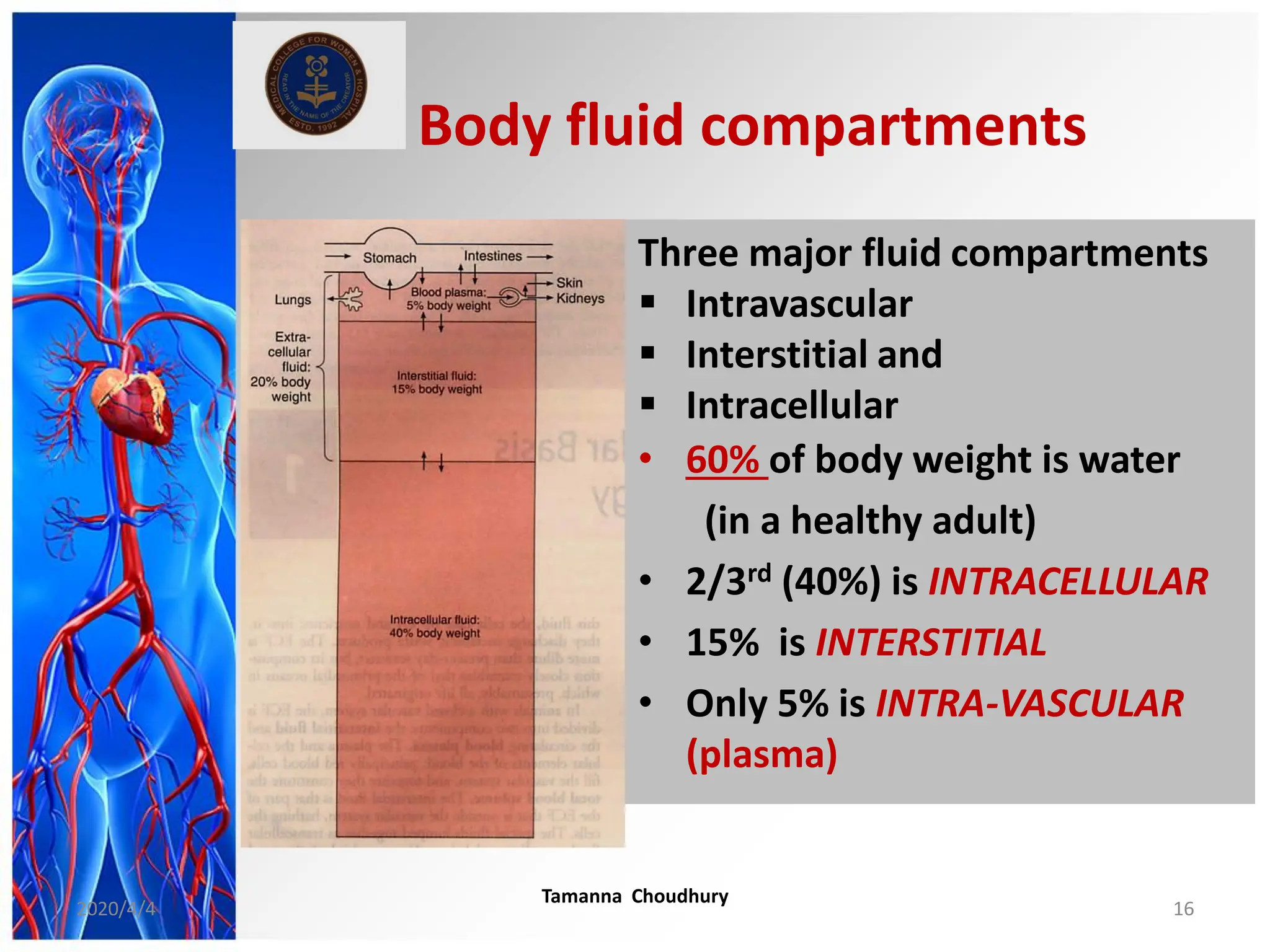
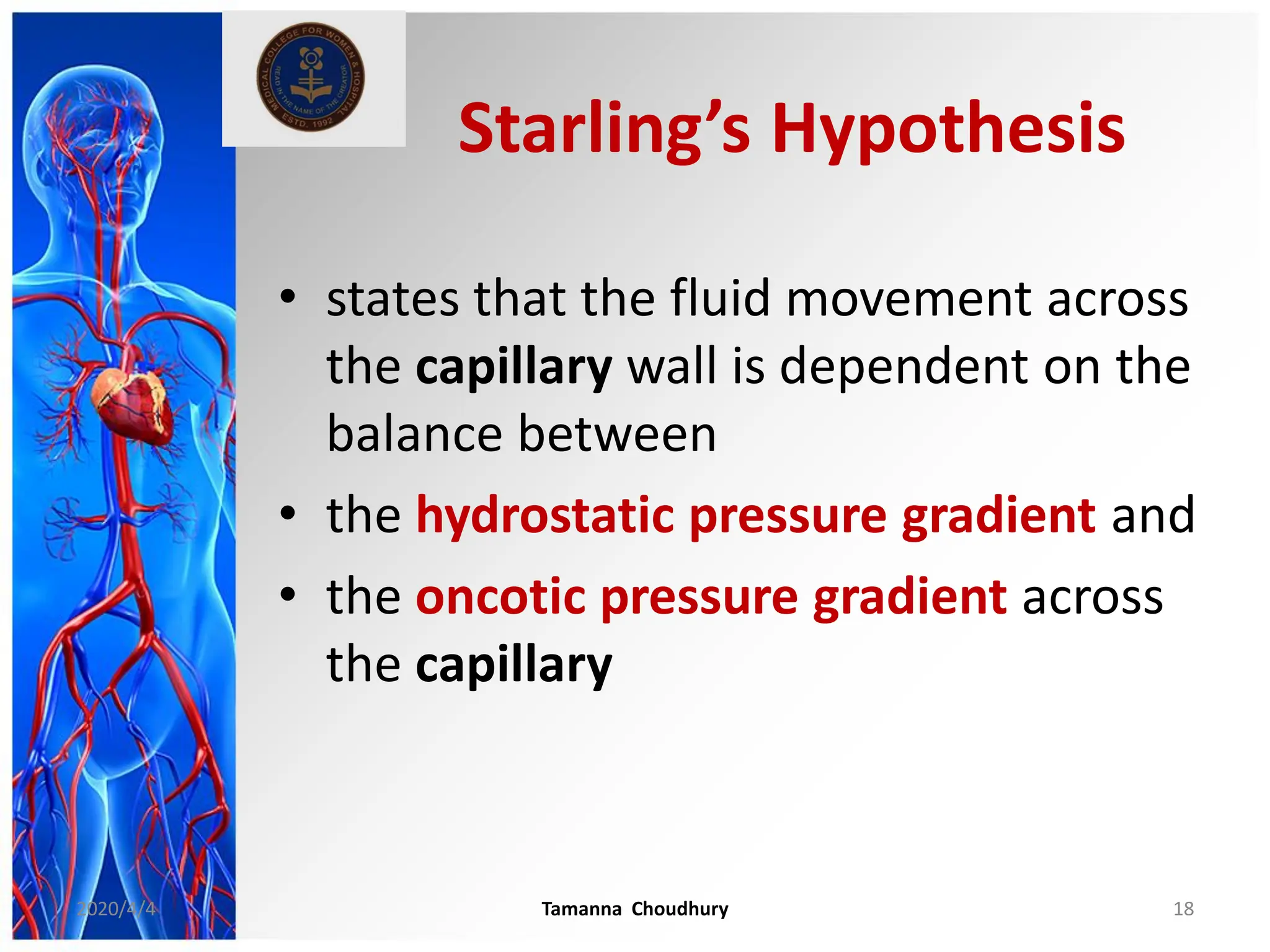
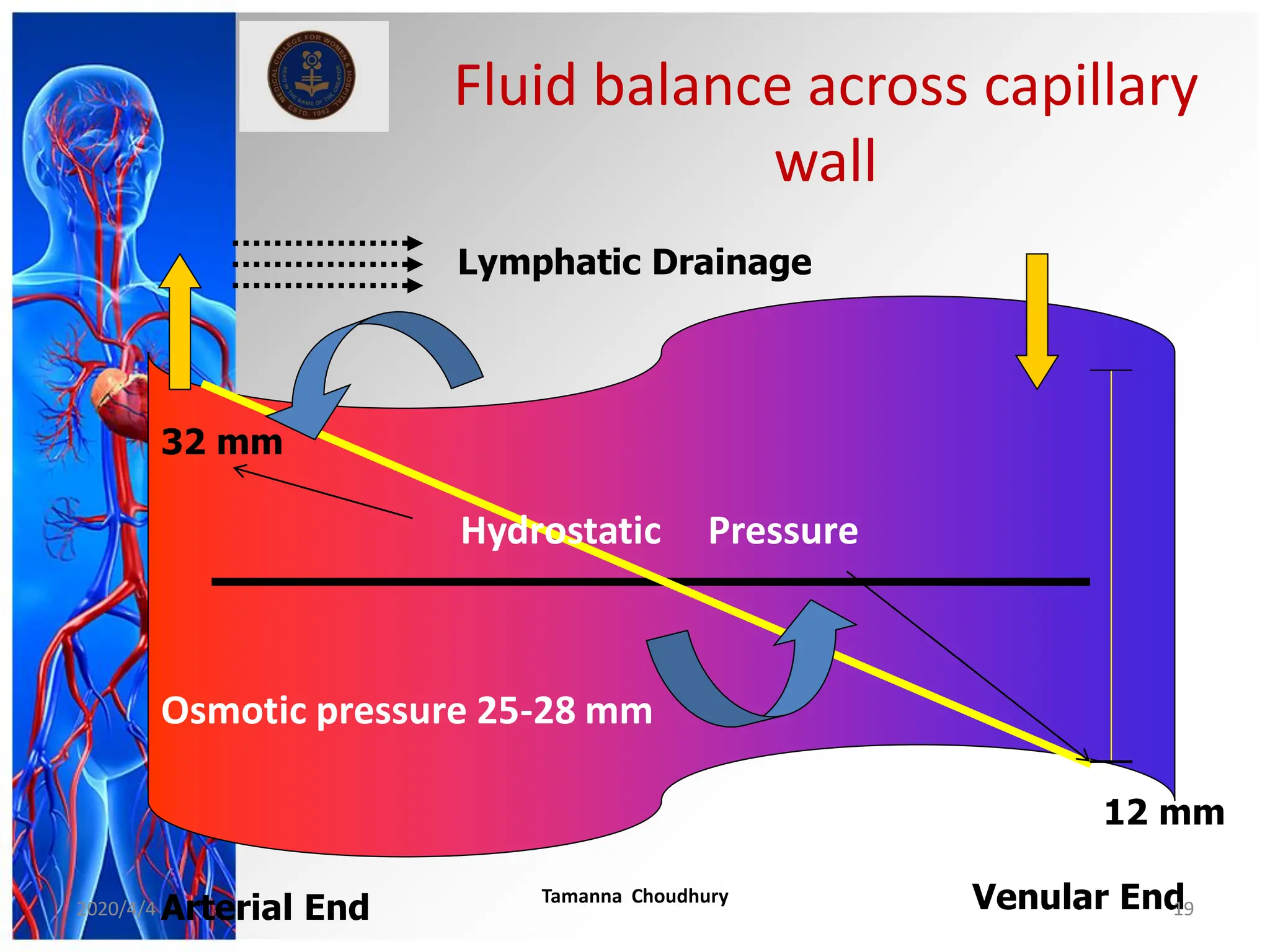
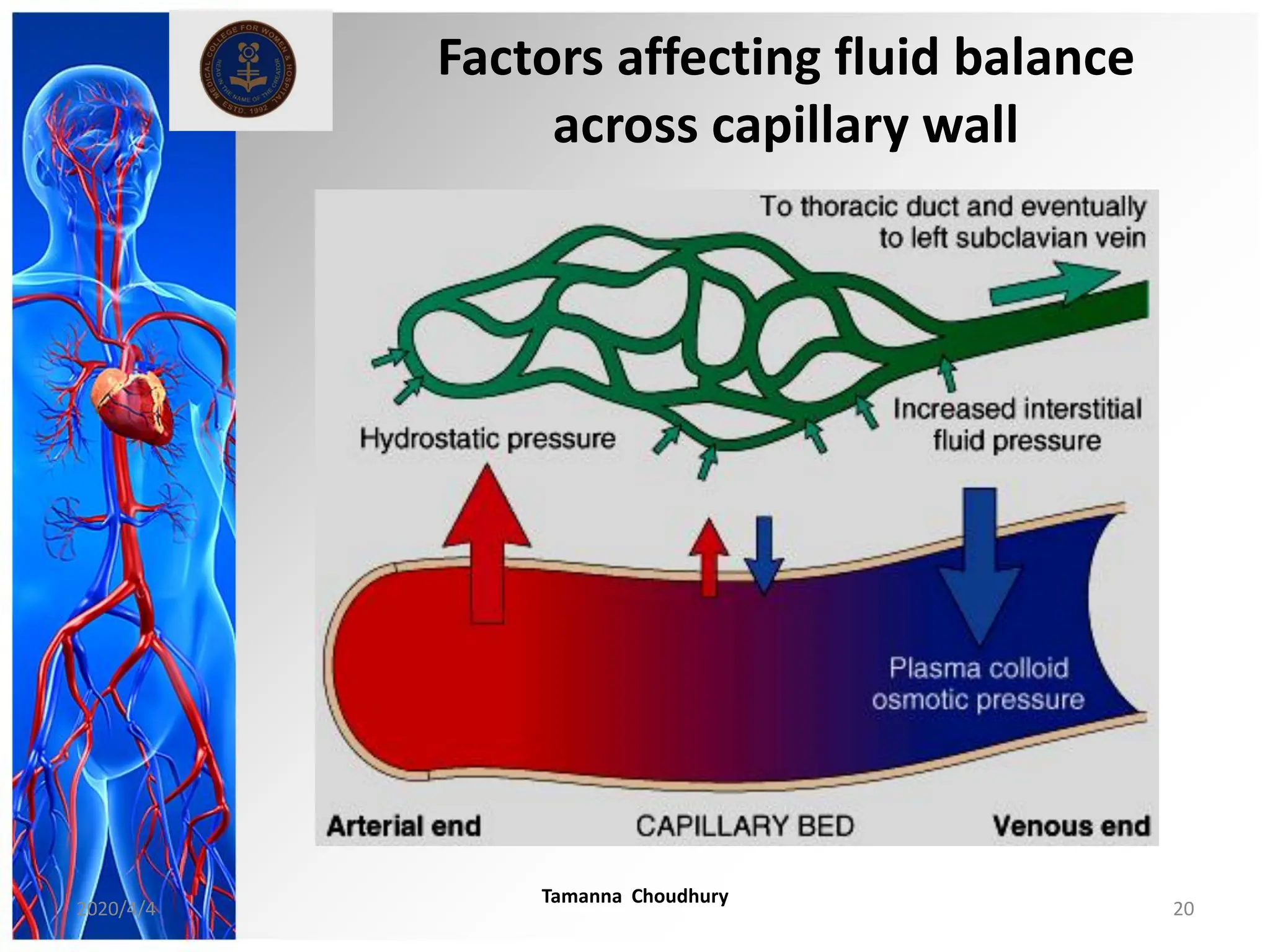
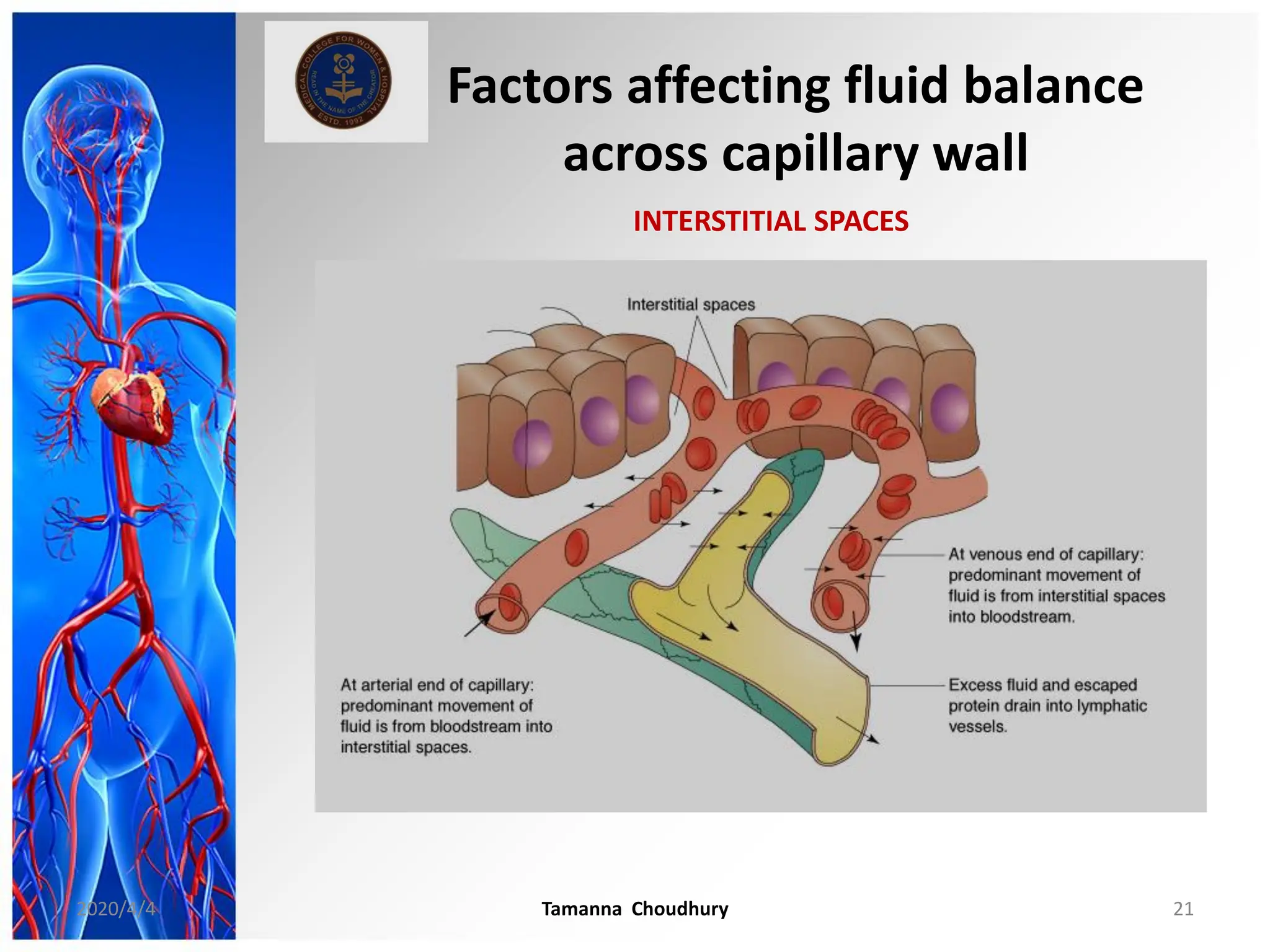
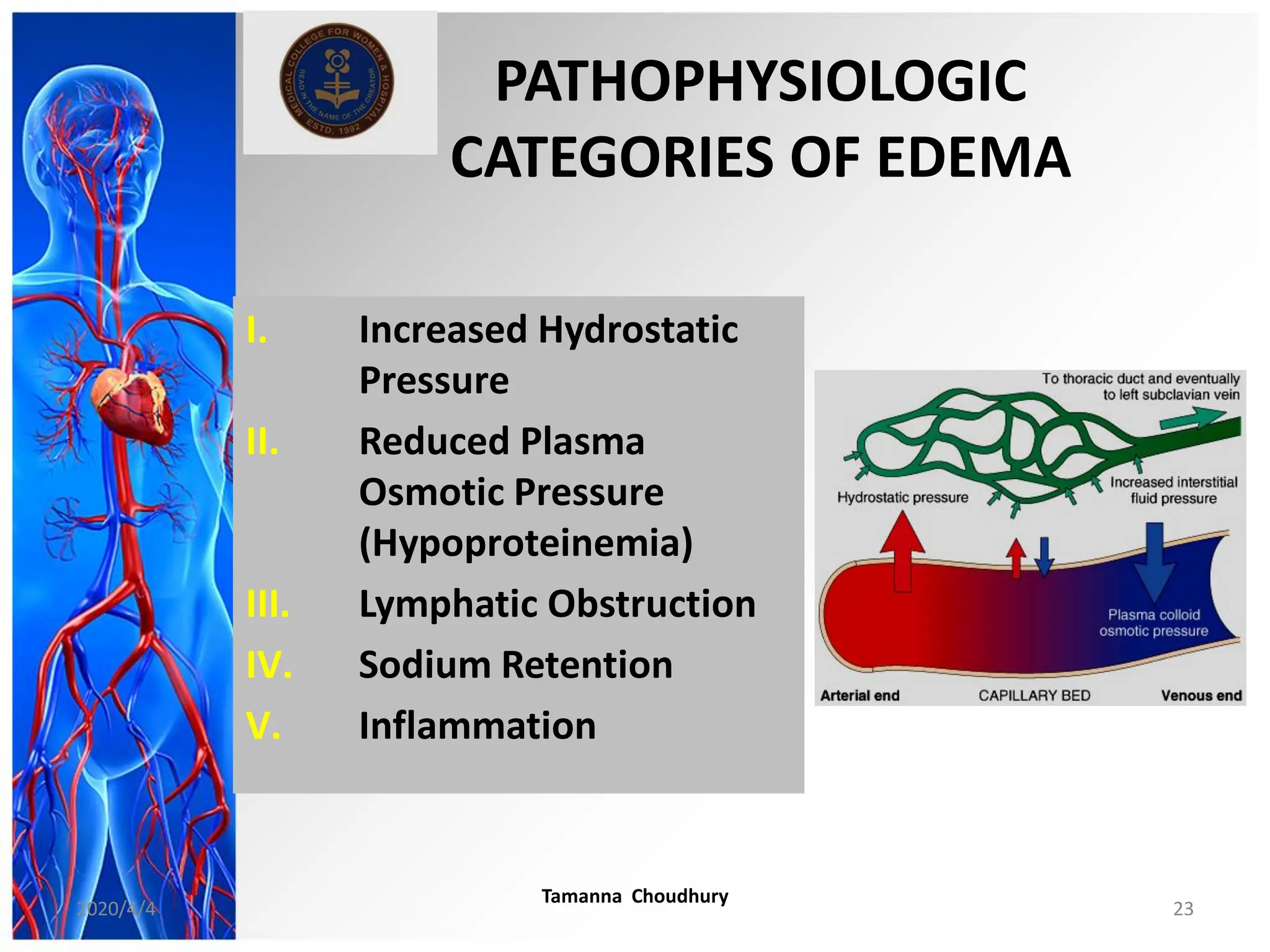
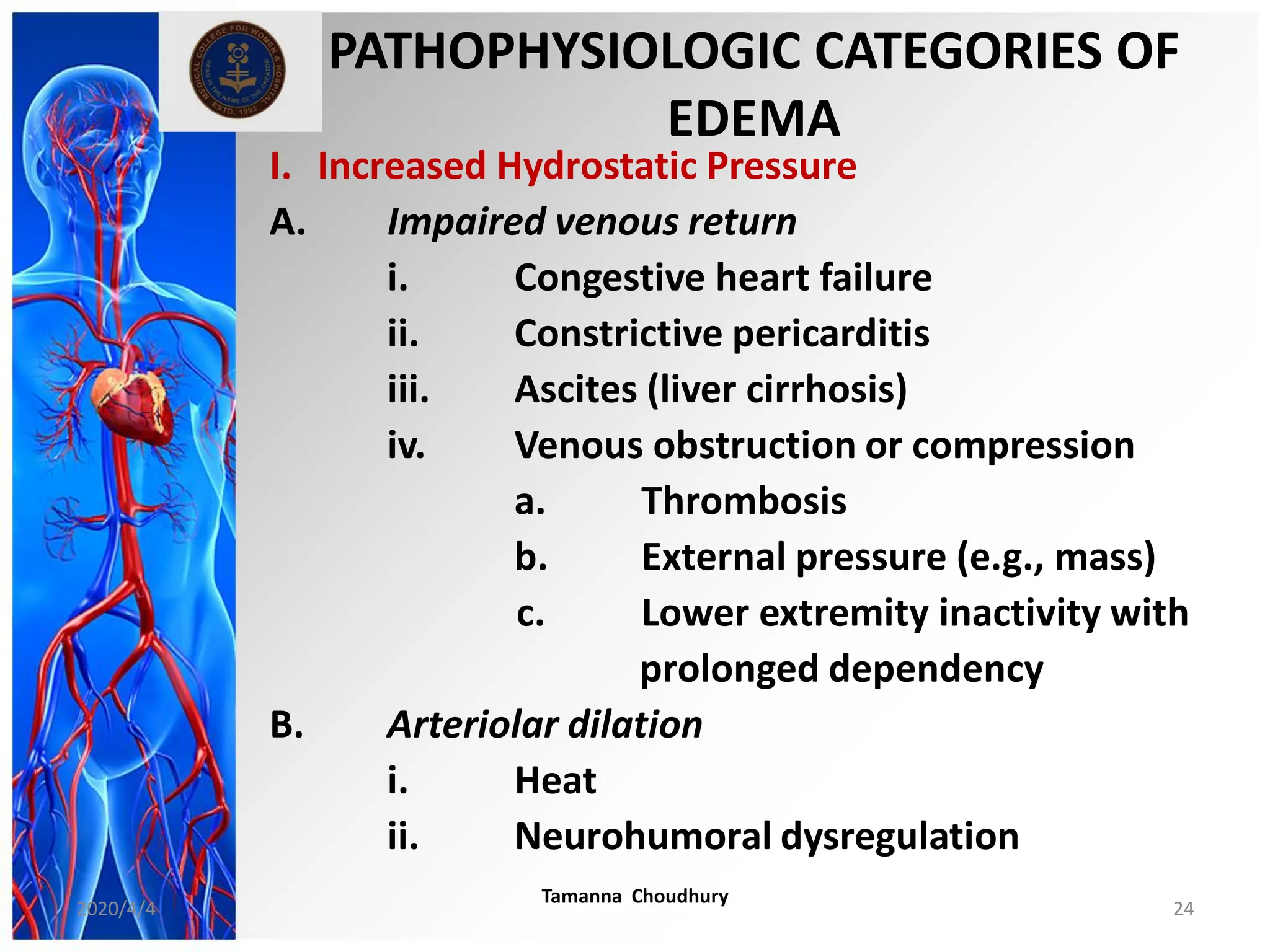
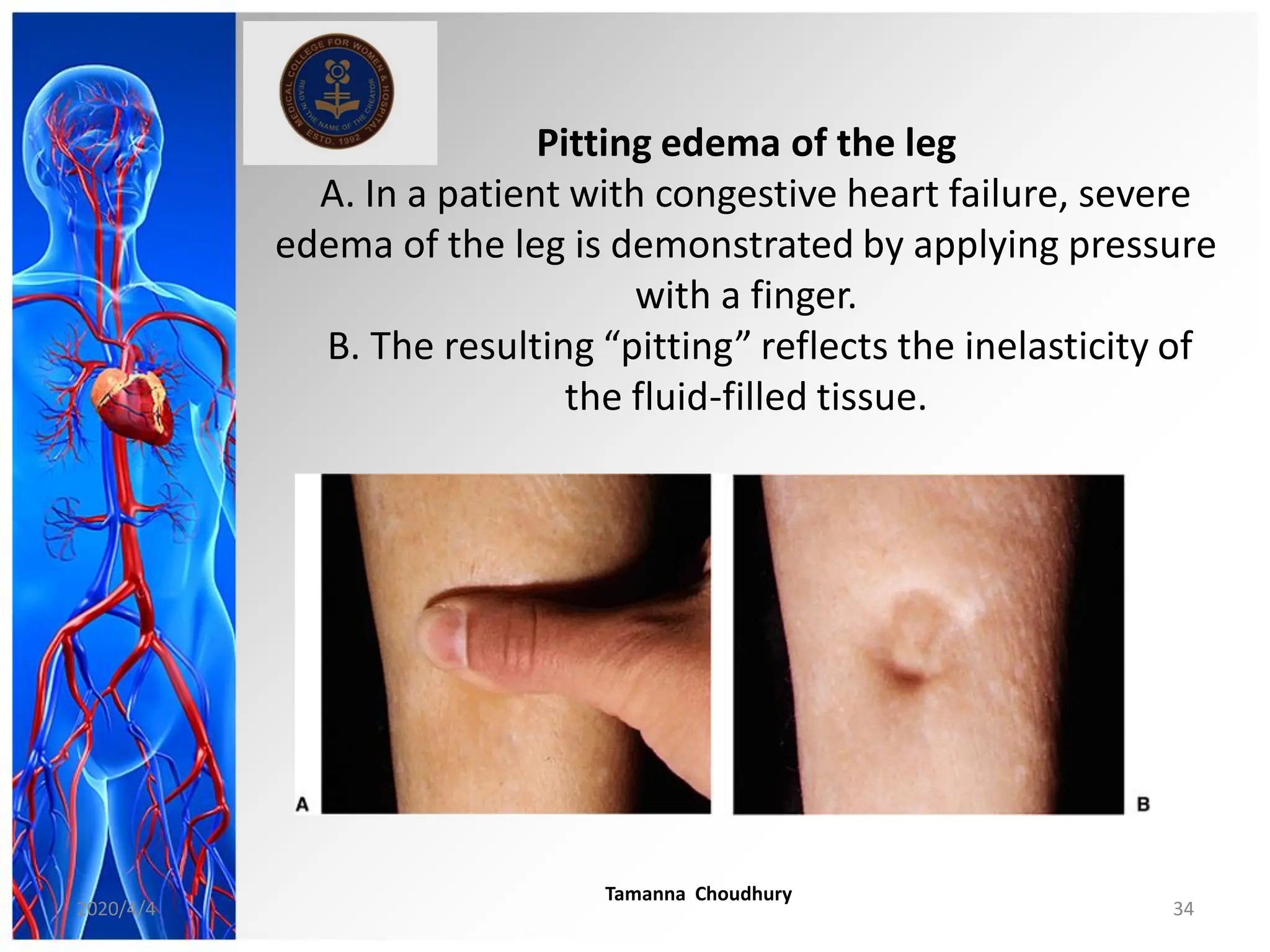
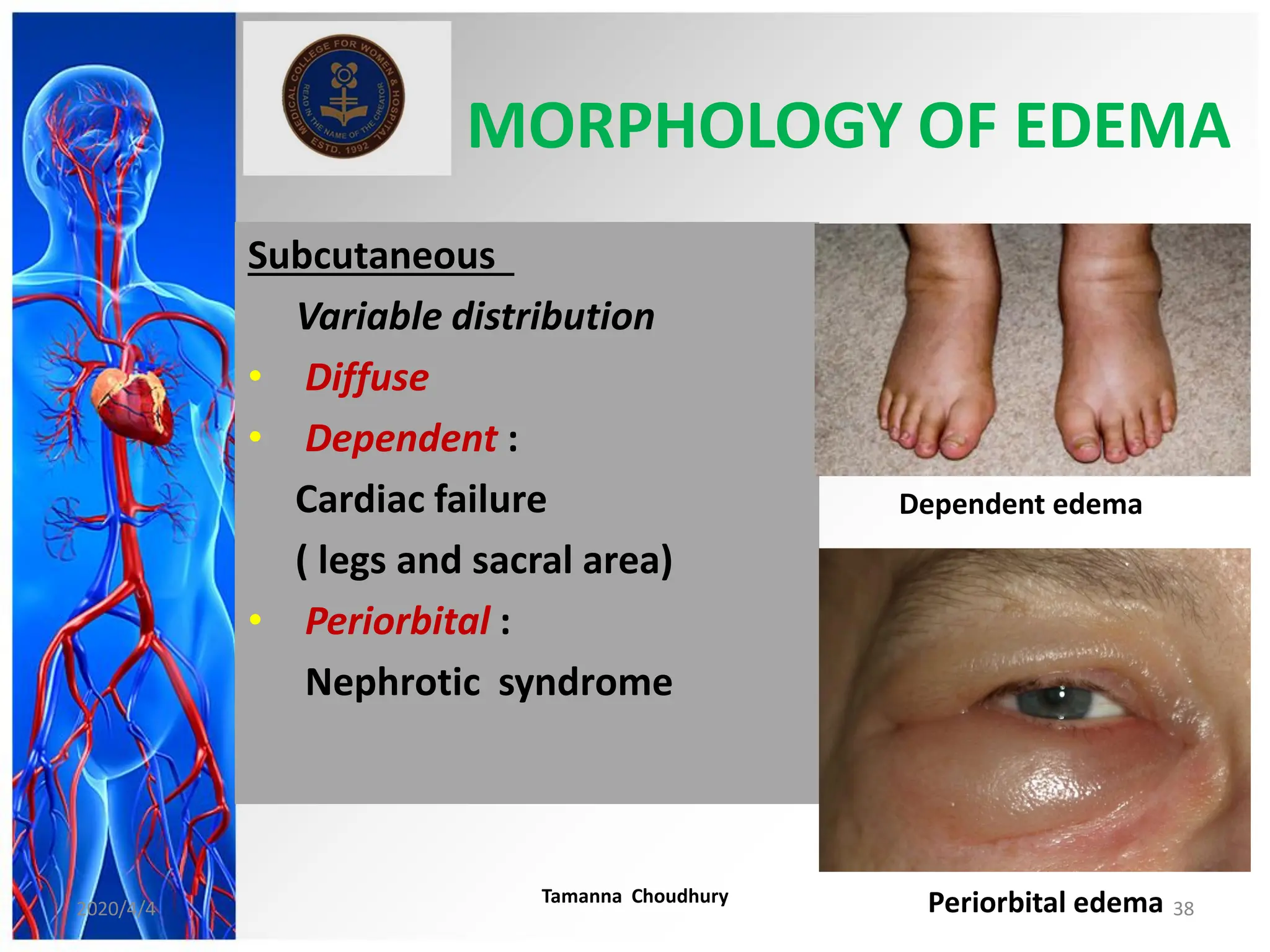
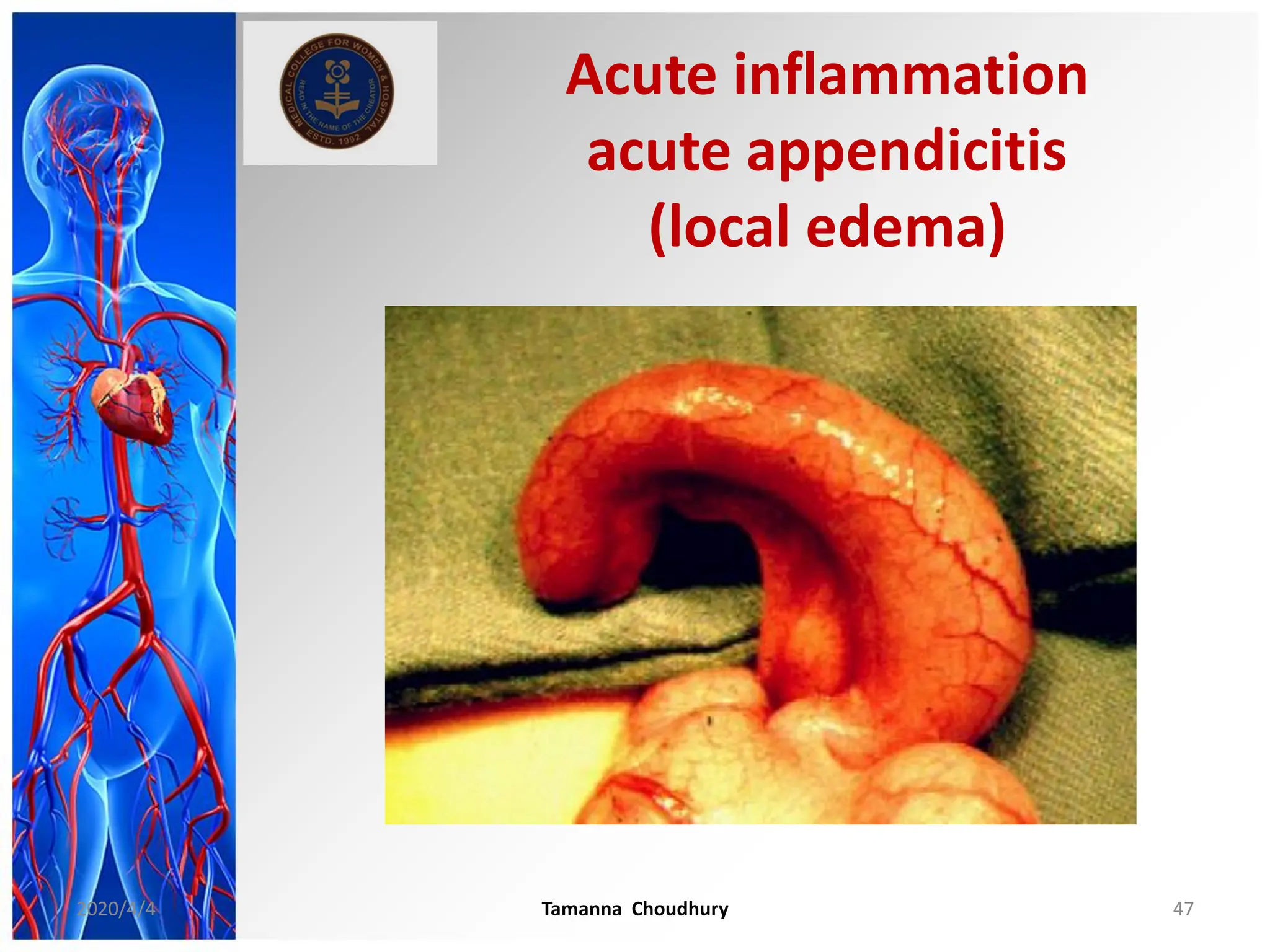
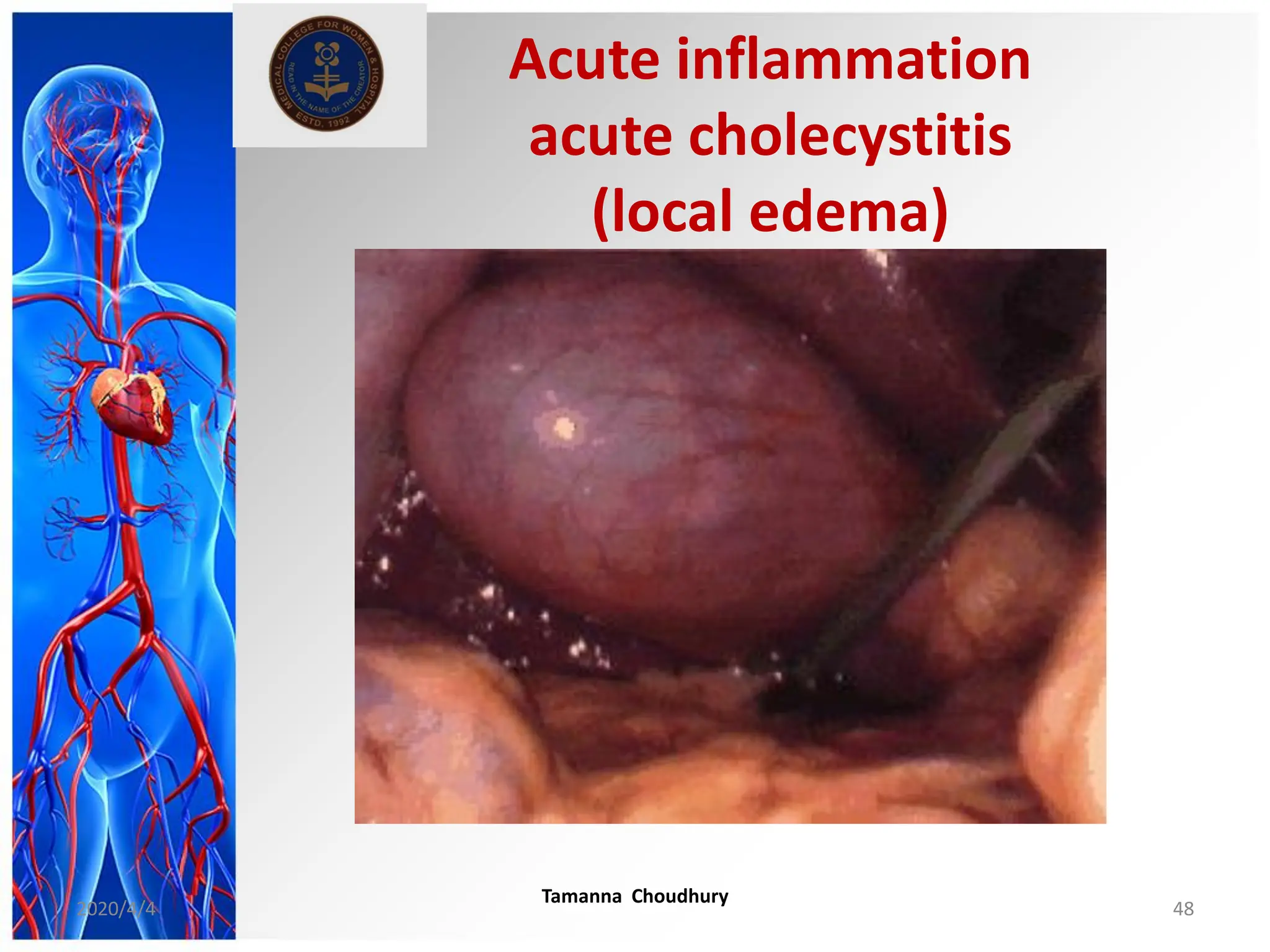
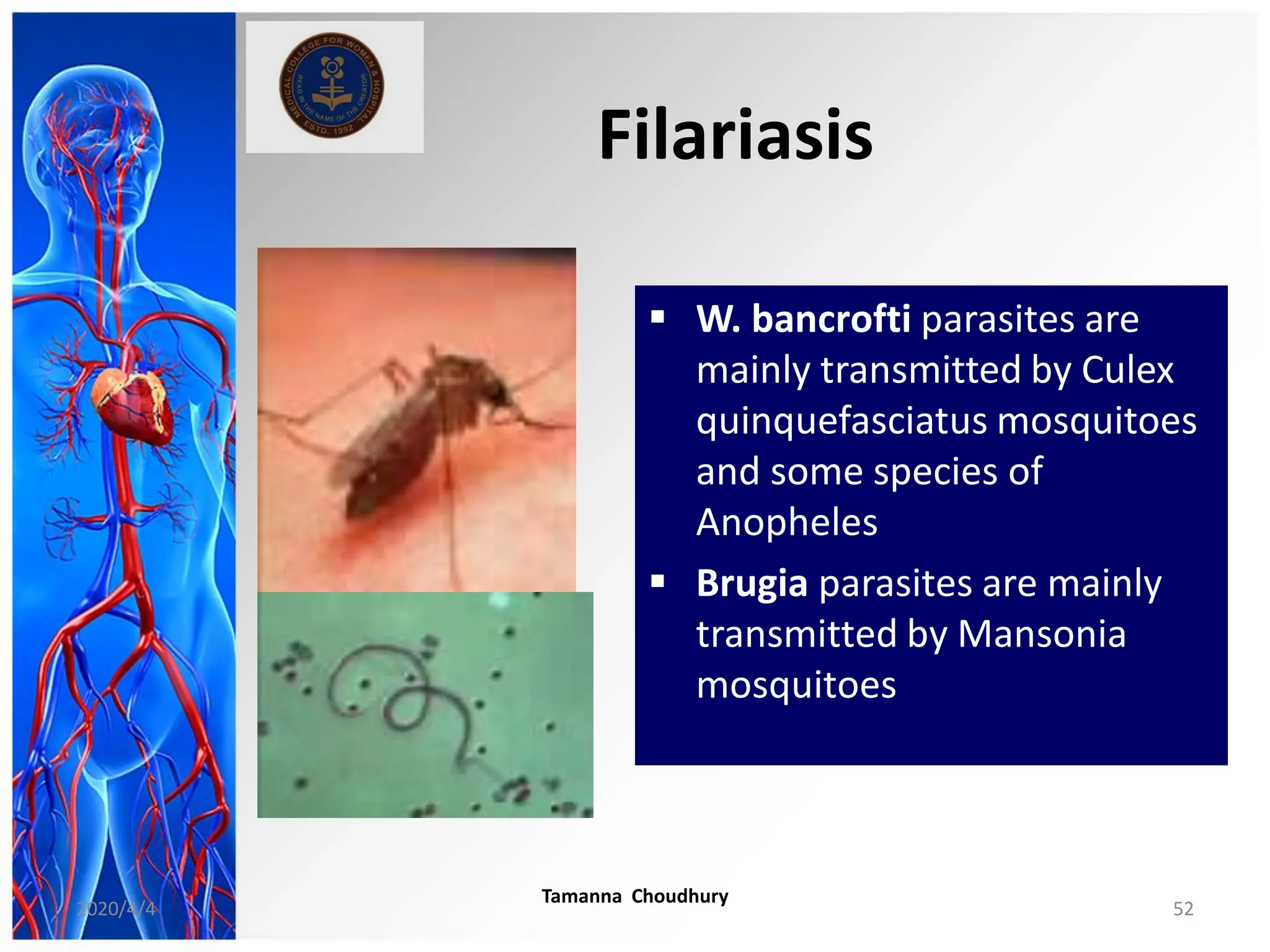
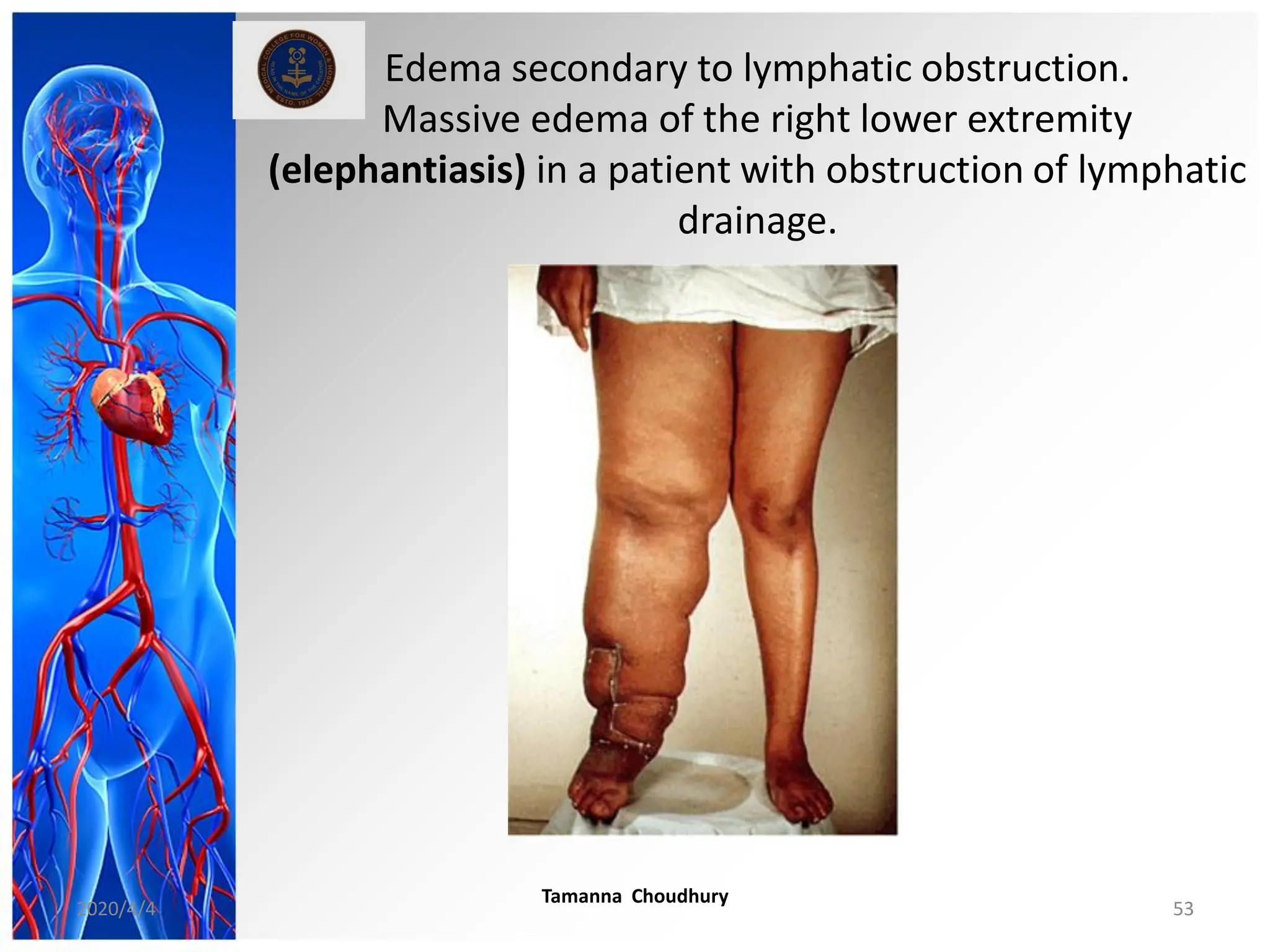
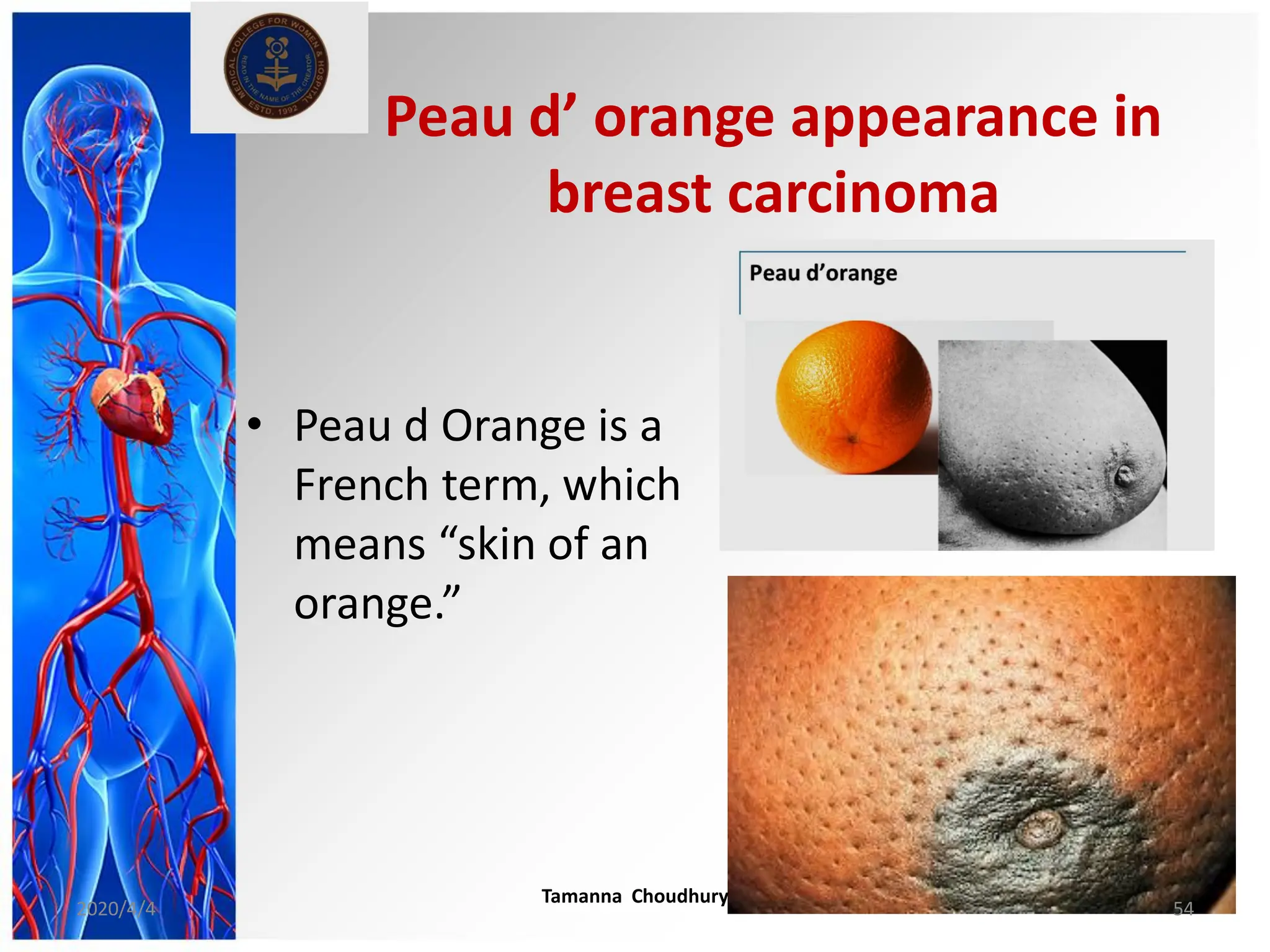
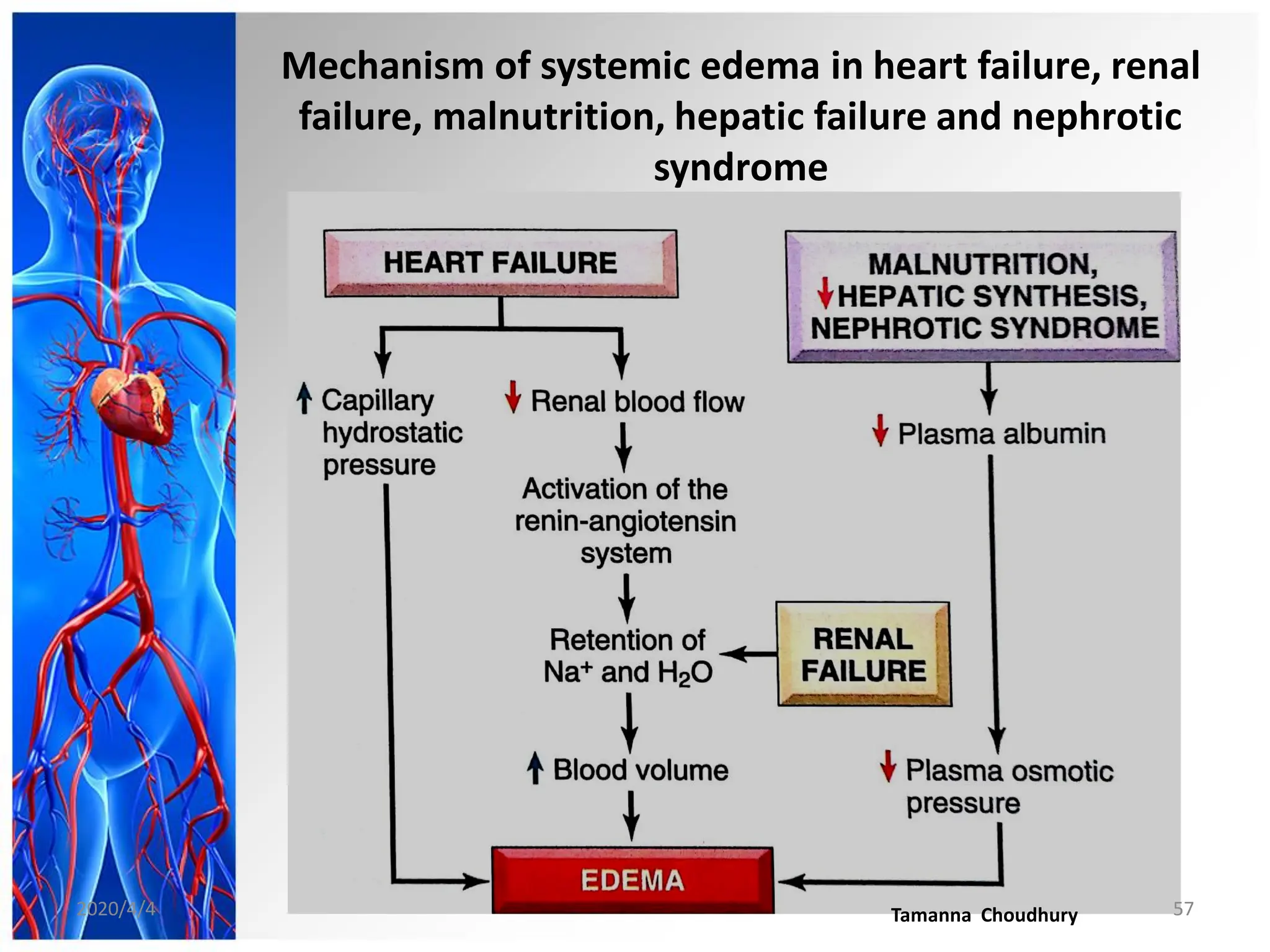
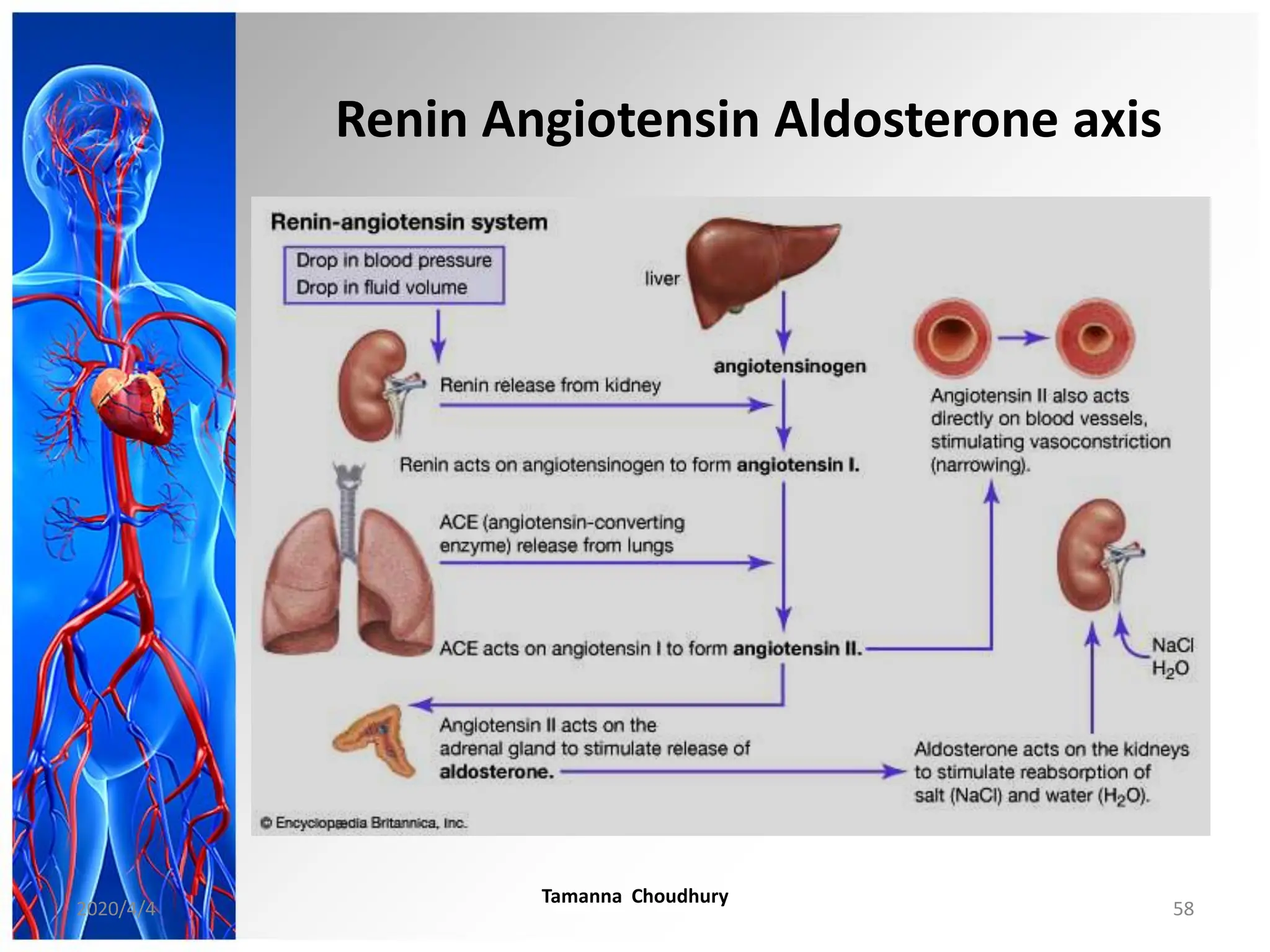
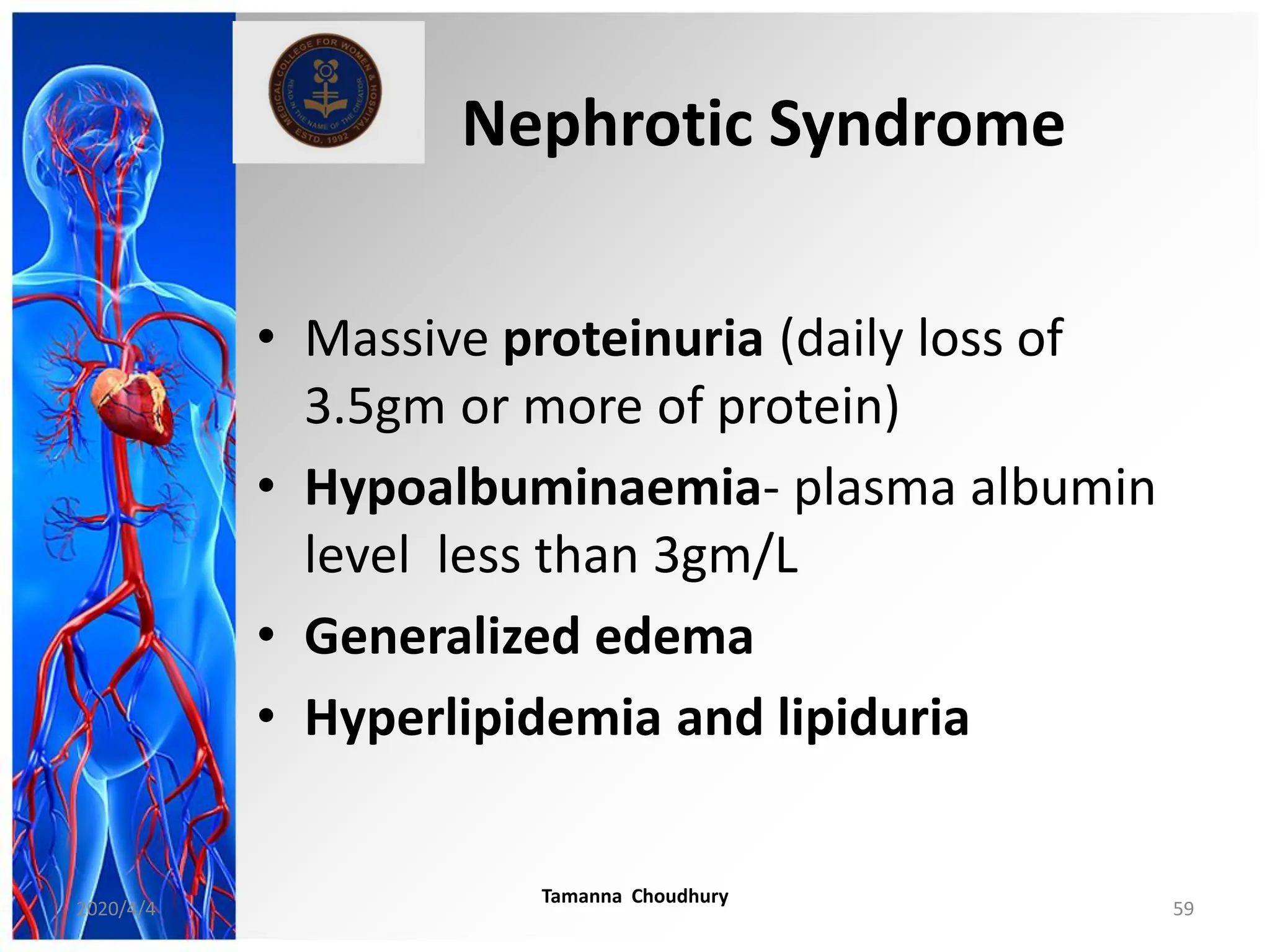
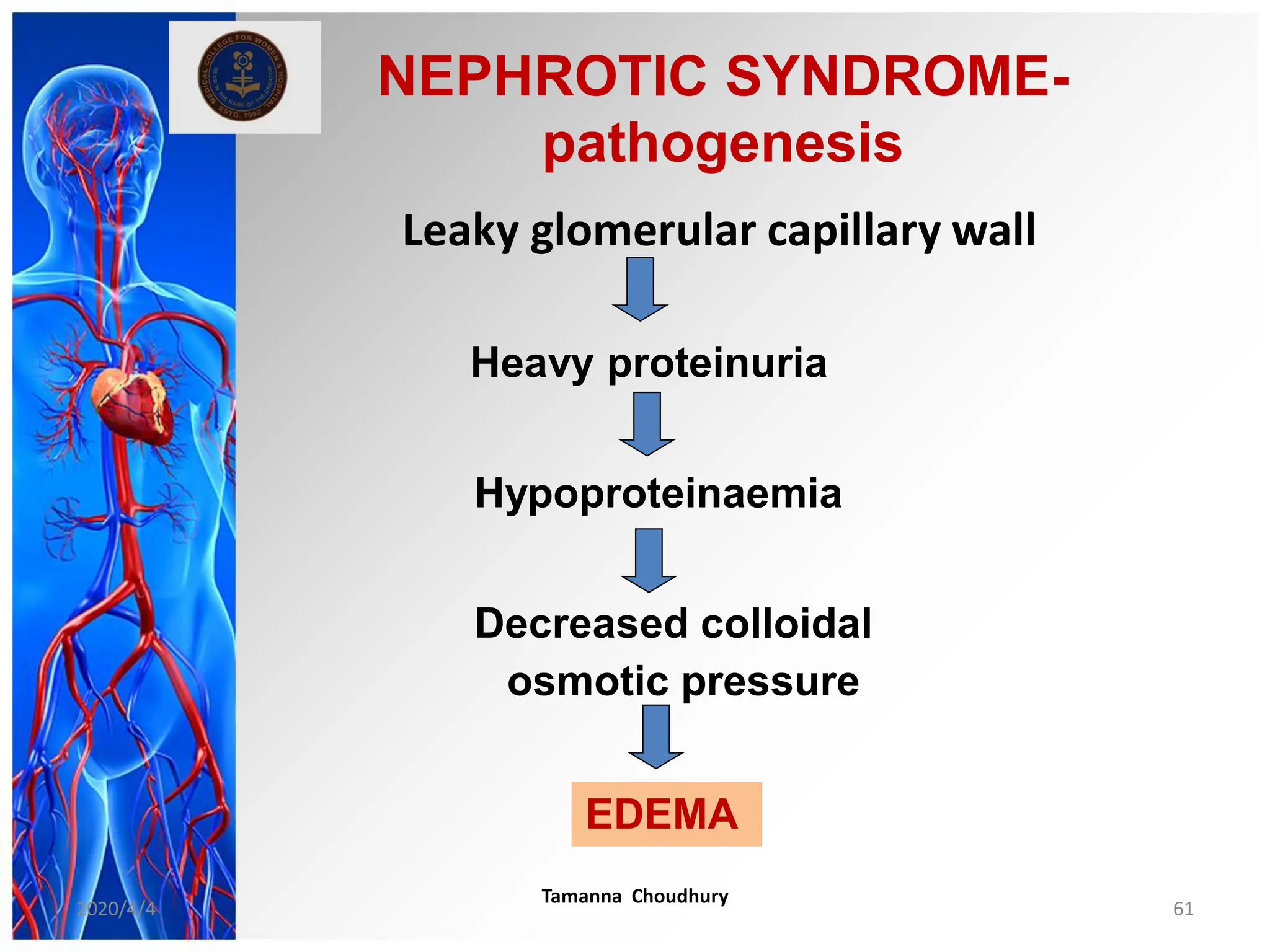
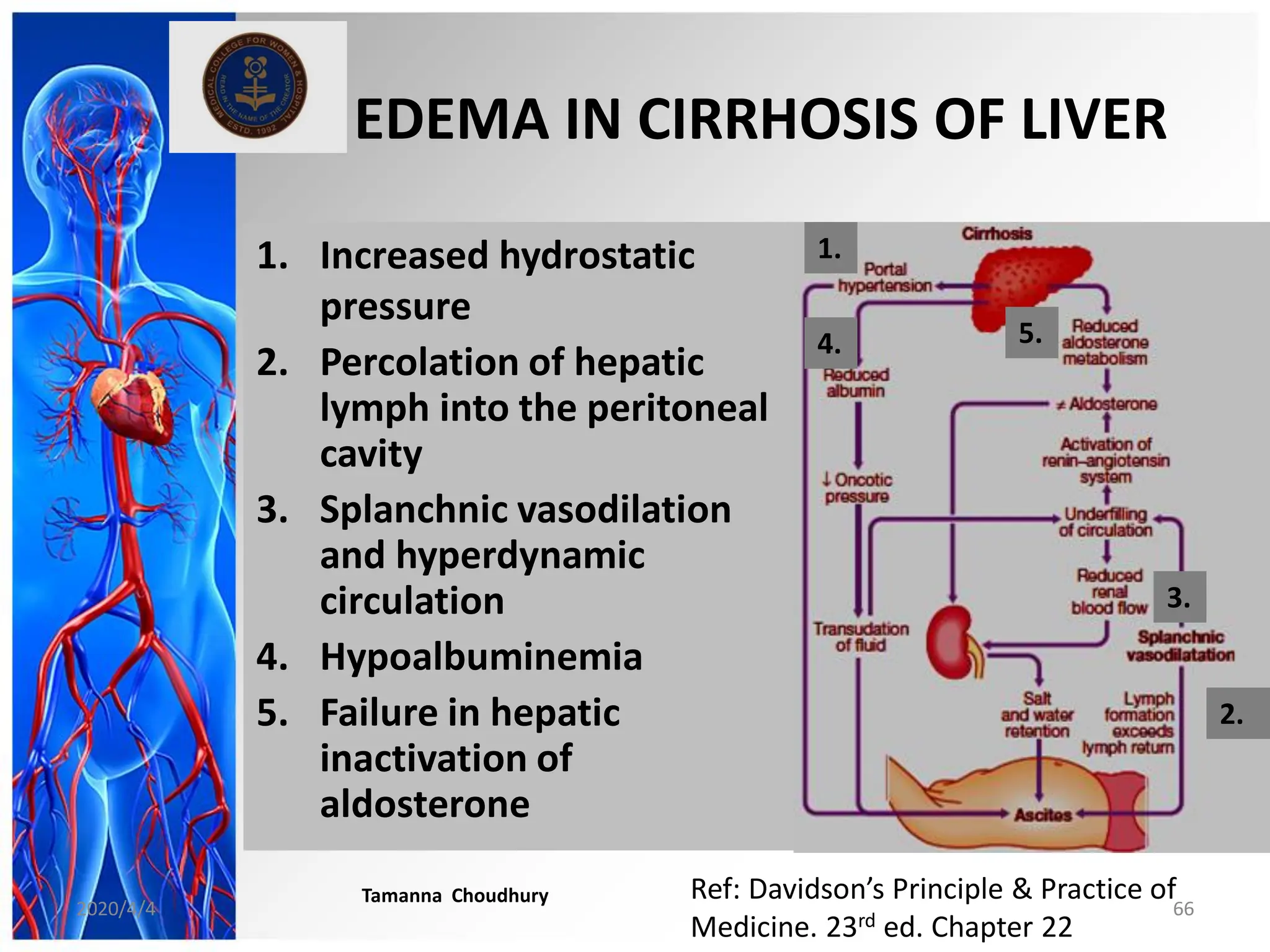
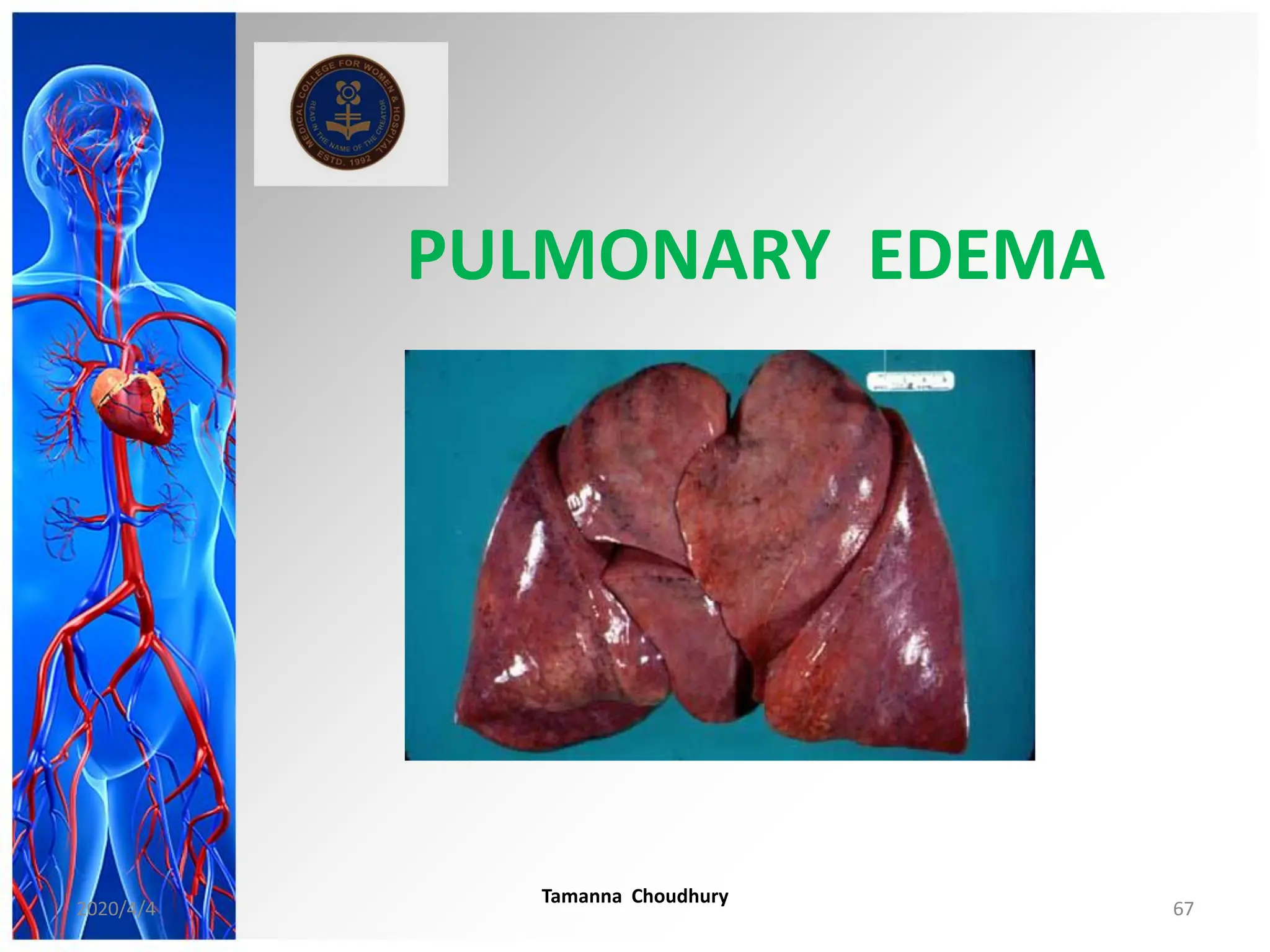
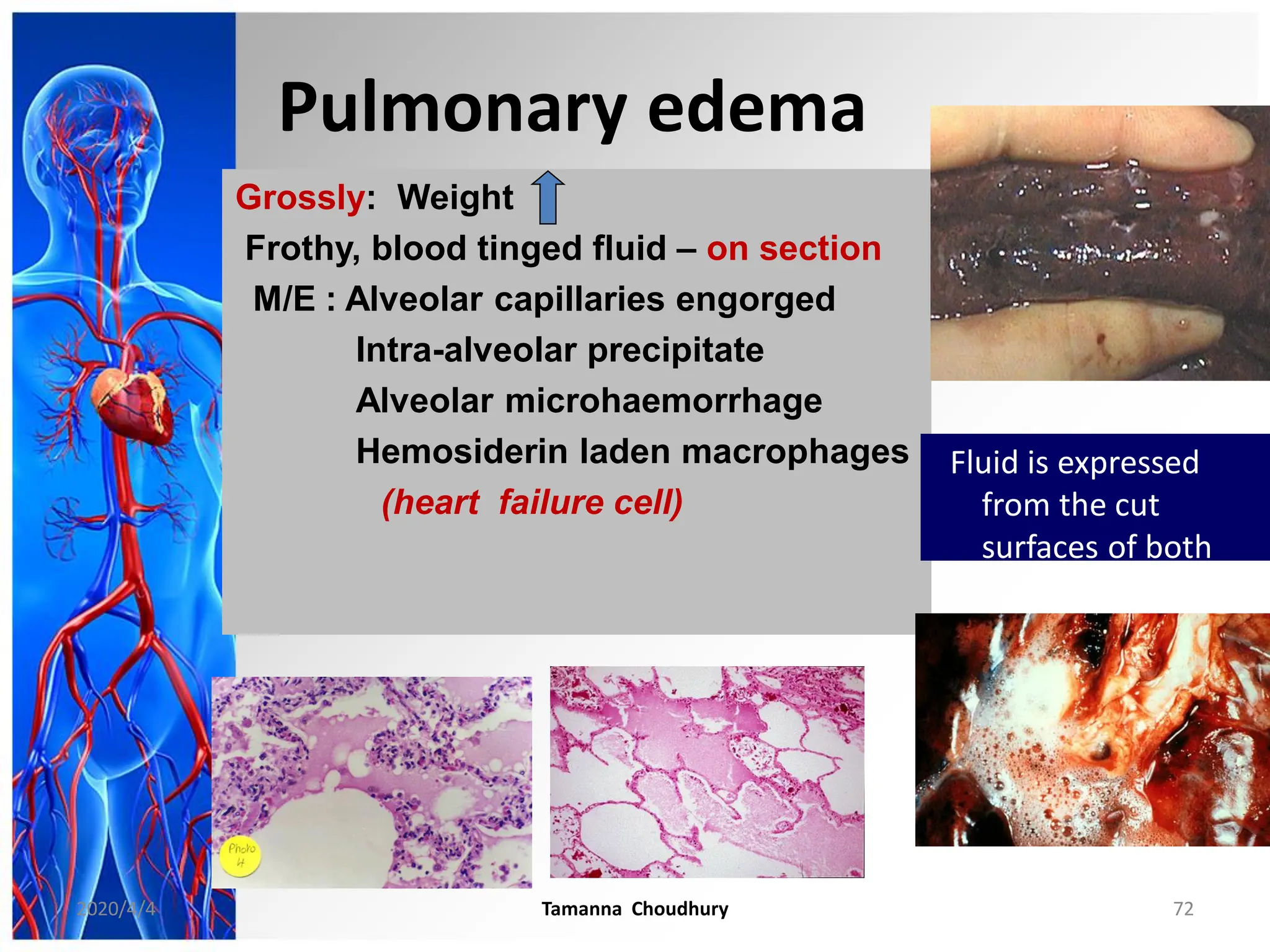
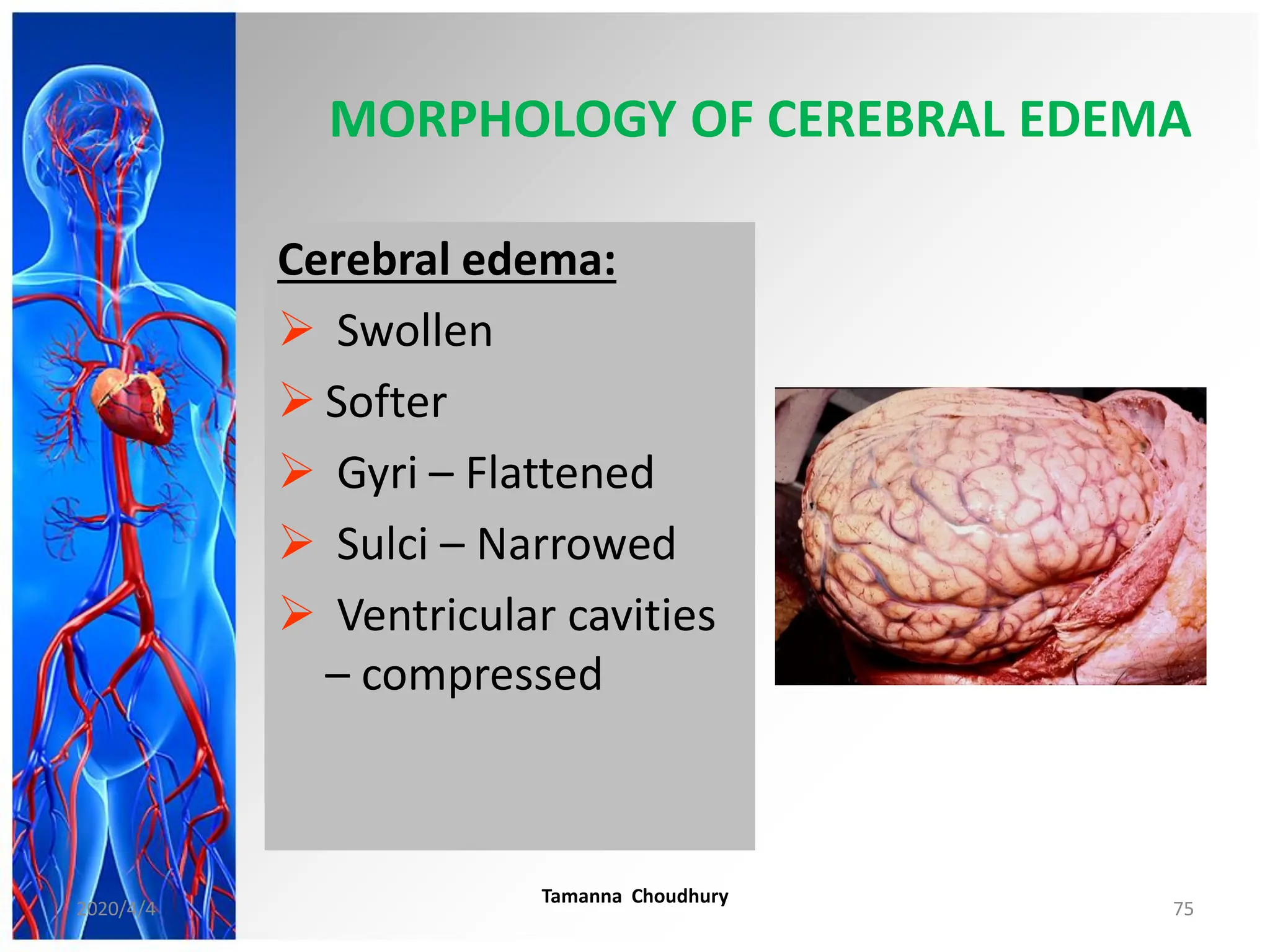
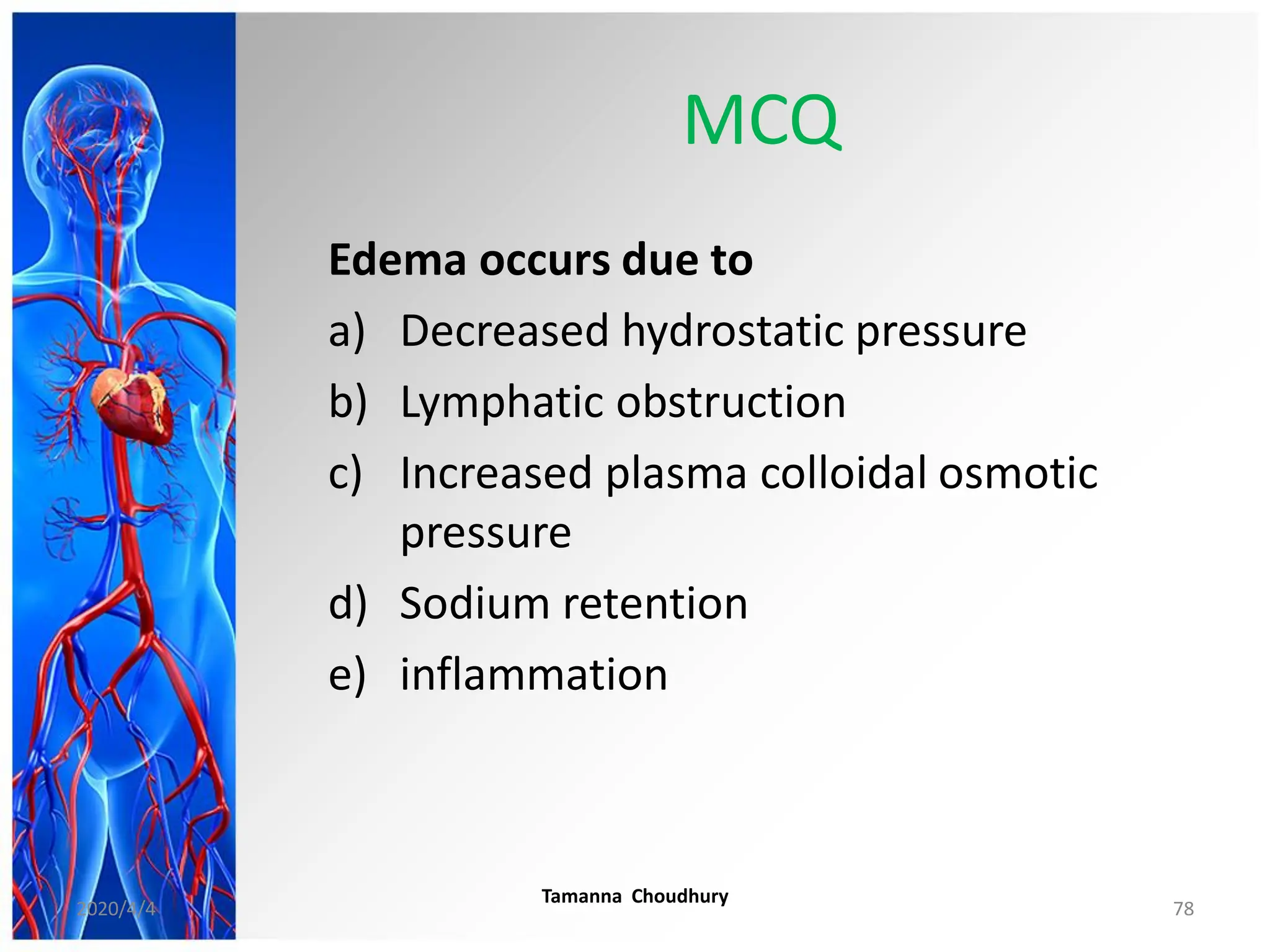
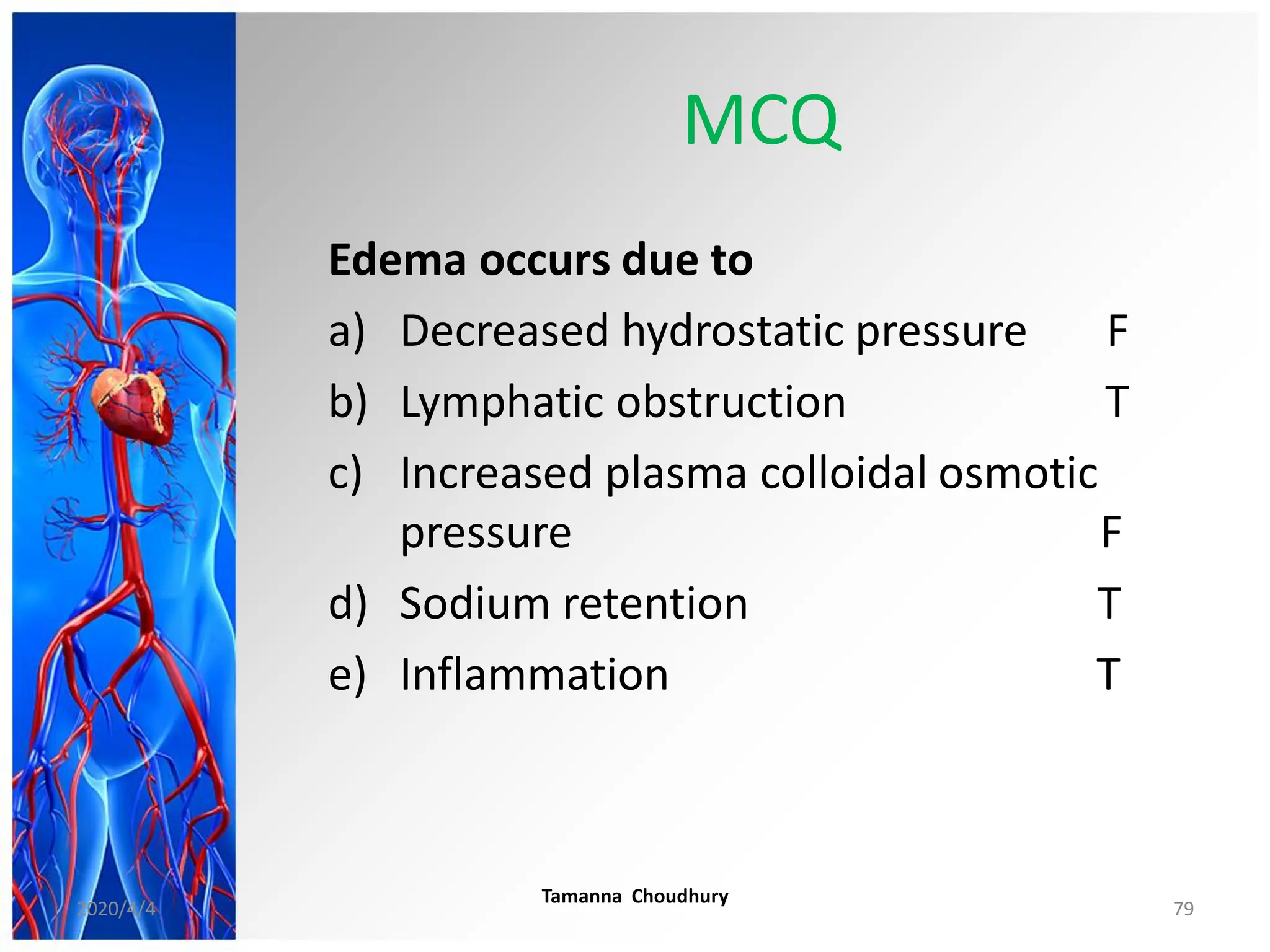
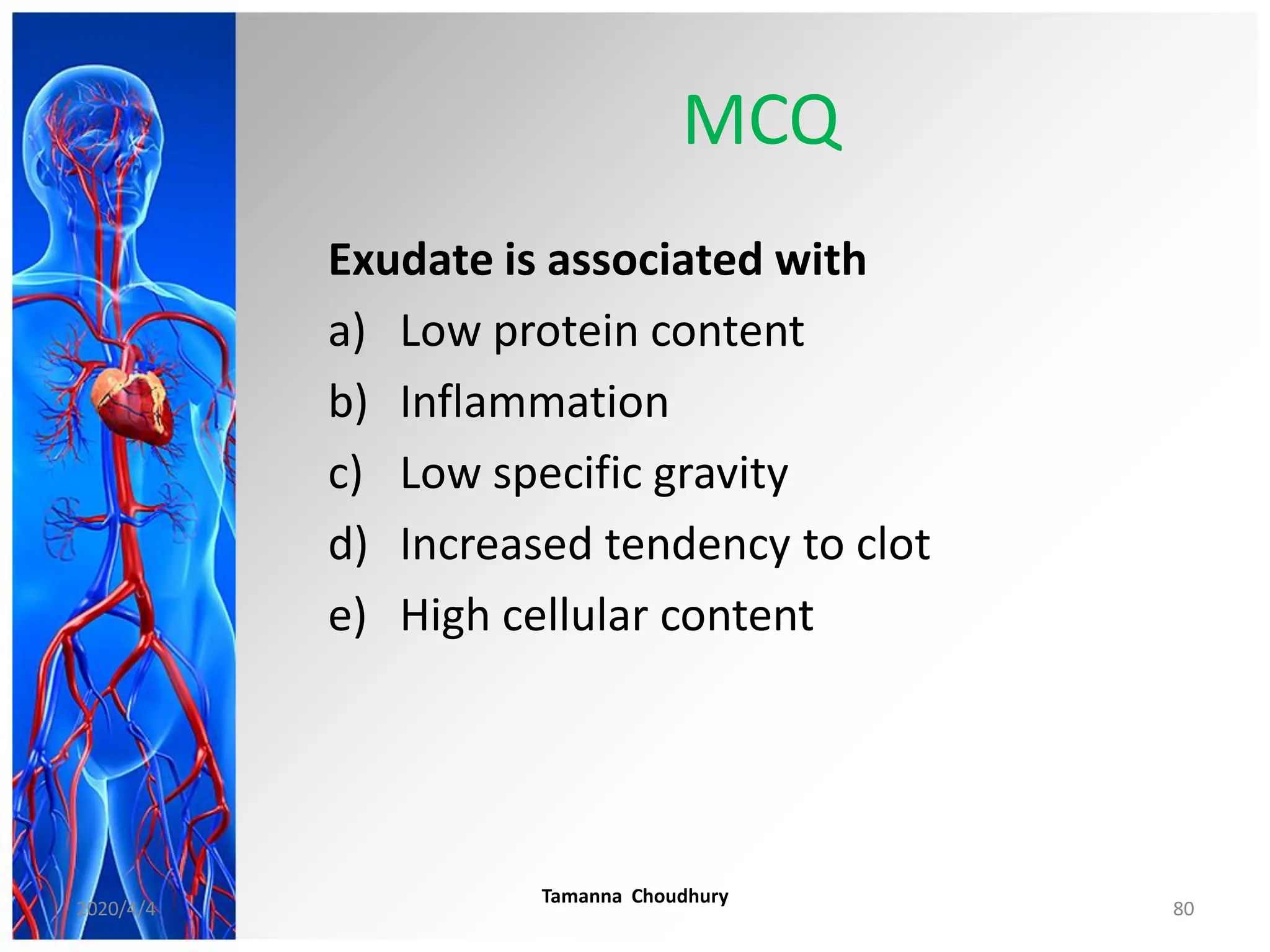
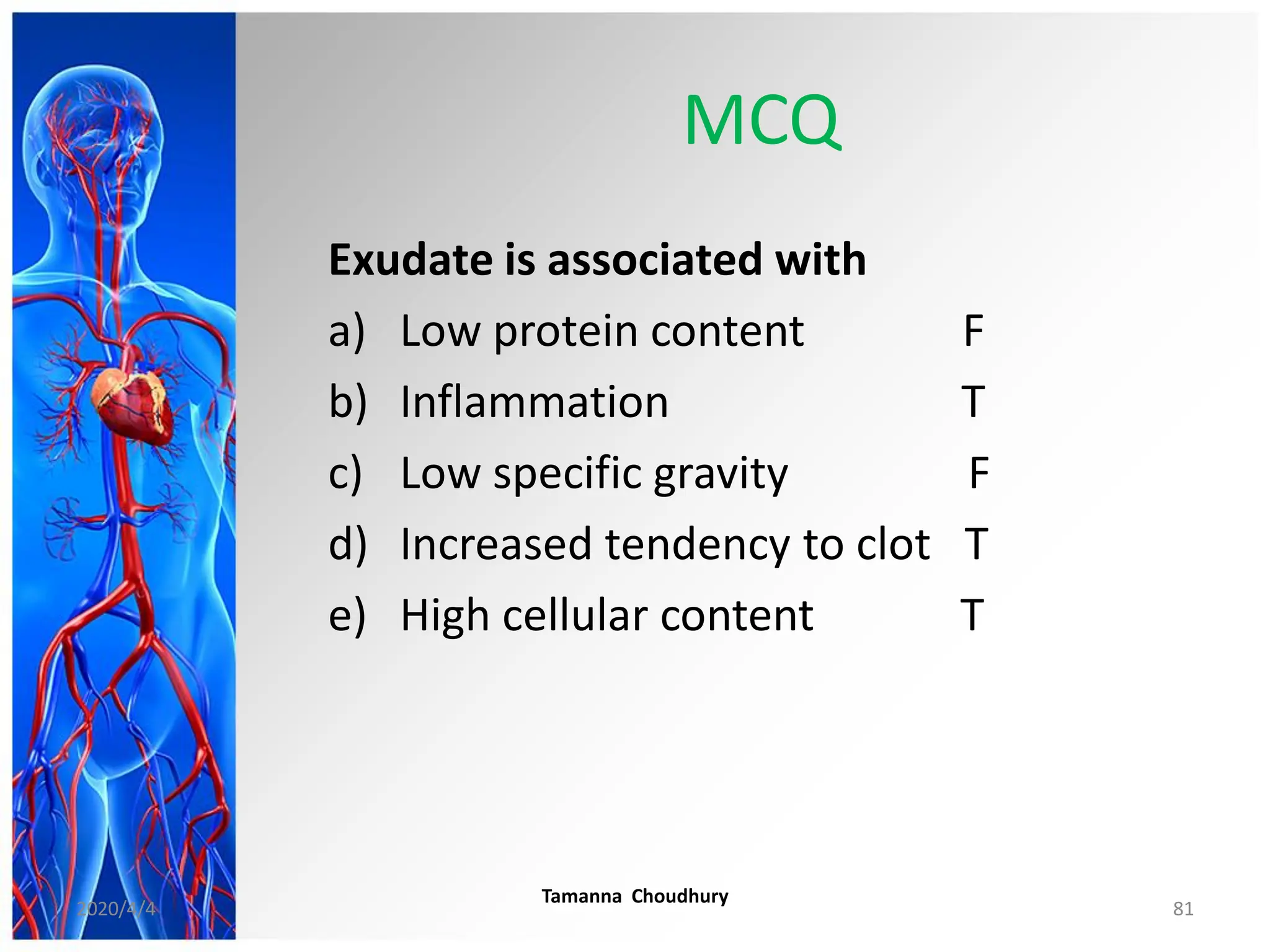
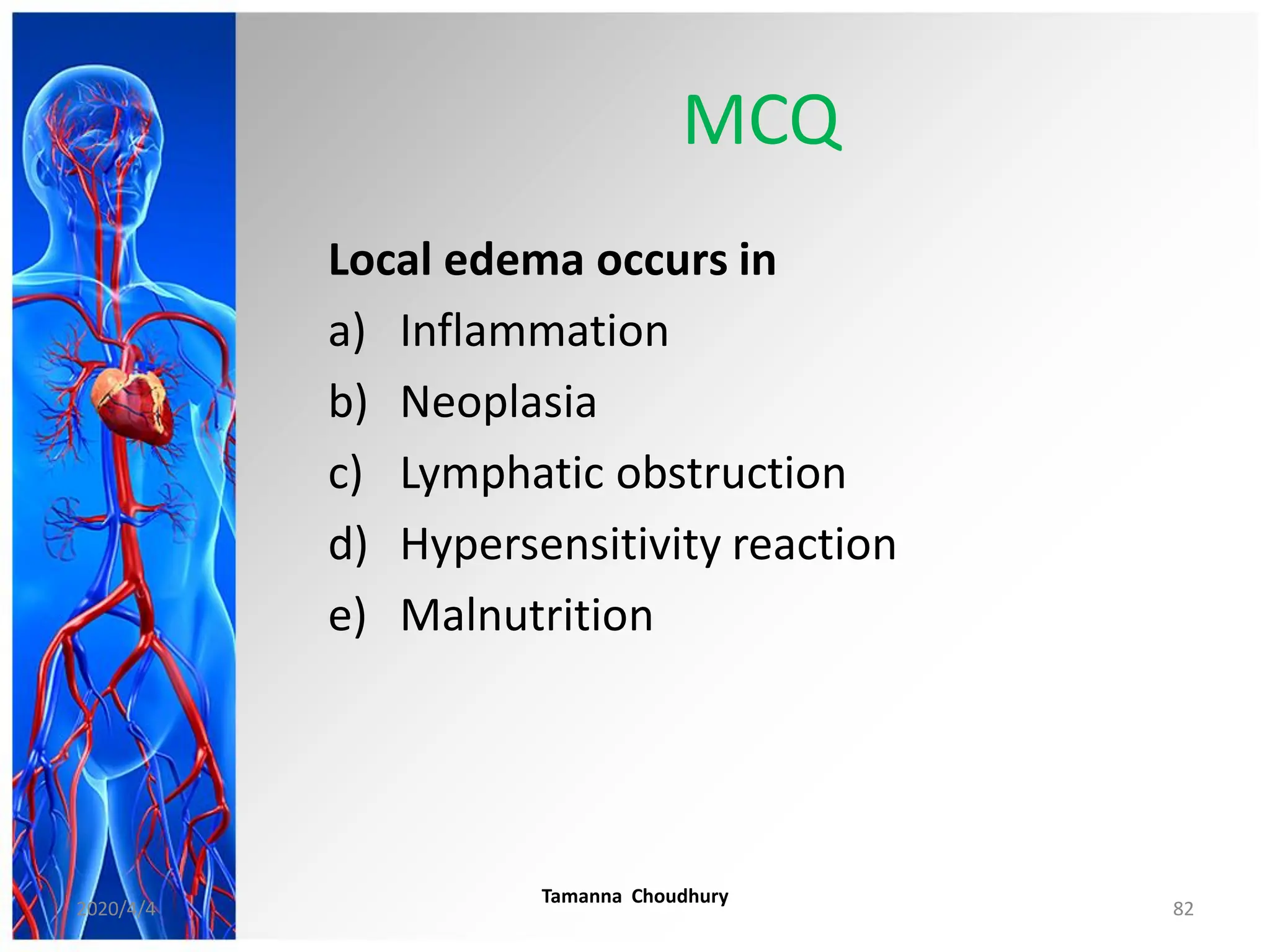
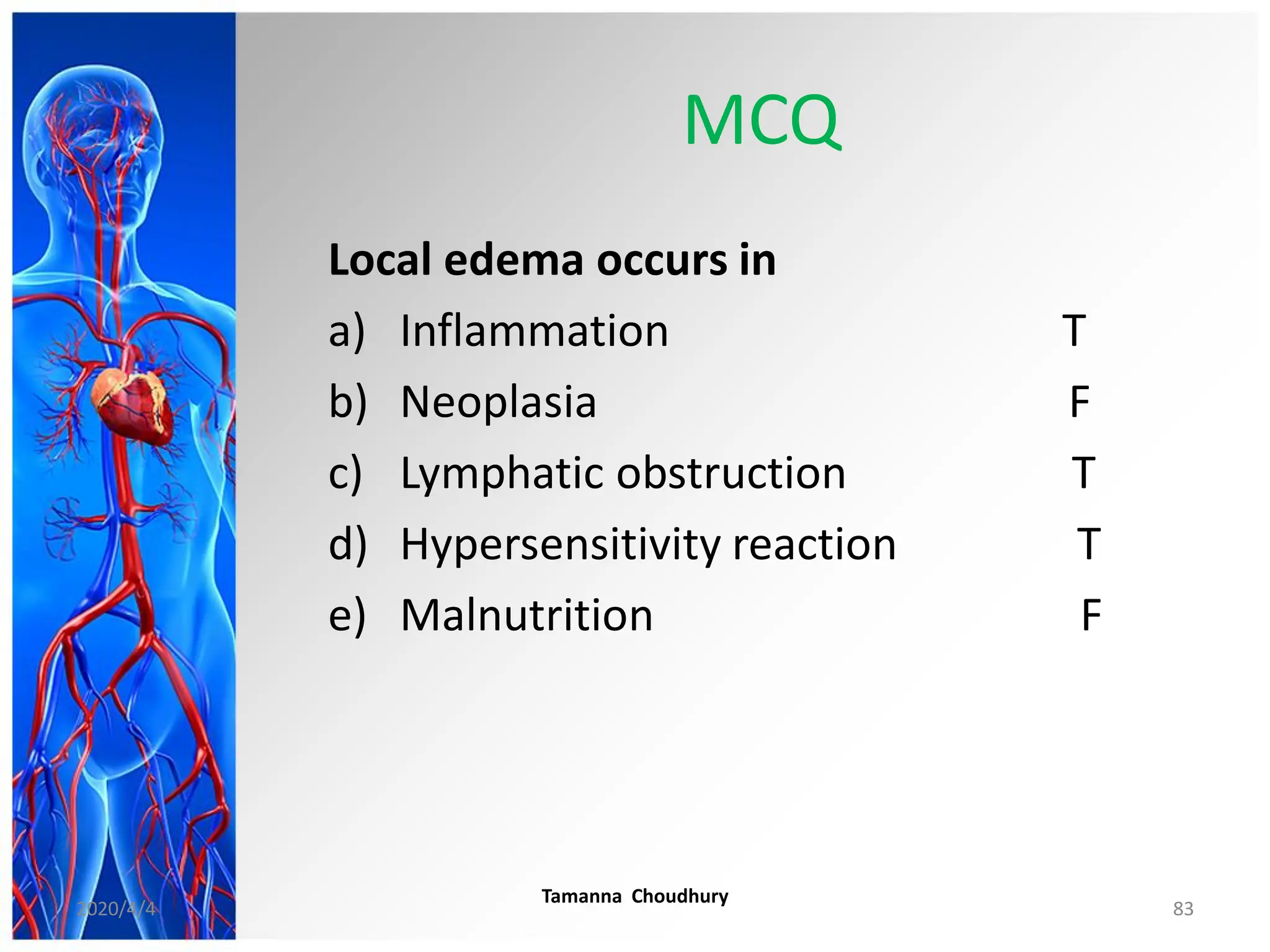
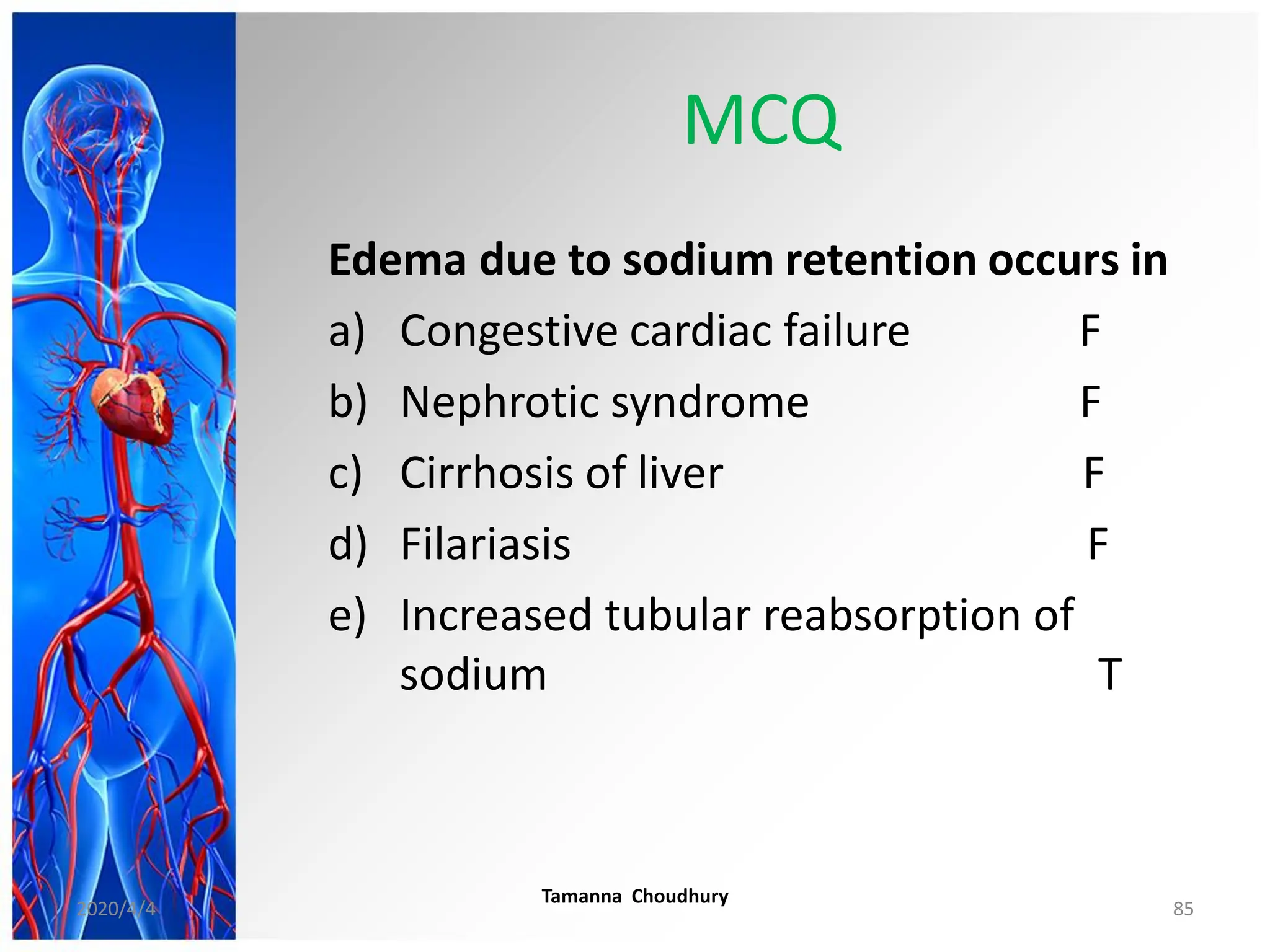
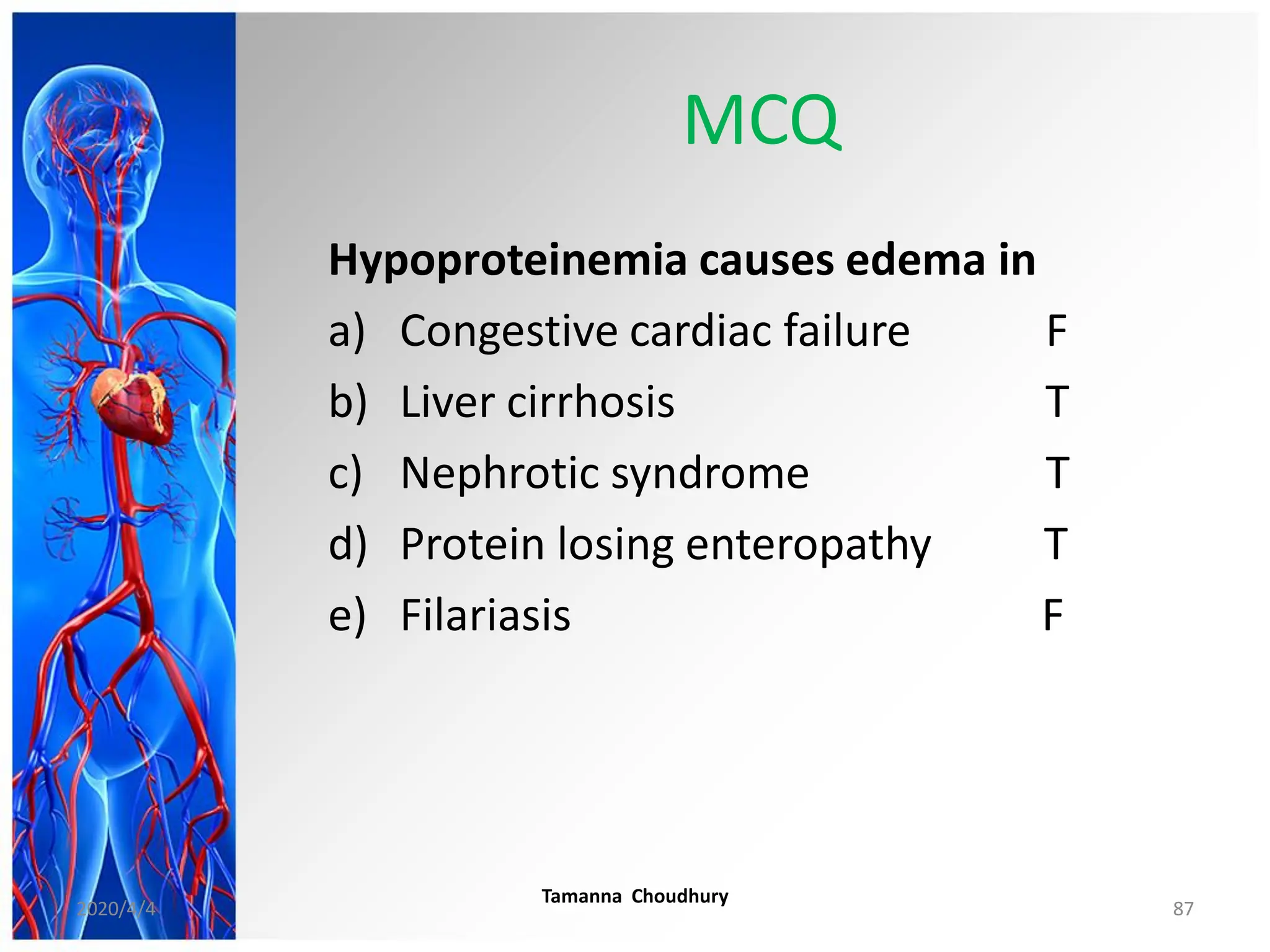
This document discusses haemodynamic disorders, thromboembolic disease, and shock. It covers topics such as edema and effusion, thrombosis, embolism, infarction, shock, hyperemia and congestion, and hemorrhage. Edema is defined as the accumulation of fluid in the interstitial tissue spaces, while effusion is the accumulation of fluid in body cavities. There are various pathophysiological categories of edema including increased hydrostatic pressure, reduced plasma osmotic pressure, lymphatic obstruction, sodium retention, and inflammation. Edema can be classified based on its pathophysiology, extent of involvement, and clinical presentation. Localized edema has causes such as acute inflammation, hypersensitivity reactions,